the maximum population size of a species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available
carrying capacity
The population of rabbits on our nature trail hill has a carrying capacity of 100 rabbits. Their limiting factor is the amount of food available. In the last few weeks, the rabbits had a lot of babies. There are now 150 rabbits living on the hill. What will happen next, and why?
The rabbit population will decrease due to insufficient food supply for the extra rabbits
A student draws a food chain of an environment near their high school. This food chain includes 8 different organisms, from the producer at to bottom to 7 trophic levels of consumers above them. What is unrealistic about this scenario?
There are too many trophic levels. The 10% rule would prevent enough energy from being passed that many times to sustain animals at the top.
Quaternary consumers: 10 kcal
Producers: ? kcal
Quaternary consumers: 10 kcal
Tertiary consumers: 100 kcal
Secondary consumers: 1,000 kcal
Primary consumers: 10,000 kcal
Producers: 100,000 kcal
The purpose is to decrease competition for resources by using them in different ways.
Example: plant roots growing in different areas of the soil, predators hunting at different times, birds using different parts of the same tree.
Symbiotic relationship between a tick and the animal it kills
predation
Imagine a scenario where there are two species of tree in a forest. One of the two trees grows faster than the other, absorbs nutrients quicker, grows above the other species and deprives them of sunlight, and eventually outcompetes them and completely removes them from the area. What is this scenario called?
Competitive exclusion
Picture a trophic pyramid. What would occur if you removed a tertiary consumer from the top? Be specific.
Trophic cascade: secondary consumers boom, primary consumers crash, producers boom
This type of ecological succession occurs on bare rock after events like volcanic eruptions or glacial retreat, where no soil previously existed.
primary succession
Is resource partitioning more closely related to habitat or niche? Explain.
Niche. Habitat is just where organisms find resources, whereas niche is where & how. The "how" is important because organisms can use the same space and resources, but in different ways (resource partitioning)
10% of energy is passed onto the next tropic level
10% Rule
A population of bacteria are growing in a flask of ideal medium at optimum temperature over a 24-hour period. They have no limiting factor other than space, and it will take them weeks to reach that point. What will their population growth curve look like after the 24 hours?
It will be exponential growth (they have not reached carrying capacity yet)
In what situation would you see an exponential curve for growth?
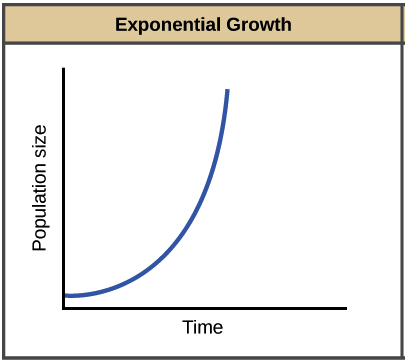
Burning fossil fuels over the last 100+ years has created a "legacy load" of excess carbon in the atmosphere. Even if we ceased all use of fossil fuels today, the legacy load would continue to negatively affect the global climate. What is one realistic way to correct this?
More plants (absorb CO2)
This term refers to the variety of all living things in an ecosystem, including the number of species, genetic variation, and the variety of ecosystems themselves.
Biodiversity
an animal that eats animals that eats plants
secondary consumer
A flood passes through an ecosystem. The ecosystem has two dominant species. One species is densely populated and the other is sparsely populated. Which will be more affected by the flood, and why?
Neither (floods are a density-independent limiting factor)
What are two things all symbiotic relationships have in common?
1) between two different species 2) at least one organism benefits
In ecological succession, this is the stable, long-term community of plants and animals that forms at the end of the process, unless disrupted by disturbance.
climax community
Why are most density-dependent factors biotic?
Biotic factors are typically involved in ecosystem relationships (like predator-prey numbers or symbiotic relationships), which tend to be density-dependent
2 species cannot occupy the same niche or they will be in interspecific competition, one species will die off
competitive exclusion principal
In a ecosystem there are grass, rabbits, snakes, and hawks. A forest fire occurs and all grass dies. What kind of limiting factor is this? What kind of succession is this an example of? What will happen to the food web?
Density independent factor, secondary succession, trophic cascade will occur where because there is no more producers the number of rabbits will decrease, causing number of snakes, and hawks to also decrease.
This is an example of what type of resource partitioning?
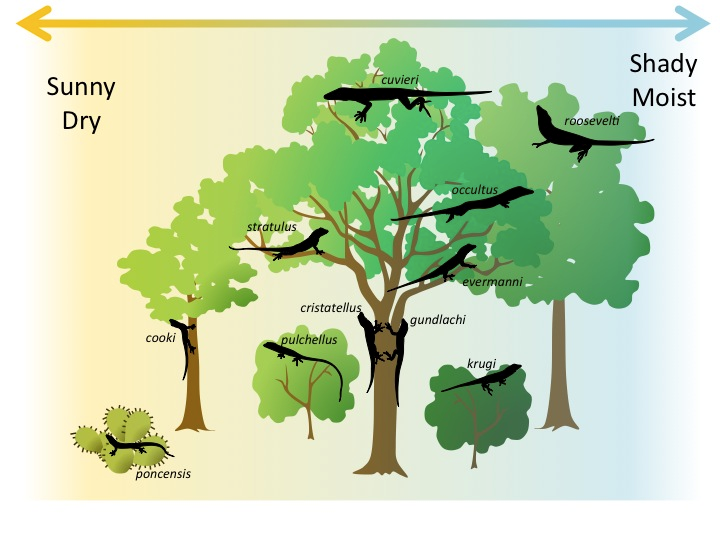
Spatial
This type of limiting factor affects populations regardless of their size, with examples including wildfires, hurricanes, and droughts.
What is a density-independent limiting factor?
What month has the most birthdays in the United States?
August
(this will not be on the test)