Define mesothelium.
Where can it be found?
A layer of simple squamous cells that line the outer surface of an organ and line the body cavity that it resides in.
Pleural cavity, Pericardial cavity, Peritoneal cavity.
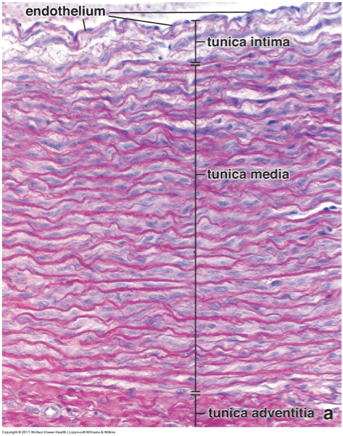
What are the three layers of all blood vessels and what components are they composed of?
Tunica intima - endothelium, basal lamina, subendothelial CT layer, internal elastic lamina
Tunica media - smooth muscle and external elastic lamina
Tunica adventitia - irregular CT
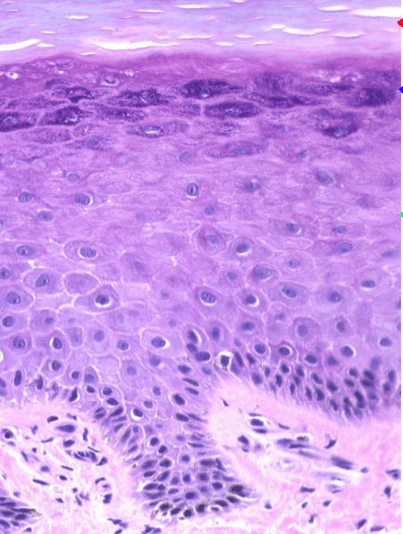 What are the layers seen here. Is this thick or thin skin?
What are the layers seen here. Is this thick or thin skin?
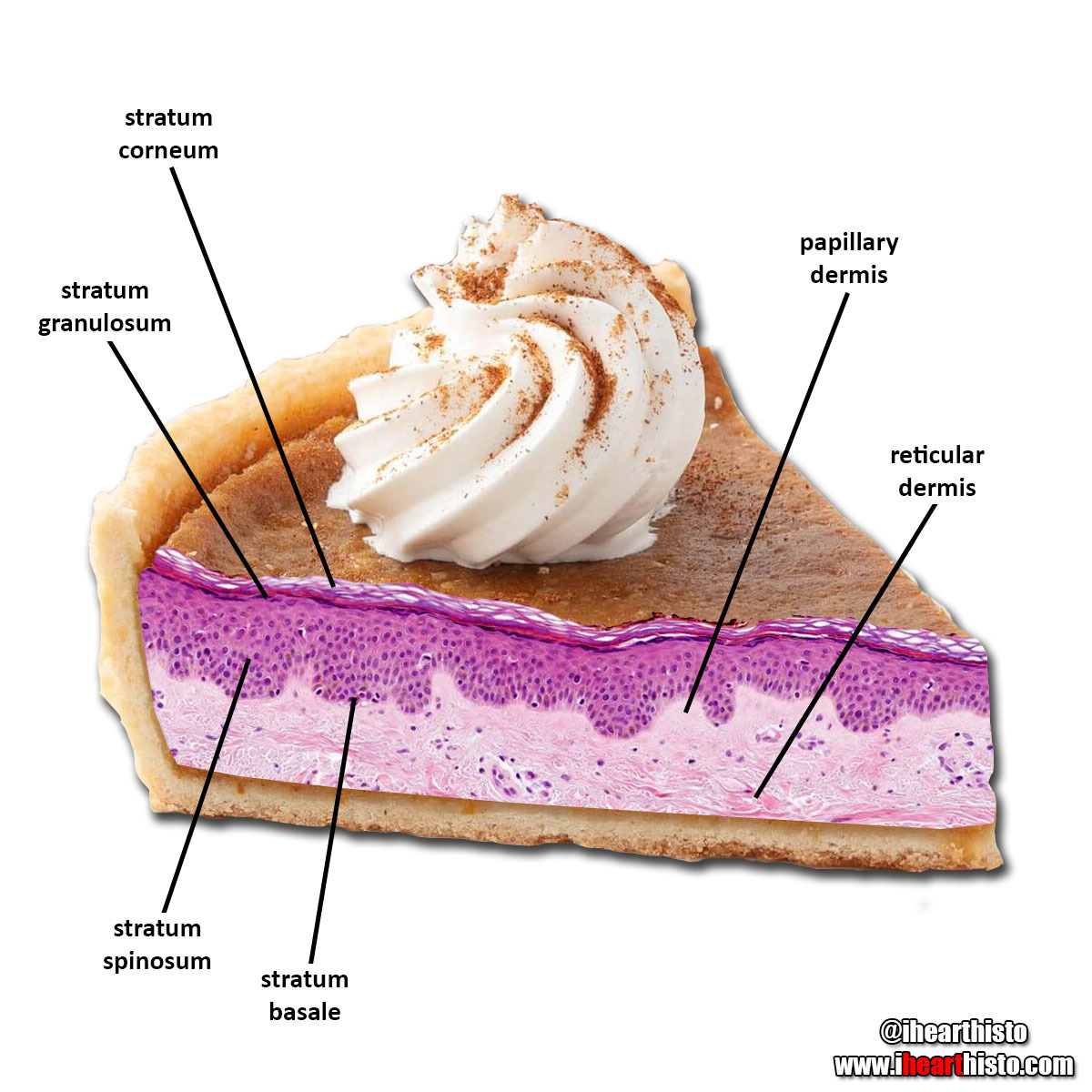
Stratum corneum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale
Thin skin because there is no stratum lucidium
What is squamous metaplasia?
Where can it be found in the respiratory system?
Where else in the body is this seen?
The transition from one cell type or one tissue type to another.
Larynx and Cervix
What is the difference between innate and adaptive immunity?
You are bone with innate. It is non-specific and involves chemical/physical barriers, secretory substances and phagocytic cells.
Adaptive immunity is specific and has two main distinctions. Humoral response which involves antibodies, and cellular response which involves NK cells, a type of lymphocyte.
What are considered to be a "histological ruler?" Why?
Erythrocytes
-they are a constant size (7-8micrometers)
-found all over the body
-other cells can be compared to them to gauge their size
Do you LOVE histology?
YES!
Find and describe the structure and function of a Purkinje cell.
What stain is used in this section?
Purkinje cells are light staining due to the high concentration of glycogen. They are modified cardiomyocytes that play a role in the intrinsic conduction system of the heart.
Mallory Azan
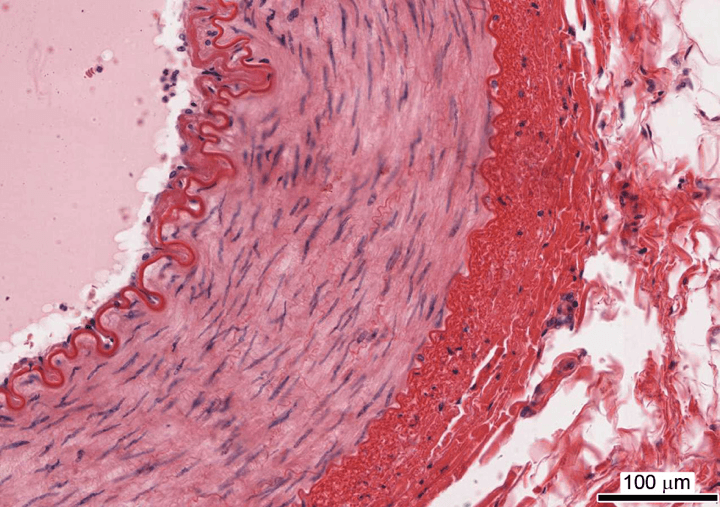 What is this vessel and how do you know?
What is this vessel and how do you know?
Muscular artery
-distinctly visible internal and external elastic lamina
-thick muscular tunica intermedia
-sturdy circular lumen
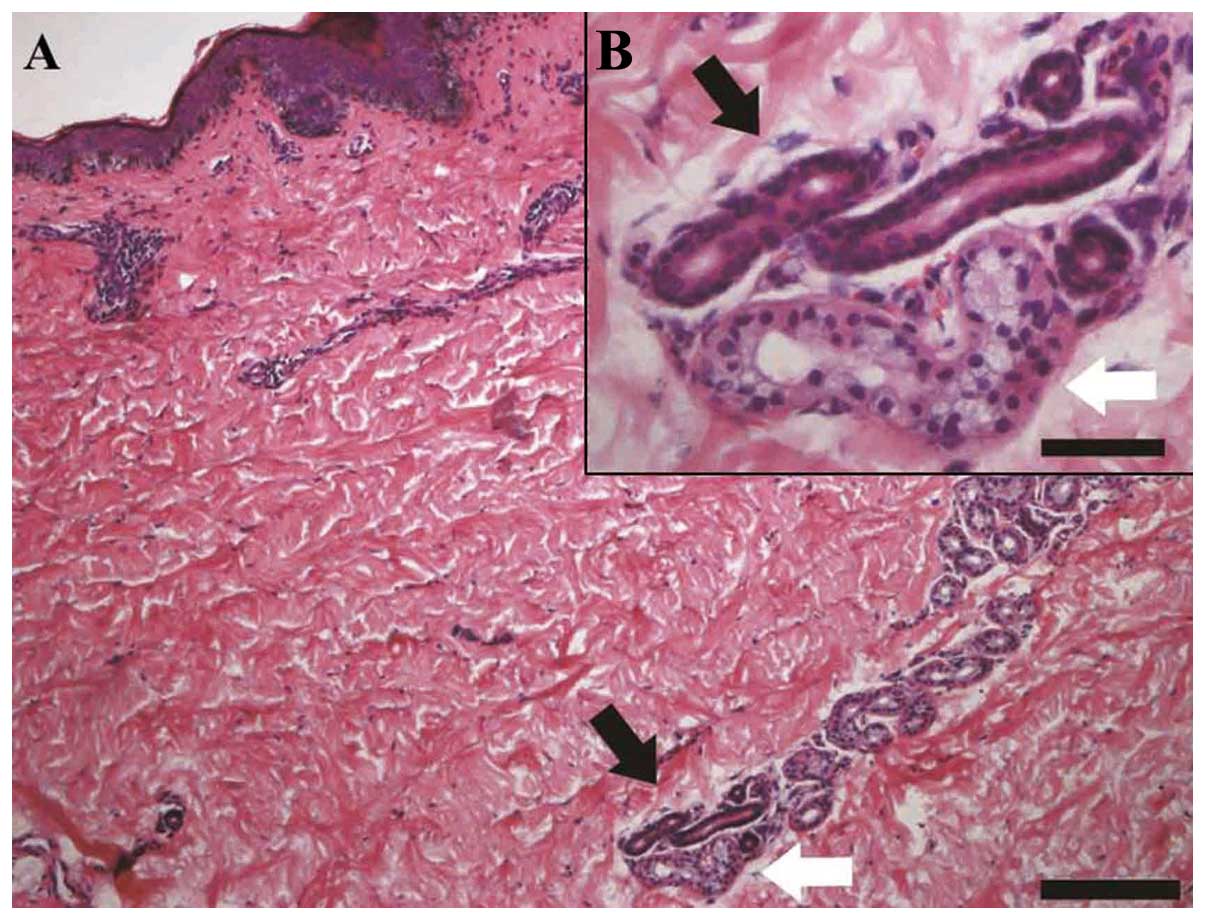
What is indicated by the white arrow? The black arrow?
How can you tell the difference?
Black - Duct of eccrine gland. Ducts are darker staining, have small more compact cells and sometimes have 2 layers of cells lining the duct.
White - Secretory portion of eccrine sweat gland. Glands are larger, columnar shaped cells with abundant light staining cytoplasm.
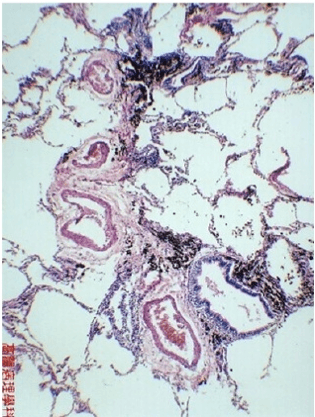 This is a section of a lung of someone who smokes. What is this condition called and what is it characterized by?
This is a section of a lung of someone who smokes. What is this condition called and what is it characterized by?
Anthracosis - black coal fragments accumulate around bronchioles
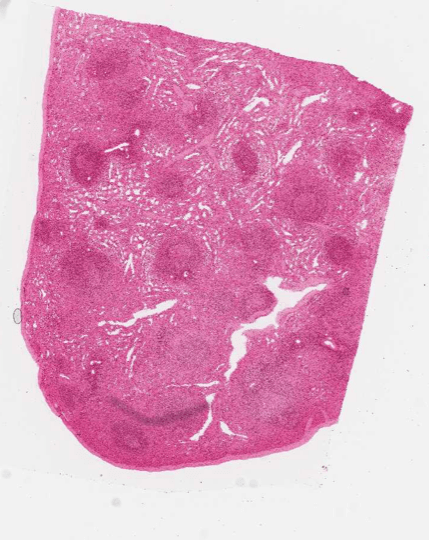 Identify this organ.
Identify this organ.
Explain the differently stained regions and what they contain.
Spleen
Dark spots interspersed throughout the organ is "white pulp" that contain splenic nodules. They contain highly compacted accumulations of lymphocytes that surround arterioles and for periarteriole lymphatic sheaths (PALS).
Surrounding tissue makes up the mass of the spleen and is red pulp. Contains cords of Bilroth and sinuses that function to store RBCs and removal of old RBCs.
What is the stain used for blood and what is it composed of?
Wright's stain
-eosin and methylene blue
What are the 3 components of an Apical Junctional Complex?
What is the purpose?
Zonula occluden
Zonula adherens
Macula adherens
Connects apical ends of lateral surfaces of cells to create barrier to prevent diffusion and seal the space between cells.
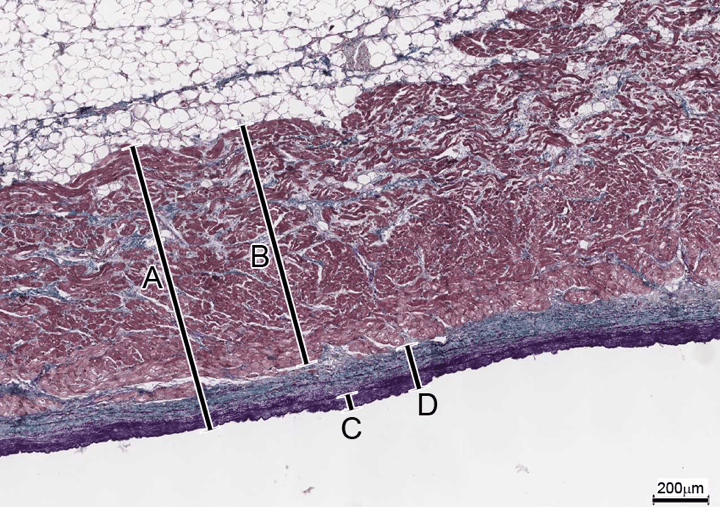 Identify A, B, C, D and the stain used in this section
Identify A, B, C, D and the stain used in this section
A- heart wall
B- myocardium
C- endothelium
D- endocardium
Stain- Aldehyde Fuchsin-Masson
 What kind of vessel is this?
What kind of vessel is this?
Histologically explain its characteristics.
What stain can be used to identify elastic fibres?
Elastic artery
Very thick tunica media containing very many elastic fibres making it hard to distinguish the inner and outer elastic lamina.
Weigert's stain or orcein.

What is the pointer indicating? What is its function
Meissner's corpuscle.
Responsible for light touch reception.
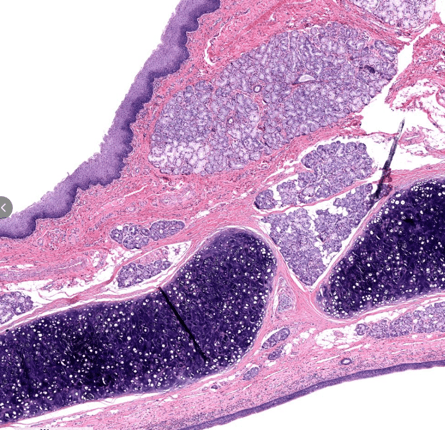
Identify this structure. What type of epithelium is on either side of this structure?
Epiglottis
- stratified squamous epithelium on the lingual surface
- respiratory epithelium on the posterior surface
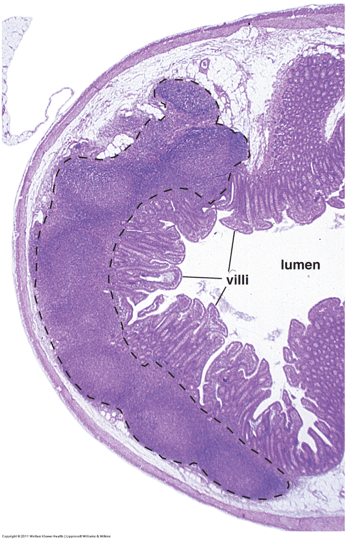 Identify this organ? What is indicated by the black dotted line?
Identify this organ? What is indicated by the black dotted line?
Explain the heterogenous staining of these structures.
Ileum - Has villi that protrude out into the lumen and the luminal surface is not smooth. Has lymphatic nodules (Peyer's patches) in the submucosal layer.
The lighter staining germinal centre contains proliferative lymphocytes while the mantle zone around the GC is darker and contains densely packed mature lymphocytes.
B-lymphocytes in centre and T-lymphocytes around periphery (CD-20, CD3 markers).
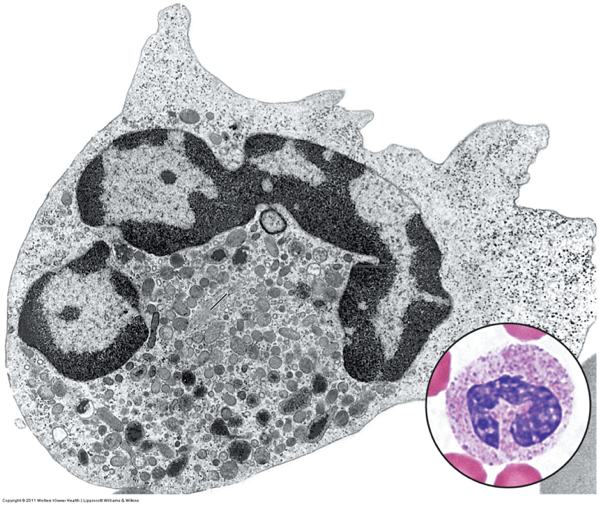 Identify this blood element and what is its function?What are the types of granules in the cytoplasm?
Identify this blood element and what is its function?What are the types of granules in the cytoplasm?
Neutrophil
-first response to infection
-granulocyte: specific granules, MPO, cytotoxic molecules, azurophilic granules
-pus is green due to myleoperoxidase
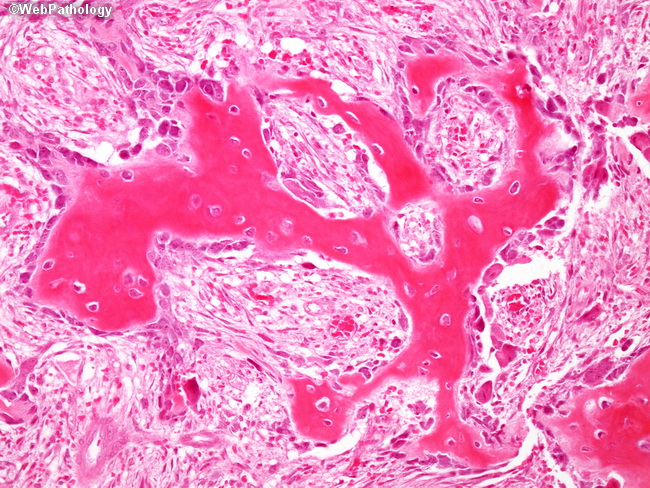 What is the tissue shown in this image. What are three cell types typically seen in this type of tissue?
What is the tissue shown in this image. What are three cell types typically seen in this type of tissue?
Trabecular bone/osteoid
Osteocyte - sits within a lacunae, is a clear cell with cytoplasmic processes that extend into canaliculi. Makes up bone
Osteoblast - produces bone matrix/secretes osteoid. Small cells located on the periphery of bone.
Osteoclast - reabsorbs bone, sits in Howship's lacuna, relatively large, ruffled border.
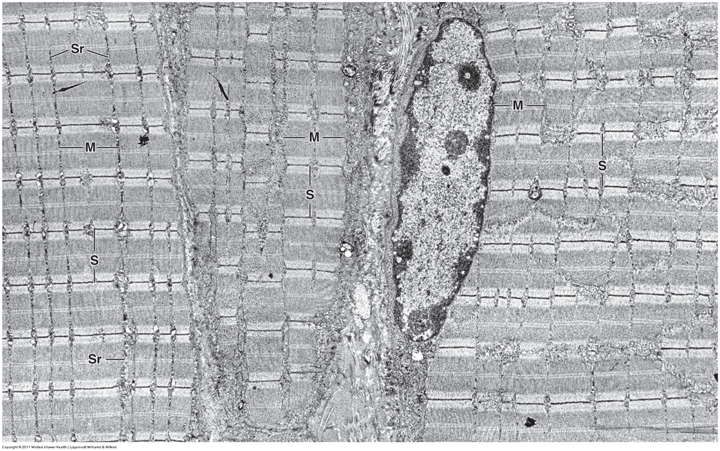 What tissue is this? Why?
What tissue is this? Why?
Skeletal muscle - has striations, has continuous fibres with no intercalated disks. Nucleus located peripherally.
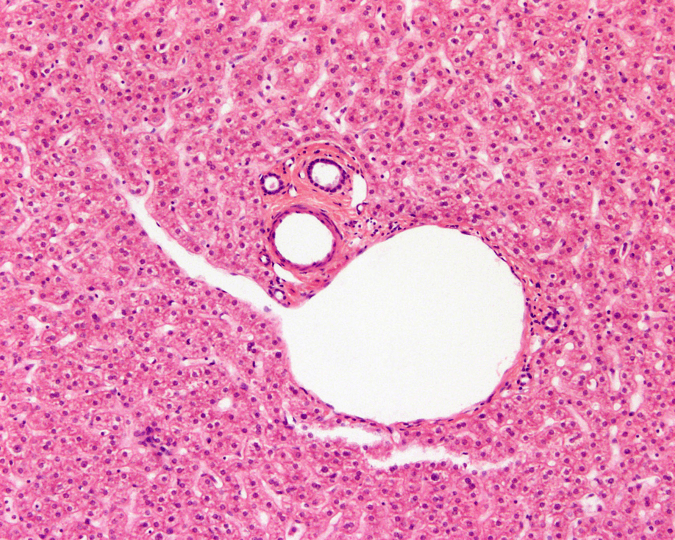
Identify the three vessels and explain why you know. Explain what each vessel will contain.
What organ is this?
Portal triad of liver.
Bile duct (top left) - lined with cuboidal cells and has thin muscular layer around it. Contains bile produced by the hepatocytes.
Hepatic artery (top right) - lined with simple squamous epithelium, has a relatively thick muscular layer around vessel compared to size of lumen. Contains O2 rich, nutrient poor blood from lungs.
Branch of hepatic portal vein (bottom) - lined with simple squamous epithelium, has a large lumen and relatively thin walls. Contains O2 poor, nutrient rich blood from the body.
All vessels drain into central vein of liver lobule.
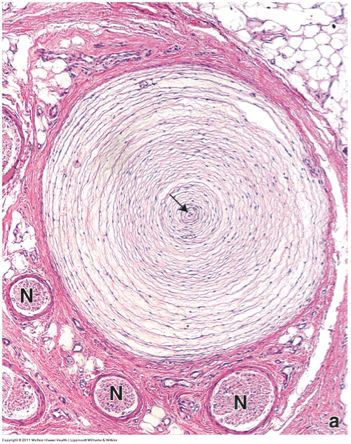 Identify this structure and explain its function. Where is it most commonly found?
Identify this structure and explain its function. Where is it most commonly found?
Pacinian corpuscles are deep pressure sensors for mechanical and vibratory pressure, most commonly found in the fingertips.
Located between the dermal and hypodermic layers.
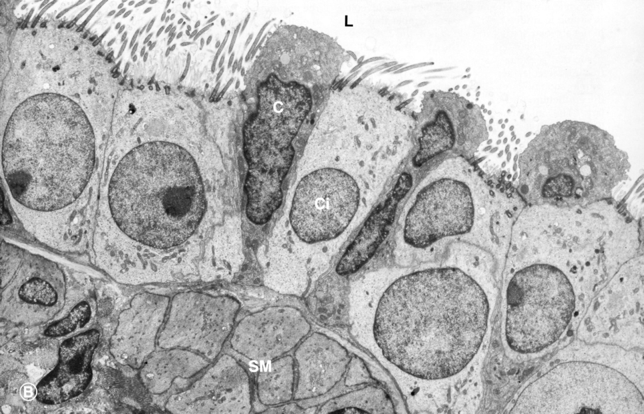
Name and histologically describe the cells labeled "C." Where is this cell found?
Club cell
Dome shaped cell that lacks cilia.
Will be found in the bronchioles.
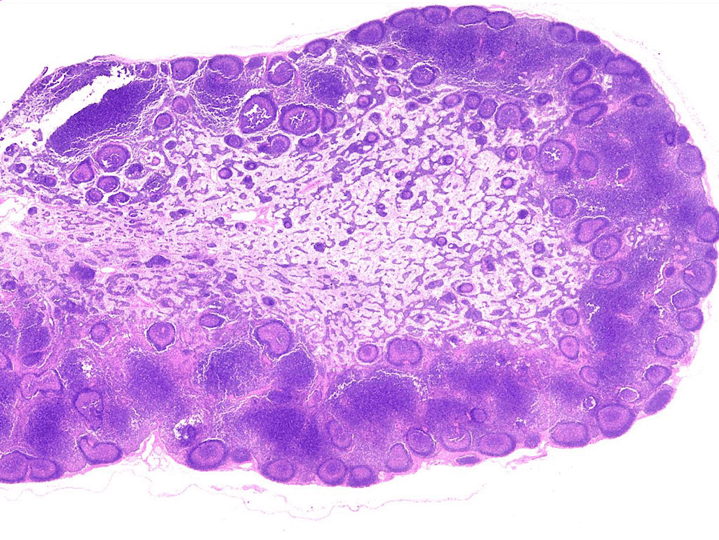
Identify the organ and give 3 histological reasons why.
What are the three sinuses of this organ.
Lymph node
- Has a capsule surrounding it with trabecular that protrude in.
- Also has a medulla and a hilum.
- Lymphatic nodule are only located in the cortex of the lymph node.
Subcapsular, trabecular and medullary
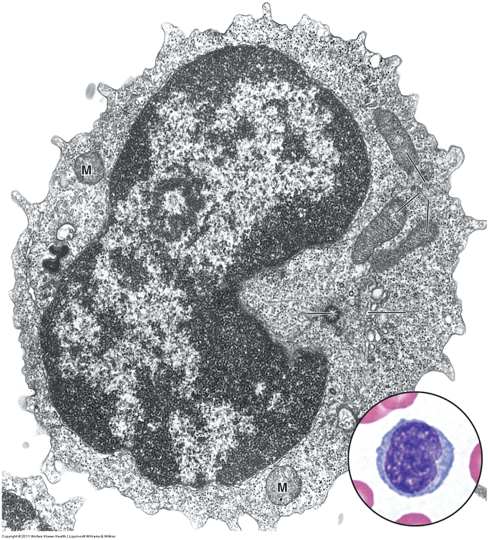 What is this? Histologically describe it. What is its function?
What is this? Histologically describe it. What is its function?
Where can this cell get its "education?"
Lymphocyte
Small cell with large, circular indented nucleus that is densely heterochromatic and very little cytoplasm.
Are immunocompetent cells that recognize and respond to antigens. (Agranulocyte)
B-lymphocytes - bone marrow
T-lymphocytes - thymus
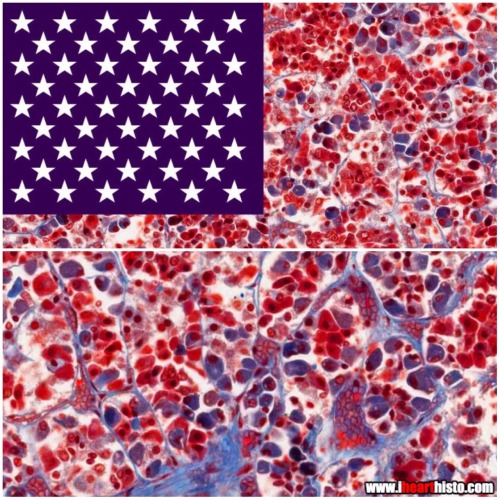 What kind of cells make up this flag, what are the functions of the specific cells that fall under these classifications, and what is this organ?
What kind of cells make up this flag, what are the functions of the specific cells that fall under these classifications, and what is this organ?
Pituitary gland
ACIDOPHILS - Somatotropes (GH), Lactotropes (PRL)
BASOPHILS - Gonadotropes (FSH, LH), Thyrotropes (TSH), Corticotropes (ACTH)
CHROMOPHOBES
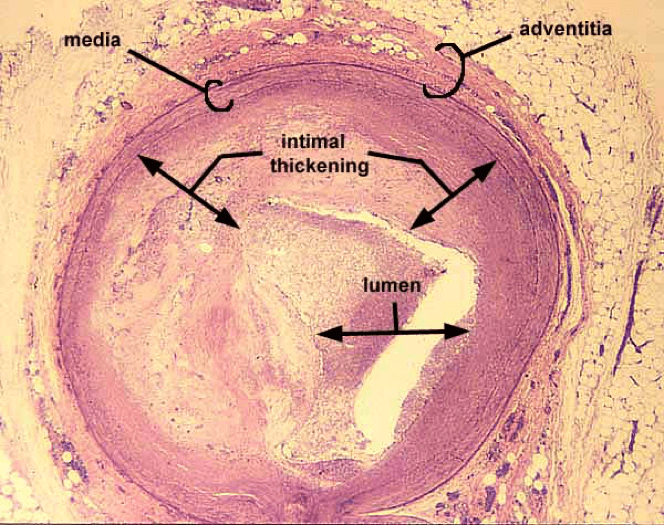 Describe what is happening in this picture.
Describe what is happening in this picture.
Build up of atheromatous plaque occluding the vessel. Has very thick tunica intima.
LDL cholesterol permeability increase and buildup. Will get oxidized when phagocytized by macrophages and become foam cells.
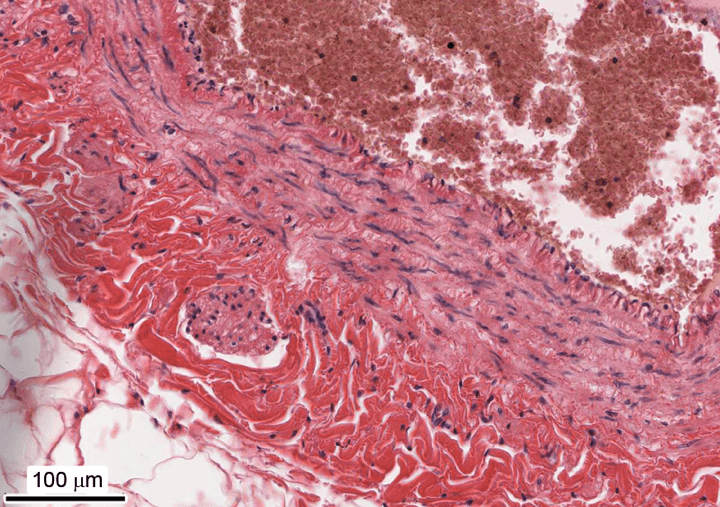 What is this vessel and how do you know?
What is this vessel and how do you know?
Muscular vein
- longitudinal section of smooth muscle within the tunica external/adventitia
- relatively large lumen
- relatively thin tunica media (muscle layer) compared to the adventitia
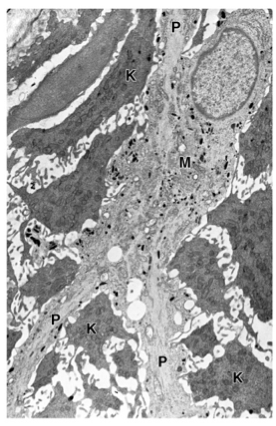
Identify "M"
Describe what M would look like under an LM and explain its function
Melanocyte.
Clear staining cell that has cytoplasmic processes. It clear itself but produces and secretes melanin granules which are responsible for the pigmentation of skin.
Identify A, B, C, D.
Explain the transition of epithelium from the upper to lower respiratory tract.
A-terminal bronchiole
B-respiratory bronchiole
C-alveolar sac
D-alveolar duct
Goes from respiratory epithelium which is ciliated simple columnar epithelium to ___ eventually to simple squamous which makes up part of the respiratory membrane.
What is this organ?
Explain the function of the five types of epithelioreticular cells and where they are located.
What is the massive cell called in the right image?
Thymus
I - make up capsule
II - in cortex of thymus, participate in positive selection of thymocytes
III/IV - barrier between cortex and medulla
V - located in medulla and participate in negative selection of thymocytes
VI - Composed Hassall's corpuscles (image on right), located in medulla.
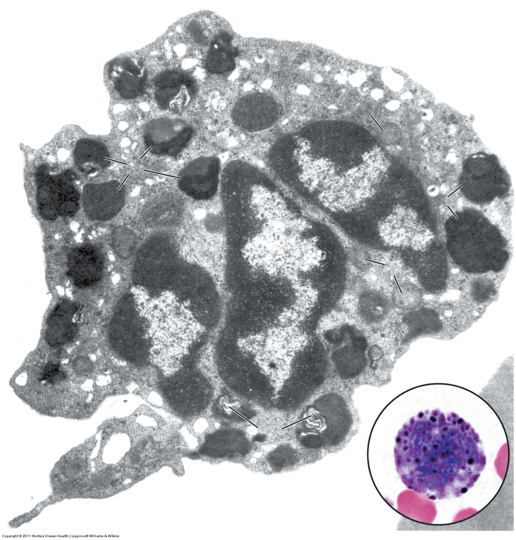 What is this EM. Histologically explain how you know.
What is this EM. Histologically explain how you know.
What is the function?
Basophil
There is a multi lobed nucleus and many large granules residing in the cytoplasm that would make this cell stain very basophilic. Has myelin figures in cytoplasmic granules.
Granulocyte - contains specific granules and has a function similar to mast cells which function in response to allergic reactions, producing histamines.
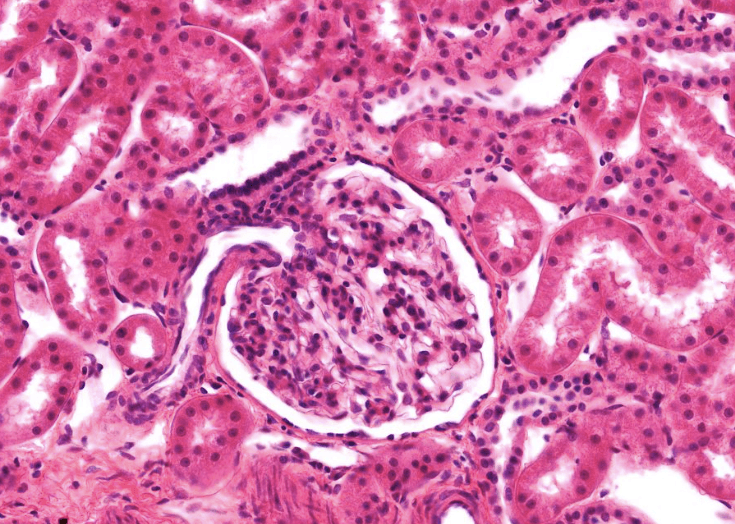
Differentiate between a PCT, DCT and CD.
Identify the urinary pole and the vascular pole.
Find macula densa cells, explain what they look like and their function.
PCT - Simple cuboidal with brush border, intensely stained cytoplasm somtimes with basal striations, smaller lumen diameter but larger tube. 3-5 nuclei
DCT - Smaller simple cuboidal without BB, has nuclei that bulge into lumen of tube, larger lumen diameter but smaller tube. 5-6 nuclei
CD - Larger cuboidal cells that have distinct borders between them and ovoid nuclei. ~12 nuclei
MD - Portion of the DCT at the vascular pole that has cells very tightly packed together. Senses NaCl levels, regulates vessel tone and secretion of renin.
What are the components of the intrinsic conduction system of the heart?
Sinoatrial (SA) node
Atrioventricular (AV) node
Atrioventricular (AV) bundle/ Bundle of His
Left and right bundle branches
Purkinje fibers - modified cardiomyocytes
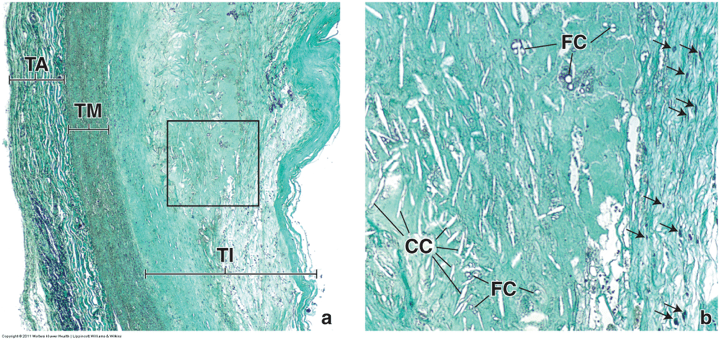 What is FC? Explain how this condition happens.
What is FC? Explain how this condition happens.
What is this stain?
Atherosclerotic lesion
Endothelial injury leading to increased permeability of LDL cholesterol, increased adherence of leukocytes
Macrophages will oxidize LDL cholesterol to form foam cells (FC)
Masson's trichrome
 What are the layers of this pumpkin pie?
What are the layers of this pumpkin pie?
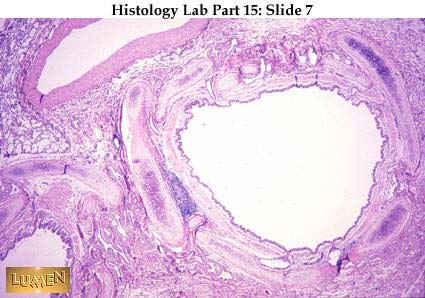 Identify this tube? Histologically explain how you know.
Identify this tube? Histologically explain how you know.
Bronchus - Has discontinuous cartilage rings around lumen of tube - Lumen of tube is slightly convoluted - size of tube is still relatively large - smooth muscle surrounds tube - visible glands around tube
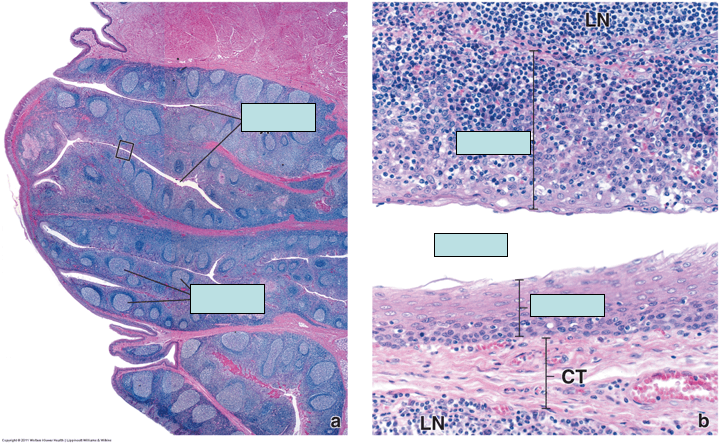
Identify this organ. Histologically explain how you know.
What kind of epithelium lines the crypts? Why does this make sense?
What stain is this?
Palatine tonsil - no capsule, has crypts, lymphatic nodules are present.
Crypts are lines with stratified squamous epithelium. This makes sense because the tonsils are located in the oral cavity which is also lined by SSE.
H & E
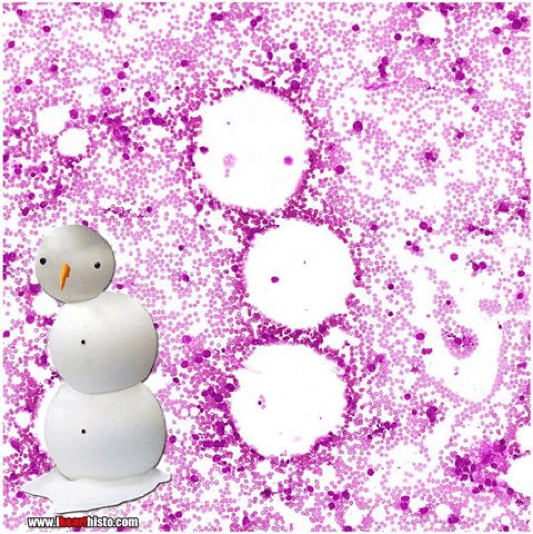 Identify this tissue.
Identify this tissue.
Can you find a megakaryocyte and explain its function?
Bone Marrow
Megakaryocytes give rise to thrombocytes that bud off of it. Thrombocytes are responsible for blood clotting.
What is the function of high endothelial vessels and where can they be found?
HEVs can be found in lymph nodes (cortex) and other well establish lymphatic nodules. They are lines with "high" endothelium, hence the name.
HEVs are where most lymphocytes will enter the lymphatic nodule.