Complimentary strand (DNA to DNA):
ATAGCATCG
What is
TATCGTAGC ?
Different forms of a trait.
What are alleles?
A person that transfers a trait without expressing (using) the trait.
What is a carrier?
Number of chromosomes expected on a human karyotype.
Code of life.
What is DNA?
Complimentary strand (DNA to RNA):
ATAGCATCG
What is
UAUCGUAGC?
Type of math used when calculating the likelihood that a trait will be present.
What is probability?
Purpose of a pedigree.
What is to track a specific trait through a family tree?
Best time to study chromosomes.
What is during mitosis, or cell division?
Copy of a gene and codes for a specific protein.
What is RNA?
The number of letters read at a time in a strand of RNA.
What is 3?
Probability that dominant traits will be expressed if both mother and father are homozygous recessive.
What is 0%?
Number of males in the 3rd generation.

What is 4?
Three things you can determine in this karyotype:
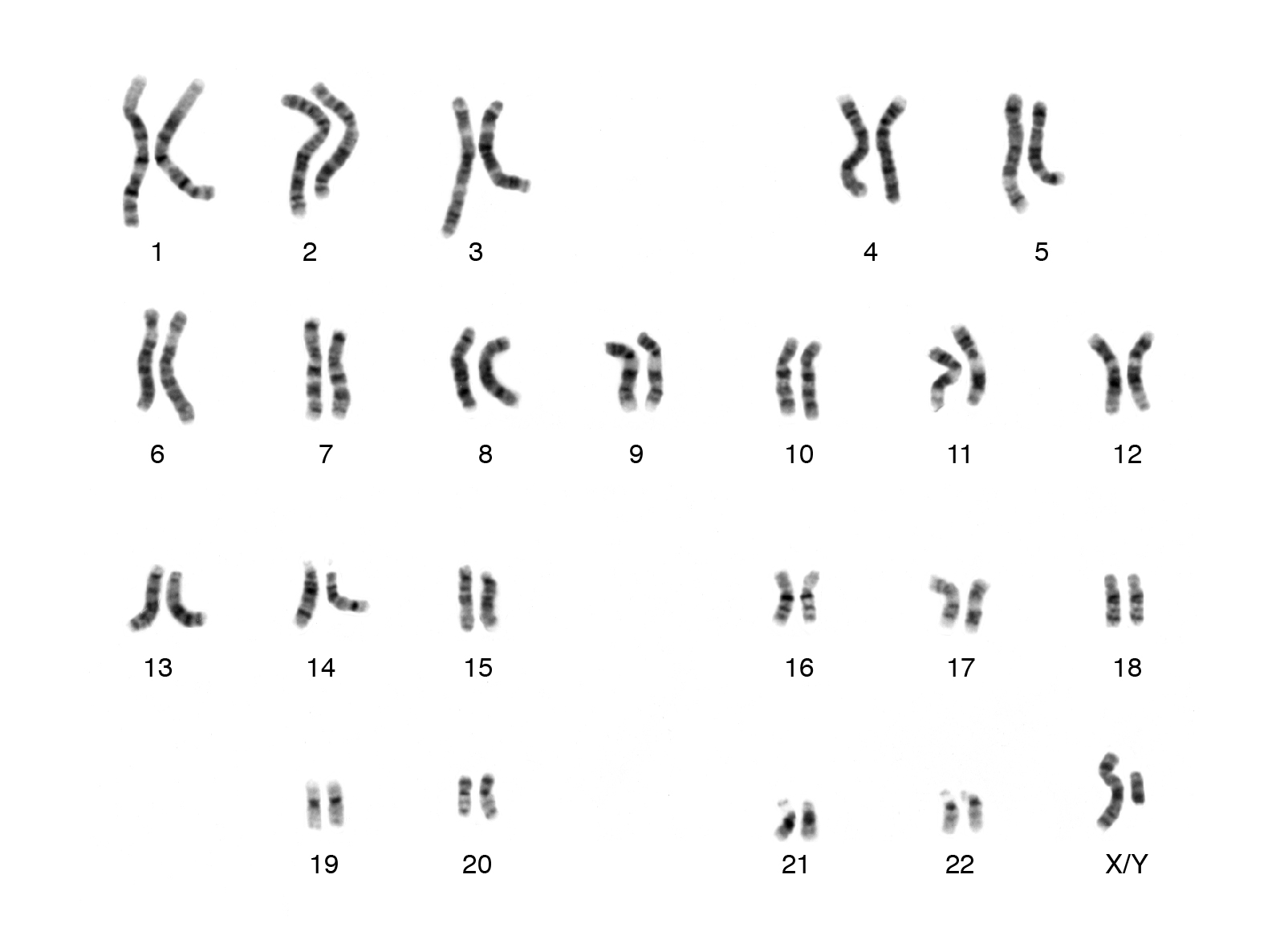
What is this a human, male, with no trisomal (3 chromosome) disorders?
Enzymes, antibodies, body tissue are all made of this.
What is protein?
Close chemical cousin to Thymine that is found in RNA only.
What is Uracil?
Probability of dominant trait expressed if mother offers Tt and father offers TT.
What is 100%?
Number of females carrying the trait (affected) in the 2nd generation.

What is 2?
Three things you can determine from this karyotype:
What is Non-human, male, and has a trisomal disorder on the 8th pair?
Long strands of DNA combine to make this.
What is a chromosome?
A permanent change to DNA.
What is a mutation?
Probability of dominant trait being expressed in offspring if both parents offer heterozygous traits.
What is 75%?
Number of female children in the 3rd generation with the blue eye mutation.
What is 2?
Disorder where an extra chromosome is present in the 23rd pair of a human karyotype.
What is Down Syndrome?
Building blocks of life that come together (much like Legos) to build proteins.
What are amino acids?