What subatomic particle (of an atom) has a negative charge?
Electrons (e-)
Type of Chemical Bond that forms when electrons are transferred from one atom to another?
Ionic
The Oxygen side of a Water molecule has a slightly ____ charge.
Negative
Water has a pH of ___
7
a macromolecule with a basic chemical ratio of CH2O is a(n) ______
Carbohydrate
An example of a polymer of a Nucleic Acid
DNA or RNA
Reactants are the chemicals that undergo a chemical reaction; ______ are the end result of a chemical reaction.
Products
The number of Protons (p+) of an atom determines its _______ ________
Atomic Number
Type of bond that holds Hydrogen to Oxygen in Water
Covalent (or Polar Covelent)
Water is considered a ______ molecule because electrons are shared unequally.
Polar
Any solution that has a pH above 7
Base / Alkaline
a monomer of a Carbohydrate is a ________.
Monosaccaride
Protein structure level that consists of a single chain of amino acids (polypeptide)
Primary
Energy needed to start a chemical reaction
Activation
An atom that may have a different mass number is called a(n) ________
Isotope
Type of molecule / compound in which atoms covalently share electrons equally.
Nonpolar
What causes 2 Water molecules to be attracted to one another?
Hydrogen Bonding
What cation rises in concentration when an acid is formed
H+ (Hydrogen ions)
a ______ Fat or Lipid has all single bonds between C Atoms and is typically solid at room temperature.
Saturated
Type of Bond that holds Amino Acids together in a protein.
Peptide Bond
NaOH + HCl --> H2O + NaCl
the " --> " means ______
Yields
An atom that has lost an ion is specifically called a(n) _______
Cation
Type of Van der Waal force that involves a slightly positive Hydrogen attracted to a slightly negative end of another molecule.
Hydrogen Bonding
Property of water that causes it to "bead" up on a smooth surface.
Cohesion
A Basic (alkaline) solution is formed when a chemical releases _____ into the solution causing ______ (same answer) concentration to rise.
OH- (Hydroxide ions)
Process by which monomers are joined together to make a polymer.
Polymerization
The following illustration is what monomer?
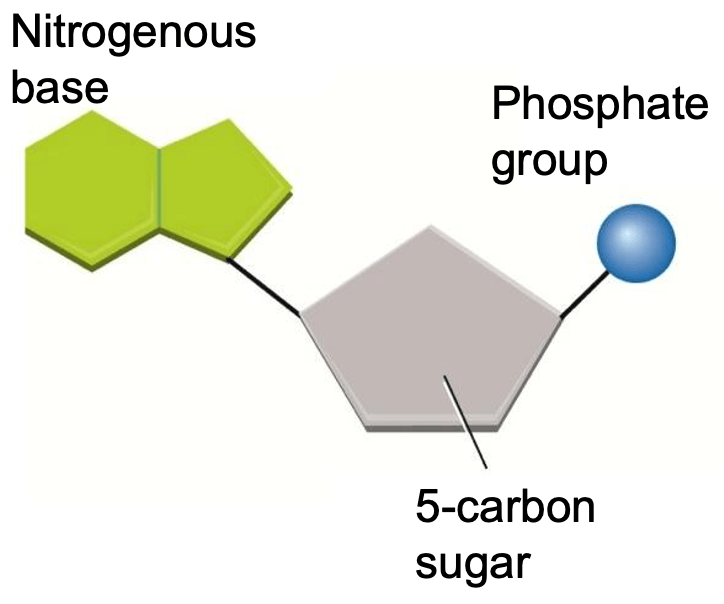
Nucleotide
The Name of the chemical that an enzyme will change or affect
Substrate
The type of electrons that are shared or transfered in a chemical bond is formed between atoms
Valence
Type of chemical bond that occurs when 6 electrons (3 pair) are shared between atoms
Triple (Covalent) bond
Water's polar nature causes it to be called the Universal _____ because of its ability to dissolve many things.
Solvent
A mixture in which the particles are not dissolved completely (i.e. Blood)
Suspension
Phosphate portion of a phospholipid is considered ______ because of its attraction to water.
Hydrophilic
Special Protein that catalyzes metabolic reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for that reaction.
Enzymes
The area where an enzyme & the chemical it's changing connect.
Active Site
How many neutrons exists in Cl-36 when its atomic number is 17
19
Weak interactive bond between molecules due to opposing charged ends of those molecules.
Van der Waals force
Property of Water that allows it to absorb a certain amount of heat with minimal temperature change.
Specific Heat
A pH of 3 is _____ times more acidic that a pH of 8
The following molecular structure indicates that it is a ________
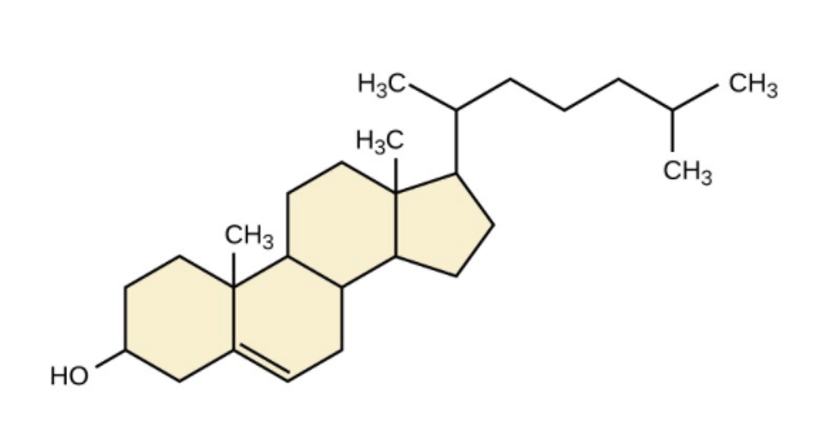
When a protein loses its shape (structure) and therefore loses its function (due to a change in temperature, pH or other environmental factor), - it has said to have _______.
Denatured
Name TWO factors that affect or influence an enzyme's function or rate of reaction.