This hormone, produced by the pancreas, helps move glucose from the blood into the cells.
What is insulin?
This is the blood glucose level commonly used to define hypoglycemia.
What is less than 70 mg/dL?
Name 2 classic signs of hyperglycemia
What is increased thirst and frequent urination?
This measurement helps patients track their blood sugar at home.
What is self‑monitoring with a glucometer or CGM?
Name the 5 criteria for a high-risk diabetes patient.
What is...
1. A1C >9%
2. New to insulin
3. New diabetic (diagnosis <6mos)
4. Admitting Diagnosis of DKA
5. Hypoglycemia Events
The A1C test reflects average blood glucose over this many months.
What is 3 months?
This fast‑acting carbohydrate treatment uses the “15–15 rule.”
What is eating 15 g of carbs and rechecking in 15 minutes?
This blood glucose value is commonly used to define severe hyperglycemia.
What is over 250 mg/dL?
The “plate method” encourages filling half the plate with this type of food.
What are non‑starchy vegetables?
If a patient is identified as a high-risk diabetes patient, they will need which additional education booklet?
What is "Your guide to understanding Diabetes Management" Booklet

This organ is primarily responsible for making insulin.
What is the pancreas?
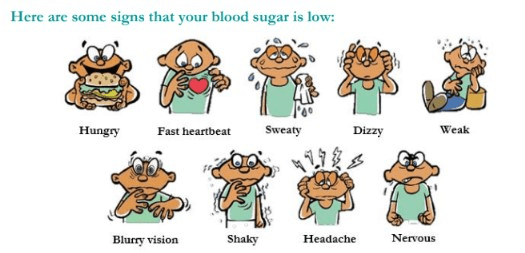
Name 3 common symptoms of hypoglycemia
What is.... pale, shaky, sweating, headache, hunger or nausea, fatigue/weak, fast/irregular heartbeat, dizzy, blurry vision, nervous
Fruity breath, rapid breathing, and abdominal pain are symptoms of this emergency.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Every diabetic patient with HAH, should receive this type of diabetes patient education.
What is the Living with Diabetes: The Basics for adults' booklet or Survival Skills Booklet? 
When a high-risk diabetes patient is identified, which HAH team is notified/consult ordered?
Who is HAH WCON?
This term describes blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis.
What is prediabetes?
This emergency medication can be given if the patient is unconscious or unable to swallow.
What is glucagon?
Illness, stress, infection, or missing doses of this medication class can trigger hyperglycemia.
What are insulin or oral diabetes medications?
What 3 main education topics are MIH CP's responsible for teaching patients?
1. Delivery of Booklet
2. Glucometer Teaching
3. Insulin Teaching/Administration
Everything else is a sugar-free cherry on top!
You can consult this teammate for nutrition and diet choices for our HAH high risk diabetes patients.
Who is Nutrition? Anna Wise (M-F)
This type of diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance and often develops in adulthood, though it can occur at any age.
What is Type 2 diabetes?
This blood glucose value defines a critical low or Level 2 hypoglycemia and requires immediate treatment.
What is a blood glucose level less than 54 mg/dL?
Will accept answer <50mg/dl
Name 3 considerations for hyperglycemia and sick day management.
What is....
Monitor blood sugar more frequently
Continue to take insulin/DM meds as ordered
Hydrate!

What 3 main education topics are Virtual Nursing responsible for teaching patients?
Go over booklet with patient virtually:
1. A1C Risk Level/Ensure A1C within 3mos/90days
2. Hypoglycemia
3. Hyperglycemia
Everything else is a sugar-free cherry on top!
An A1C > 7% means a patient is at high risk for diabetes complications. Can you name the 5 major complications of uncontrolled diabetes?
What are retinopathy(eye), nephropathy(kidneys), neuropathy(nerves), cardiovascular disease (heart/stroke), and foot complications(ulcers)?