Termometer
Equipment to measure temperature in Celsius
Matter
It's everything that has mass and volume
Transpiration
Plants contribute to the water cycle when water evaporates from the aerial parts of the plant, such as leaves and stems.
Neutron
Subatomic particle with no charge. It's located in the nucleus
Bunsen burner
To heat solids or the contents of beakers and test tubes
Particle theory
Says that everything is made of particles, which are molecules and atoms
condensation
Water vapour cools and condenses to form clouds.
Atomic number
It's the number of neutrons in one type of atom
Evaporating dish
To evaporate a liquid from a solution
solids
Have a definite shape and volume. Particles are organised and very close together.
runoff/accumulation
Water flows over the ground and returns to bodies of water, completing the cycle.
Mass number or Atomic mass
It's the relative mass of an atom, the sum of neutrons and protons.
Tongs and test tube holders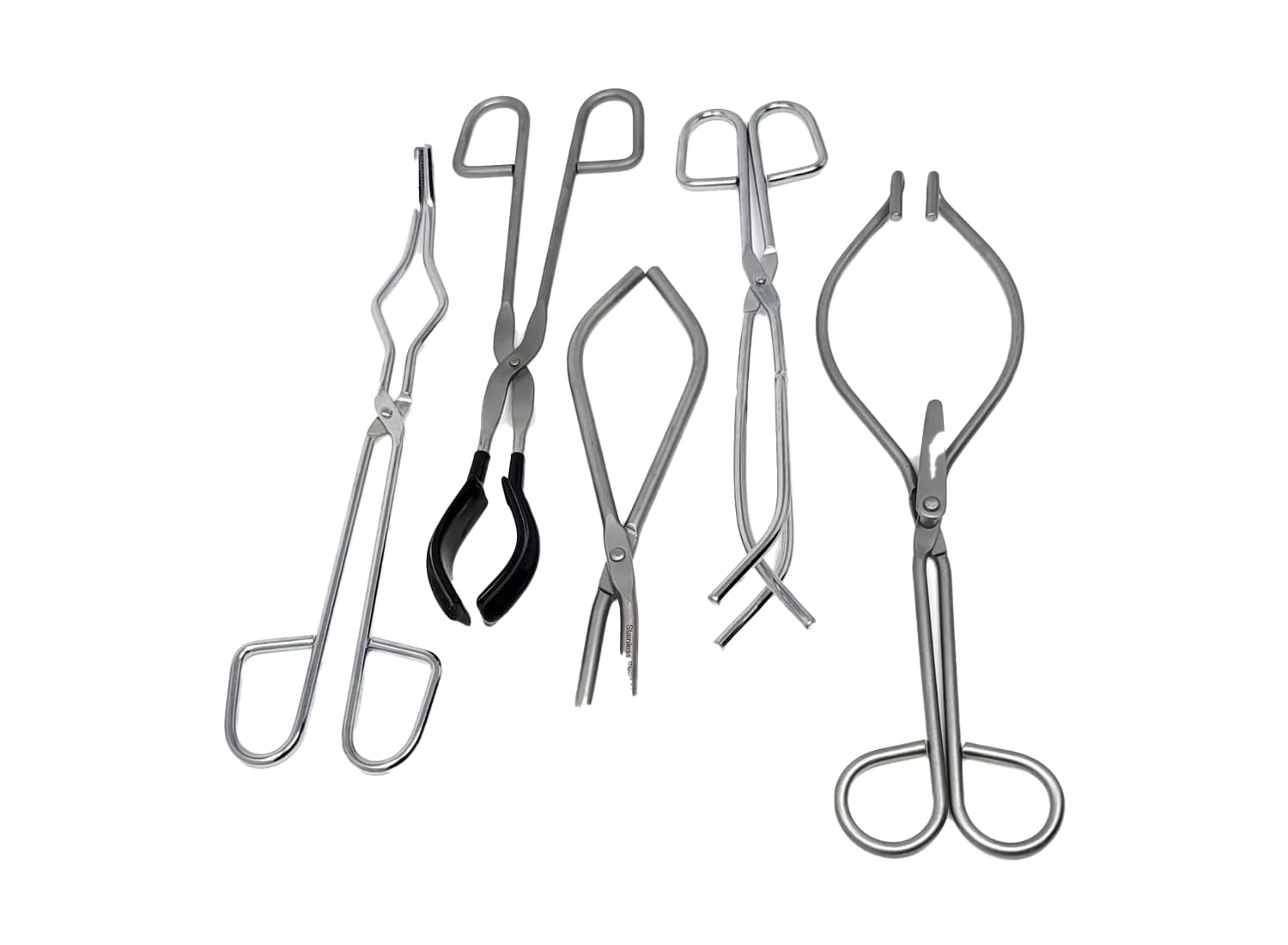
To hold hot apparatus or to hold a test tube in a hot flame
Liquids
Matter with definite volume but no definite shape. It takes the shape of their container.
infiltration
The water that falls back on the earth’s surface moves between the layers of soil and rocks and is accumulated as the underground water reserves known as aquifers.
Thomson model
Plum pudding model. Discovery of the electron. A ball of positive charge and electrons inside it.

Volumetric flask. To measure and heat liquids
Sublimation
When a matter can change from a solid to a gas (and back again).
Evaporation
The heat of the sun causes water from the surface of water bodies such as oceans, streams, and lakes to evaporate into water vapor in the atmosphere.
Rutherford model
A positively charged nucleus that contains nearly all the mass of the atom.