This is the equation for the ideal gas law.
What is PV=nRT?
This is the strongest type of intermolecular force.
What is a covalent network?
This type of solid has its atoms arranged in a highly ordered, repeating pattern.
What is a crystal lattice or a crystalline solid?
Kinetic molecular theory states that this variable is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of gas particles.
What is temperature?
This property of a mixture of gases shows the amount of each gas in relation to the total amount of a gas.
This is what happens to the temperature of a gas when the volume is decreased by half.
This type of force is present between all molecules, regardless of polarity.
What are London dispersion forces?
This is the phase change from a liquid to a gas, starting at the surface of the liquid.
What is evaporation?
Graham's Law says that the rate of effusion of 2 gases is inversely proportional to the square root of this property.
What is molar mass?
What type of solid is shown by the picture here?
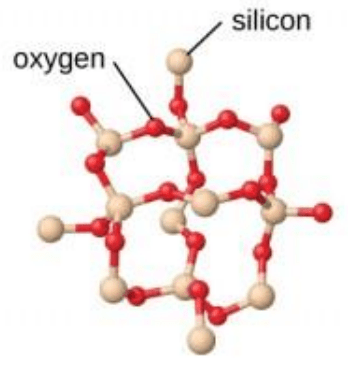
What is a covalent network solid?
This is the pressure of 1 mole of an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP).
What is 1 atm?
What is a hydrogen bond?
The fixed nature of this property means that liquids cannot be easily compressed.
What is volume?
This is the relationship between the velocity of gas particles and their molar mass.
What is an inverse relationship?
The particle diagram shown here might show which state of matter?
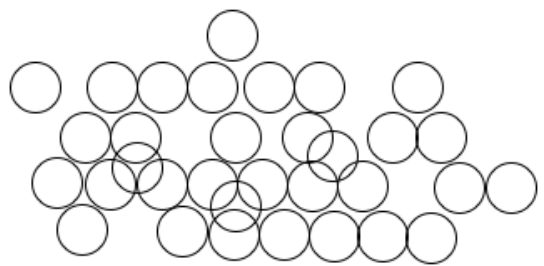
What is a liquid?
This is what happens to the pressure of a gas if the volume is decreased by half.
What is the pressure doubles?
The relatively high boiling point of water is due to the strength of this type of intermolecular force.
What is hydrogen bonding?
This is the amount of energy required to change a liquid into a gas.
What is the heat of vaporization?
The area under the curve in a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution represents this property of a gas.
What is the total number of particles?
This property of a liquid describes its resistance to flow due to intermolecular forces.
What is viscosity?
This is the volume occupied by 1 mole of an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP).
What is 22.4 L?
These are all of the intermolecular forces present in a sample of hydrogen chloride (HCl).
What are London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions?
This type of bond allows for the conduction of electricity due to free-moving electrons.
What is a metallic bond?
Kinetic molecular theory is used to derive this law.
What is the ideal gas law?
The fact that the pressure of a gas mixture is the total pressure of all the individual gases added up is described by this law.
What is Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures?