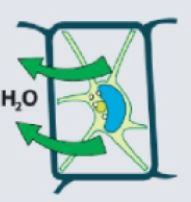
What is happening to this cell and why?
Due to osmosis, water is leaving the cell because there is a higher concentration of solute outside the cell. OR there is a higher concentration of water inside the cell.
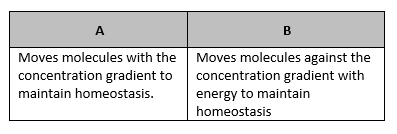
A student is trying to fill in the titles of the table above. What would be the correct labels for the A and B portion of the table?
A- Passive B- Active
What are TWO characteristics that both passive and active transport have in common?
Both maintain homeostasis or equillibrium, transport molecules in and out of a cell, types of transport
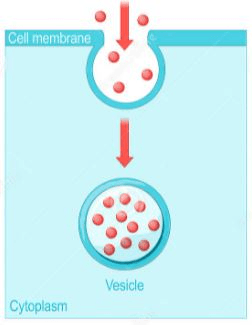
What type of transport does this represent? AND why might a cell do this?
Endocytosis. Cells like an amoeba may engulf nutrients to support the cell. (Amoeba eating a paramecium)

Which numbers in the table are describing PASSIVE transport?
1, 2, and 5
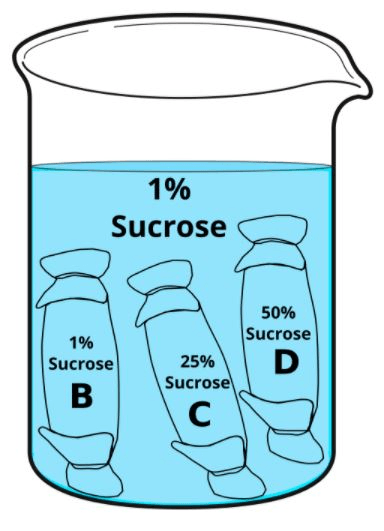
What will happen to cell model B? C? and D? AND explain.
B will stay the same because its in an isotonic solution
C and D will swell because they are in a hypotonic solution.
DOUBLE DAILY - which one will swell more?
The state at which a cell is in balance or equilibrium
Homeostasis
What type of passive transport moves water molecules through the cell membrane from high to low concentration?
Osmosis
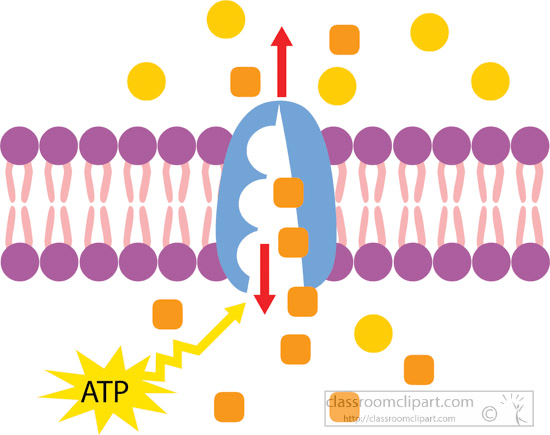
Why is this considered active transport? (Provide 2 reasons)
ATP energy is used AND molecules are moving from LOW to HIGH
What type of transport is being shown in the image below?

Facilitated diffusion
What type of transport moves molecules from low to high, against the concentration gradient?
Active transport
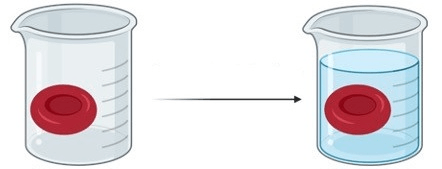
What type of solution was this cell placed in?
Isotonic
The name of the structure that controls what goes in and out of the cell
Cell membrane
What type of passive transport moves small molecules directly through the cell membrane from high to low concentration?
Simple diffusion
Active transport requires ______ to move molecules against the concentration gradient
energy (ATP)
What type of transport is being showed in this image?

Simple diffusion
What is the type of transport where molecules move from high to low?
Passive transport
Which beaker, A or B, is hypotonic to the other?
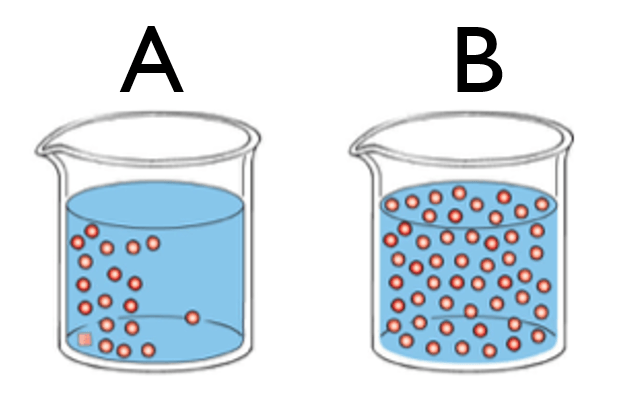
A is hypotonic to B
What type(s) of transport help the cell maintain homeostasis?
Passive and active transport
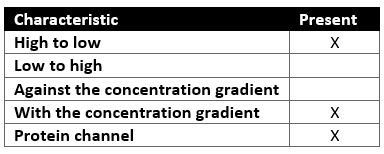
What type of transport is represented by this attribute chart?
Facilitated diffusion
Provide an analogy to explain ACTIVE TRANSPORT.
Ex: Monomers are like Legos because they both build bigger things.
Teacher choice!
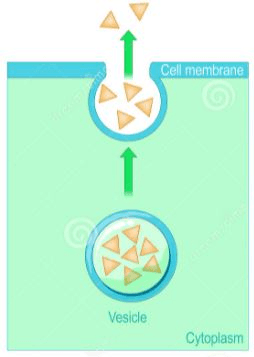
What process is occurring? (Be specific)
Exocytosis, a type of active transport
Use these two terms in a sentence that makes sense.
homeostasis; semipermeable
Ex: Transport of molecules through a semipermeable membrane helps maintain homeostasis.
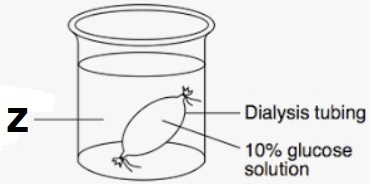
Examine this experiment. After 20 minutes, this cell model loses mass. Explain how this could have happened. (Be sure to mention the tonicity of Z)
Z was a hypertonic solution. This caused water to move from the hypotonic solution within the dialysis tubing to the solution outside the cell model.
The feature of the cell membrane that allows certain molecules in and out
Semipermeable
What type of passive transport is being shown in the red blood cells below?
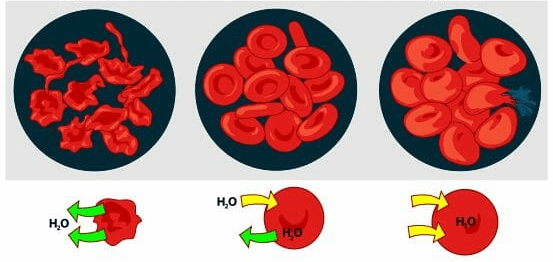
Osmosis
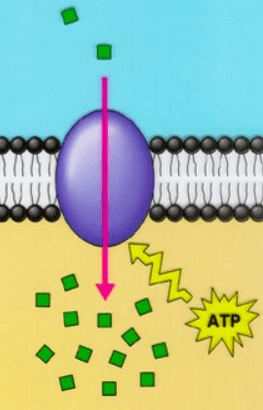
Which biomolecule is directly involved in active transport?
Protein or protein pump
What type of transport is being shown in the image below (A, B, C)?
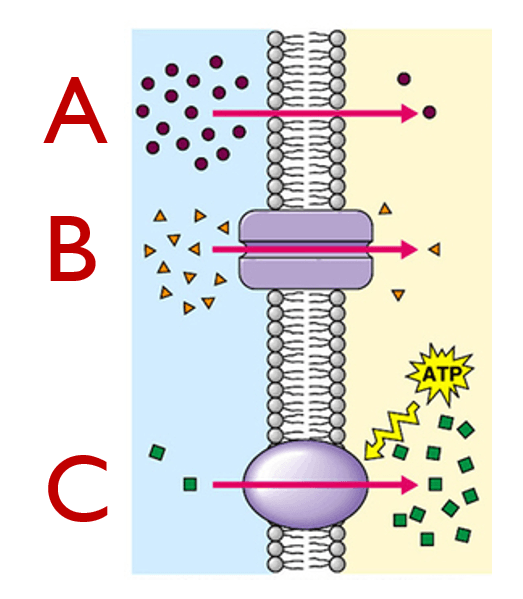
A= Diffusion
B= Facilitated Diffusion
C= Active transport
Provide 2 characteristics (not examples) of PASSIVE TRANSPORT
High to Low, With the concentration gradient, no energy needed
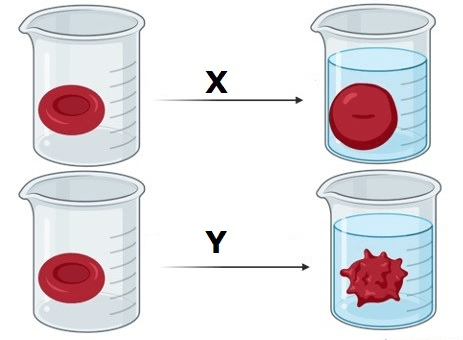
What type of solution was X placed in? AND What type of solution was Y placed in?
X= Hypotonic solution
Y= Hypertonic solution