To draw/pull the Tongue and larynx caudally. You would expect the patient to have difficulty swallowing
what is the most distal action of the semitendinosus
extend the tarsal joints
the difference between a digit, phalanx, and phalange
What is "a digit is the whole body region of a finger, including vessels, nerves, muscles, etc... A phalanx is on digital bone on any given digit.... And phalanges are 2 or more phalanx"
The roots that efferent and afferent neurons traverse through in that order?
efferent: Ventral root
Afferent: Dorsal root
The meaning for the root word "Bulla"
What is Blister?
The Components of a Joint Capsule
What is "Fibrocartilage, Synovial Membrane, Synovial Fluid, Articular Cartilage"
The coolest, most awesome and funny, best guy at vet school
What is "My dawg Brenden"
The most distal action of the caudomedial antebrachium muscle group & identify the muscle in this group that is unlike the others. What is that muscles primary action?
What is "Flex the digital joints; the Ulnaris Lateralis; Flex the carpal joints"
The primary defecit you would notice if the Rump and Caudal Thigh Muscles were non-functional. What does that look like clinically?
what is "extend the coxal/hip joint; inability to draw the pelvic limb caudally
what are the 3 things needed to determine orientation on an X-ray
1. Flipped or not
2. What view are we given
3. whats the body part
Name the types of neurons that are located in all spinal nerves
GSE, GSA, GP, SP
The meaning for the root word "Choan"
What is Funnel?
The significance of the Dorsal Ligaments (Be species specific)
(Dog): To passively keep the distal interphalangeal joint hyper extended; minimally developed, equal in size
(Cat): To passively keep the distal interphalangeal joint hyper extended; Well-developed, Asymmetrical in size, allow cats to sheath claws.
The Best Star Wars Trilogy
4,5,6
A new hope, empire strikes back, return of the jedi
What is the most proximal action on the caudal arm muscle group? Name an antagonist to this group and its origin and insertion.
Flex the Shoulder Jt.
Biceps Brachii or Brachialis
Supraglenoid Tubercle & Proximal/medial aspects Ulna and radius
or
Proximal Part of the lateral humerus & proximal/medial aspects of the radius and ulna
The most proximal action of the sartorious muscle when the limb is bearing weight
flex the coxal/hip joint
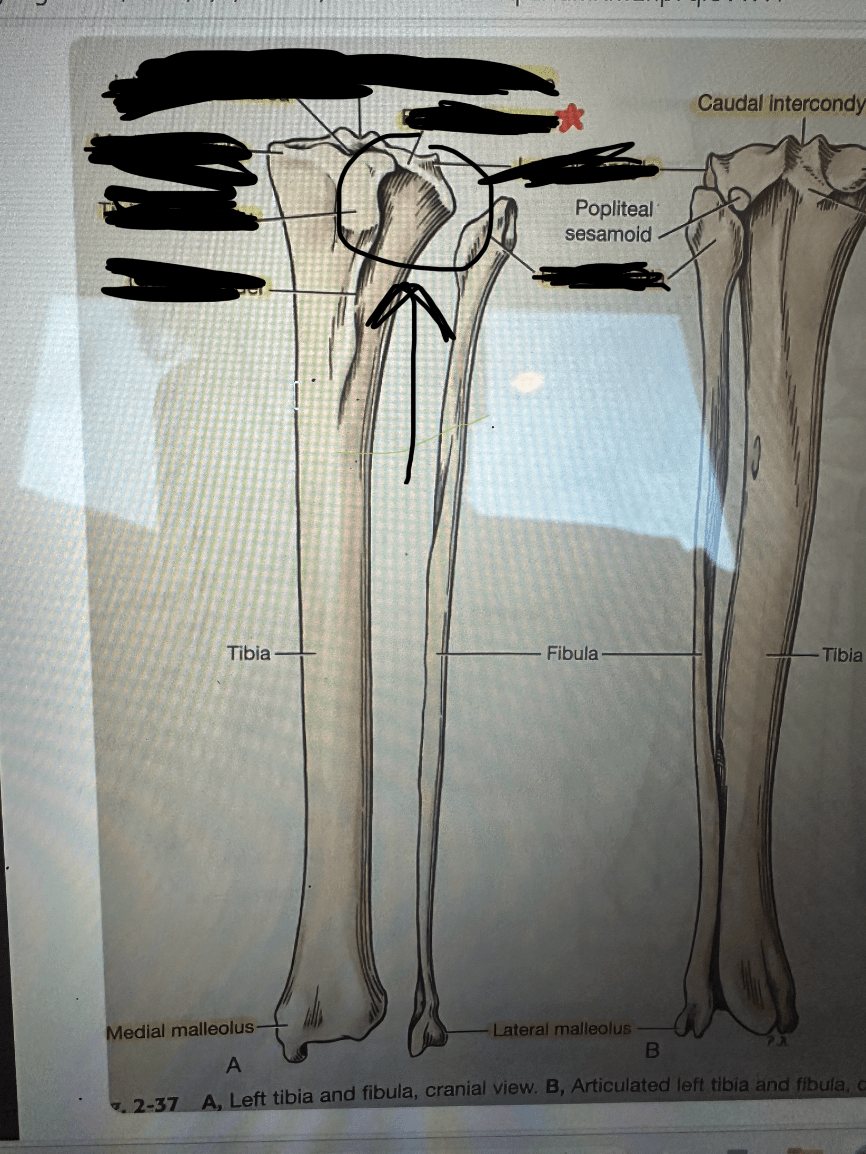
What is "extensor groove"
What so located in the gray matter and white matter in that order? And why GVA and SVA are clinically irrelevant?
Gray: Cell bodies
White: Anxons
GVA and SVA cannot be tested in animals clincially
Break down the word "Blastocoel"
What is "Bud/germ Cavity"
What is "the site where the deep digital flexor rises to become superficial on the palmar aspect and where the superficial digital flexor ends (on the middle phalanx of the digit)
The origin of Brenden's dog's name
What is "Aurora borealis"
A dog presents to the hospital with a 104.3 fever, Lethargy, and inappetence. Upon physical exam, you palpate an engorged structure on the ventrolateral aspect of the cervical region. What is the structure that you palpated? What hollow structure (located in the carotid sheath) is associated with this structure? and what muscle lies just superficially to this structure?
What is "the superficial cervical lymph nodel; The Tracheolympahtic Trunk; The Omotransversarius
The 3 minor contributors to the common calcanean tendon
What is "Biceps Femoris, Semitendinosis, Gracillus"
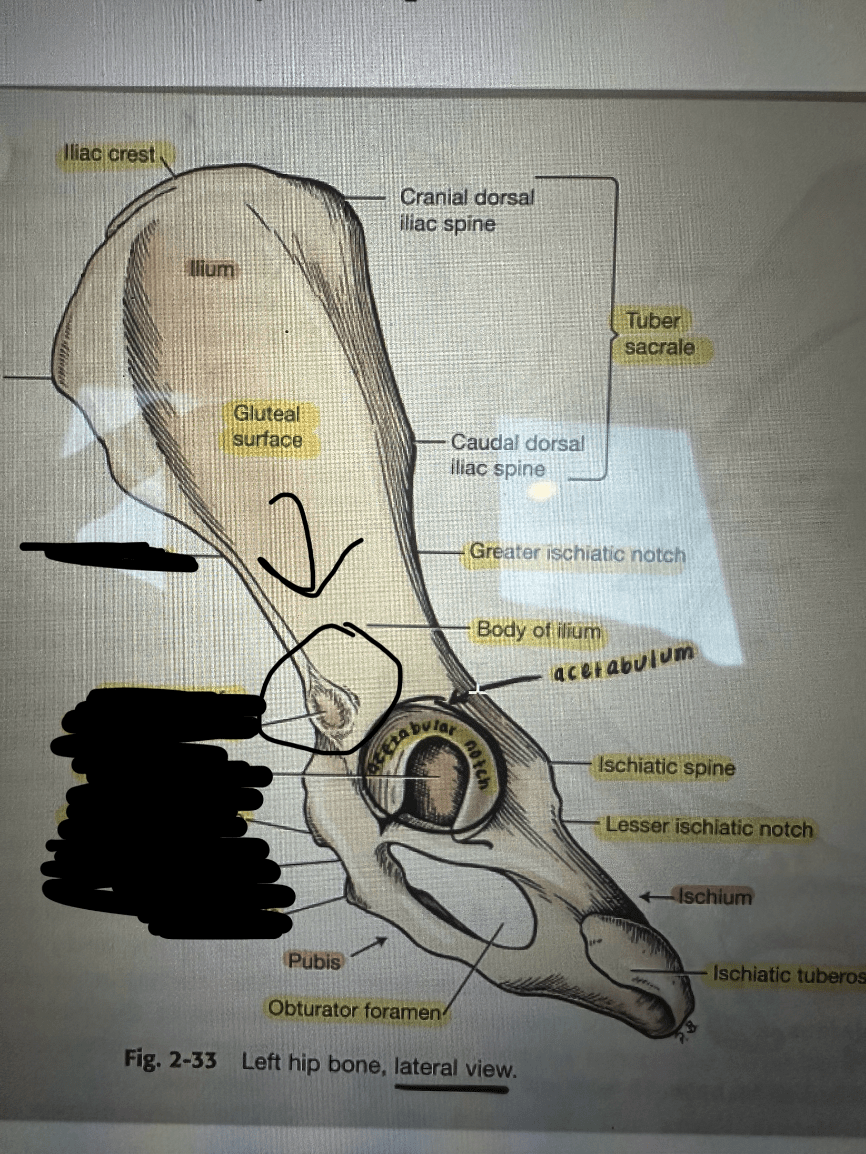
What is " Lateral Area of the Rectus Femoris"
The name of cell bodies and cell processes in the CNS and PNS respectively
Cell Body:
CNS- Nucleus
PNS- Ganglion
Cell Processes:
CNS- Tracts
PNS- Nerve
Break down the word "Ankylodactly"
What is "Bent Finger/Toe"
The 3 types of Joints, their subtypes and their degree of mobility; Composition and example of each
Fibrous Joints: little mobility
1. Suture Jt: On Dorsal Skull; made of Collagenous Connective Tissue
2. Gomphosis Jt: On teeth roots; made of Collagenous Connective Tissue
3. Syndesmosis Jts: Everywhere else; specifically, between the metacarpal bones. also, Collagenous Connective Tissue
Cartilaginous Jts: Little movement
1. Symphysis jts: made of Fibrocartilage, found at Pelvic symphysis and Mandibular Symphysis
2. Synchondrosis jts: made of Hyline cartilage, found at the sacroilliac joint
Synovial Jts: very mobile
comprised of joint capsules and ligaments (previously answered hopefully)
Brenden's favorite TV Show
How I Met Your Mother
Name all differences between the dog and cat in the throacic limb (Hint: there is 6)
1. Clavicle is ossified in cats NOT dogs
2. Cats have a Suprahammate Process of the Scapula
3. Cats have a Supracondylar Foramen of the Humerus; Dogs have a Supratrochlear foramen of the Humerous
4. Superficial Pectoral M. inserts on proximal ulna and distal humerous in the Cat; and on crest of greater tubercle in dogs
5. Brachiocephalicus inserts on proximal ulna in Cats; and distal crainial humerus in dogs
6. The dorsal Ligament is more developed in Cats and asymetrical. Cats can actively flex this ligament.
Name the OIA's of the medial thigh muscles
Gracillus - Pelvic Symphysis; crainial tibia/tuber calcani; Adduct the limb (principal) action; extend coxal and tarsal joints; flex the stifle joint
Adductor - ventral surface of os coxae; caudal surface of femur; adduct the limb (primary) and extend the coxal joint
Pectinius - iliopubic eminence; Distal body of the femur; adduct the limb
Sartorius - illium; patella and crainial tibia; flex the coxal joint and variable action of stifle
Name all of the bones in the carpal complex
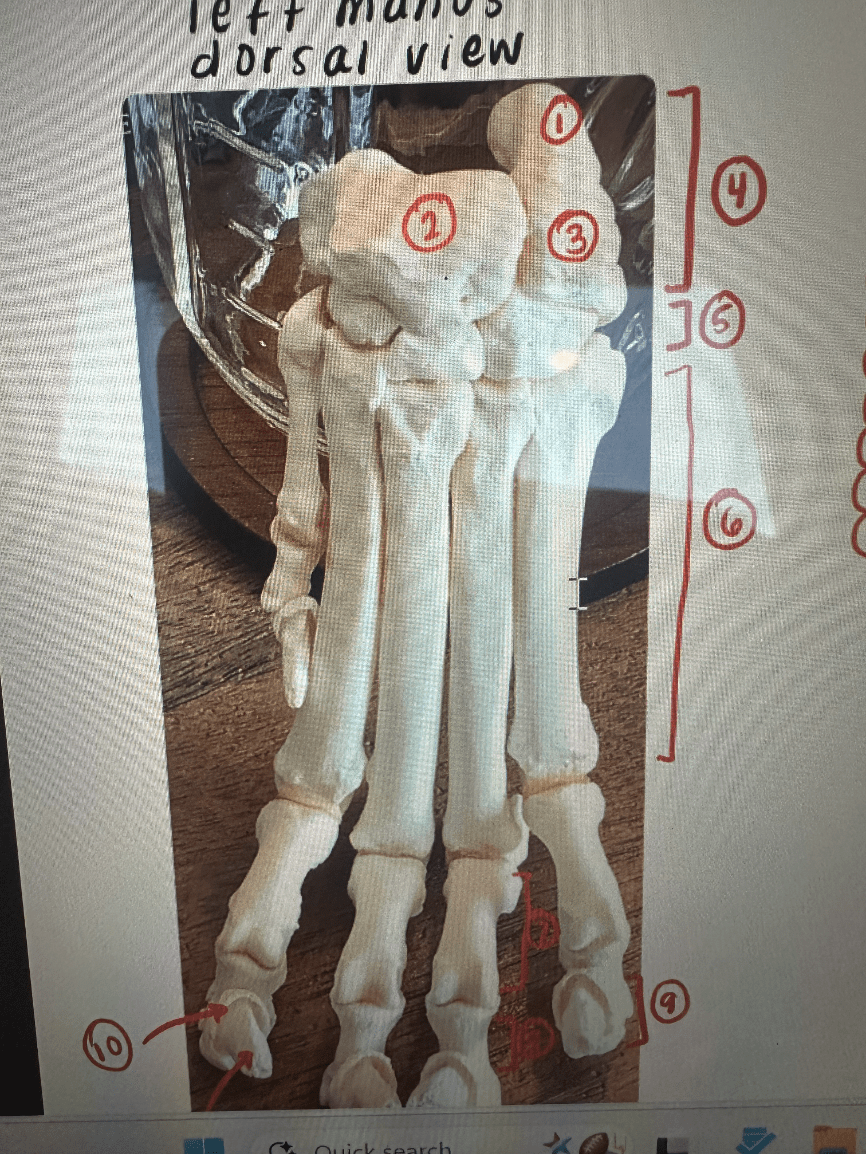
Accessory Carpal, Ulnar Carpal, Intermedioradial Carpal, Distal Carpal bones 1-4
Name the cell structure for GSE, GVE, GSA, SSA, GP & SP; and what type of organs/information do they receive?
GSE: Multipolar, conscious motor function of skeletal muscle
GVE: Multipolar, unconscious motor function of smooth muscle
GSA: Sensory pseudounipolar; Touch, Temperature, and Nociception
SSA:sensory bipolar; vision and hearing
GP: Pseudounipolar; proprioception
SP: Pseudounipolar; proprioception
Break down the words "Cyanoderma", "Cholecentesis", and "Ansasubclavia"
What is "Blue Skin", "Bile Perforation", and " Loop/Handle Under Clavicle"
List and Draw the tarsal joint complex, and which joints communicate with each other.
Tarsocrural Jt.
Talocalcaneal Jt.
Talocalcaneocentral Jt.
Calcaneoquartal Jt.
-------------------------------------
Centrodistal Jt.
Tarsometatarsal Jt.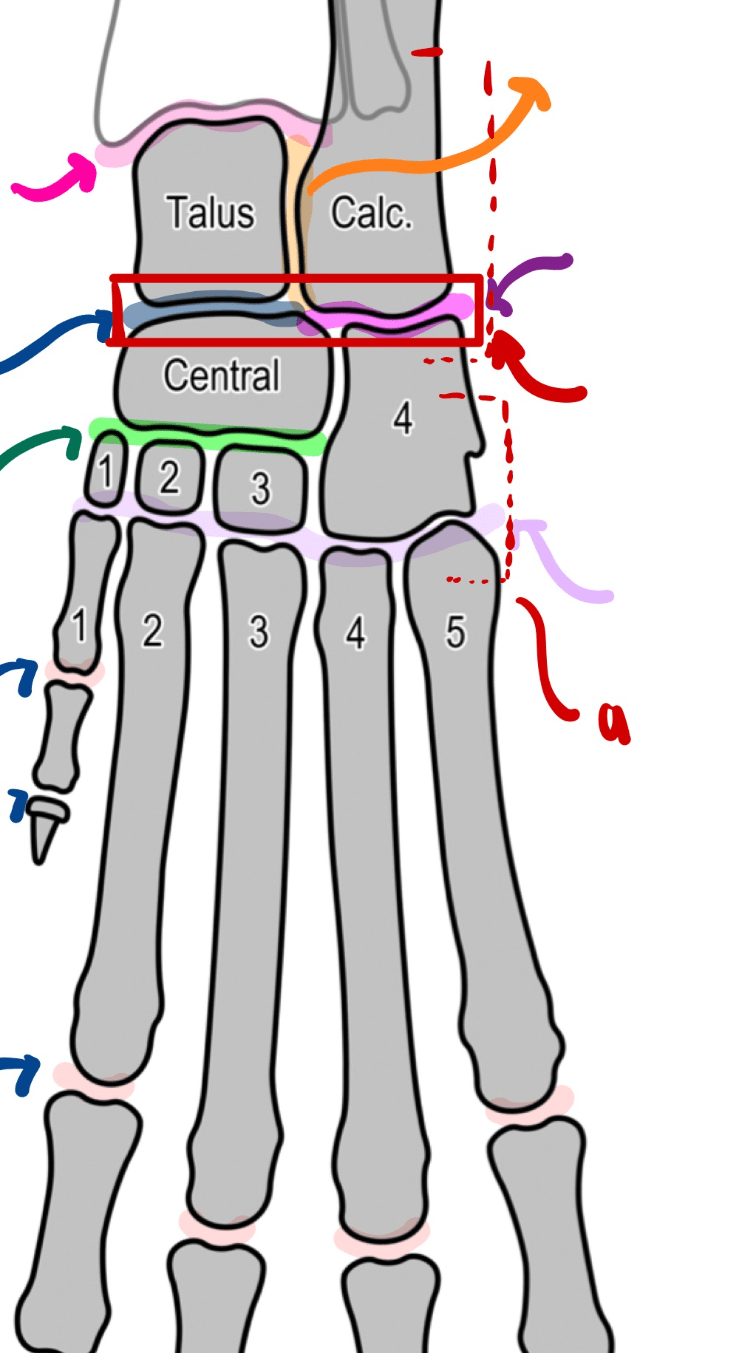
Brenden's Highschool nickname
Cub