This is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
What is osmosis?
This process uses protein channels to move larger molecules, such as sugars, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
What is facilitated diffusion?
This process allows plants to make their own food in the form of sugars/carbohydrates.
What is photosynthesis?
Cellular respiration requires this gas, but fermentation does not.
What is oxygen?
This thin, flexible structure acts as a barrier between the cell and its surroundings, letting in some materials and keeping others out.
What is the cell membrane?
Endocytosis, exocytosis, and moving materials from low concentration areas to high concentration areas are all considered forms of active transport because they require this.
What is energy? Endocytosis, exocytosis, and active transport all require energy.
This is the process by which a large particle enters a cell after being “wrapped up” or engulfed by part of the cell membrane.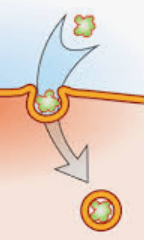
What is endocytosis?
If there are more molecules of solute outside of the cell than inside the cell, this is how they will move.
The molecules will move into the cell.
(Water will move out, and the cell may shrink in this hypertonic solution.)
This is the substance that cells use for energy.
What is ATP? (Adenosine Triphosphate)
Some microorganisms use this whip-like tail to help with movement.
What is a flagellum?
When there are fewer molecules in the solution than in the cell, this would be the type of solution.
What is hypotonic?
(Molecules would flow out of the cell and into the solution. Water would enter the cell, causing it to swell.)
This process moves particles out of the cell in vesicle “packages” formed by part of the cell membrane.
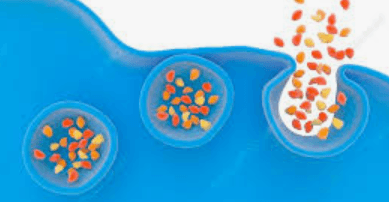
What is exocytosis?
This type of bacteria is rod-shaped.
What is bacilli?
Lactic acid, alcohol, muscle cramps, and yogurt are all produced through this process.
What is fermentation?
These tiny, hair-like extensions cover some protozoans and help with movement.

What is cilia?
Channels and pumps in the cell membrane that can act as passageways to help move materials in and out of the cell are made from this.
What is protein?
These are the three ingredients that are necessary for photosythesis.
What are water, carbon dioxide, and energy from sunlight?
Although some may make you sick, some varieties of this type of organism help with digestion, break down and recycle waste, produce vitamins, and help produce some foods.
What are bacteria?
This animal-like, single-celled protist is eukaryotic because it contains a nucleus. (Examples include amoeba and cilliates.)
What is a protozoan?
Similar to our own respiration process, cellular respiration releases these two waste products.
What are carbon dioxide and water vapor?
A virus must infect one of these in order to reproduce.
What is a host cell?
These proteins which can come from vaccines or exposure to a virus will bind with the virus and prevent it from infecting cells.
What are antibodies?
When the concentration both inside and outside the cell is the same and molecules move both in and out, the solution is described by this term.
What is isotonic?
This type of bacteria has a round or spherical shape.
What is cocci?
These two processes both help cells break down sugars and release energy.
What is cellular respiration and fermentation?
This phrase describes the cellular membrane because it is made up of many different components and is constantly shifting and changing.
What is fluid mosaic?
This is the pigment that helps plant cells collect energy from sunlight and reflects green light.
What is chlorophyll?
Name the organelles where each process takes place.
A.) photosynthesis
B.) cellular respiration
A.) What is the chloroplast?
B.) What is the mitochondria?
Anaerobic bacteria are able to survive in extreme environments like the early earth because they do not require this.
What is oxygen?
These cells do NOT have a nucleus. (Examples include archaea and bacteria.)
What are prokaryotic cells?