Provide an example of negative punishment
access to reinforcer -> bx --> no reinforcer
What are 3 main components of an FBA?
indirect assessment, direct assessment, functional analysis
Antecedents and consequences are arranged so that their separate effects on problem behavior can be observed and measured
Why is it important to measure behavior?
•Tells you if behavior needs to be changed
•Allows you to determine if behavior has changed after a treatment has been implemented
What is a line graph?
Each point shows the level of the behavior in relation to a specific point in time or environmental condition
Shows repeated measurements of the same behavior
access to attention is which function?
social positive reinforcement
Provide an example of positive reinforcement
no reinforcer -> bx --> reinforcer
What are 2 types of indirect assessments?
interviews
rating scales
What is the attention condition of an FA? Include therapist behavior, EO manipulated, consequence
Therapist only provides attn contingent on target bx
EO: absence of attention (deprivation from attn)
consequence: attention
What is reactivity?
a temporary reaction to being observed
What is a bar graph?
Each bar shows the frequency of the behavior in different categories or conditions
Can use to summarize group performance
removal of attention is which function?
social negative reinforcement
What are two types of negative punishment?
time-out and response-cost
provide one example of an indirect assessment
FAST, QABF, FAI, MAS
What is the escape condition of an FA?
Therapist only provide a break from work following target behavior
EO: aversive work/demand presented
consequence: removal of demand for 20-30s
Provide an example of continuous recording
recording every instance of behavior
frequency, duration, intensity, latency
 Describe the required components of a graph
Describe the required components of a graph
1. y-axis and x-axis
2. labels on y- and x-axis
3. numbers on each axis
4. data points on graph are connected
5. phase lines
6. phase labels
access to tangible is which function?
nonsocial positive reinforcement
Provide an example of positive punishment
no aversive --> behavior --> aversive
What are some direct assessments?
ABC narrative
ABC checklist
What is tangible condition of an FA?
Remove a preferred stimulus and then "give it back" only following challenging behavior
EO: removal of a preferred stimulus
consequence: return of the preferred stimulus
Provide an example of permanent product recording
Finished product of an art piece
A completed worksheet
Looking at a desk after a student sat there for class
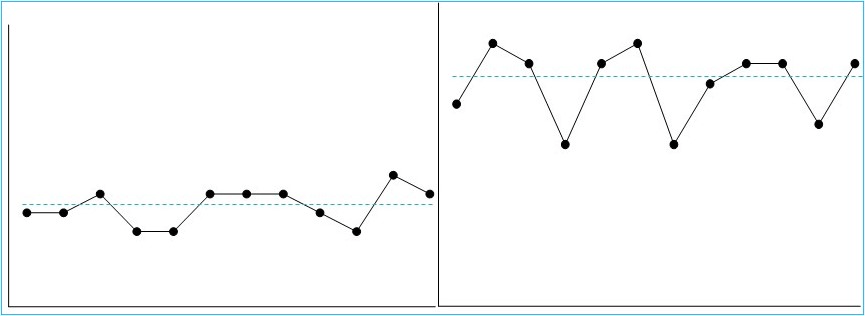
Which graph components are missing here?
- x-axis and y-axis labels
- numbers on each axis (with hash marks)
- phase labels
removal of a tangible is which function?
nonsocial negative reinforcement
Provide an example of negative reinforcement
aversive --> bx --> no aversive
What information is provided by indirect and direct assessments versus FA?
hypothetical function
actual function
What are the differences between the alone condition and the play (control) condition?
Alone: no programmed consequences, no potential reinforcers are present
Play: all potential reinforcers are presented, no programmed consequences
Both may assess automatic function
Provide an example of a discontinuous measurement system
partial-interval
whole-interval
momentary-time sampling
Describe variability, trend, and level when completing visual analysis
Variability: are the measures of behavior consistent across repeated observations
Level: value on the y-axis where the data converge
Trend: overall direction of the data path
Which functions are: 1) access to sensory stimulation and 2) removal of sensory stimulation?
1) sensory positive reinforcement (aka automatic positive reinforcement)
2) sensory negative reinforcement (aka automatic negative reinforcement)