The main organ of the integumentary system
What is the skin?
The primary organs of the skeletal system
What are bones?
The primary organs of the muscular system
What are muscles?
Levels of organization from smallest to largest
What is cell-tissue-organ-organ system?
The system which breaks down food, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines.
What is the digestive system?
A controlled, stable internal state
What is homeostasis?
Protein found in the epidermis which waterproofs the skin
What is keratin?
Dense, strong bone providing protection
What is compact bone?
Primary function of the muscular system
What is movement (of the body itself and substances through the body)?
The tissue type composing nerves, sending electrical signals throughout the body
What is nervous tissue?
The system responsible for defense against germs and foreign invaders of the body
What is the immune system?
A signal, or change away that triggers a response
What is a stimulus?
3 functions of the integumentary system
What are: protection, temperature regulation, vitamin production, senses, secretion of waste
Bone-forming cells
What are osteoblasts?
Muscle tissue type responsible for moving substances through the body
What is smooth muscle?
Examples of this tissue type include: blood, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage
What is connective tissue?
The only system in the body that has different organs for male and female individuals of a species
What the reproductive system?
A response to change that brings a system back to homeostasis, also functioning as the stop signal
What is a negative feedback loop?
Pigment produced in the skin to protect from UV radiation: the body produces more when exposed to more sunlight
What is melanin?
The difference between red bone marrow and yellow bone marrow
What is red makes blood cells and yellow stores fat (mostly in young children)?
The muscle tissue type pictured here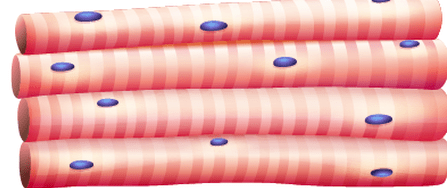
What is skeletal muscle?
Tissue type pictured here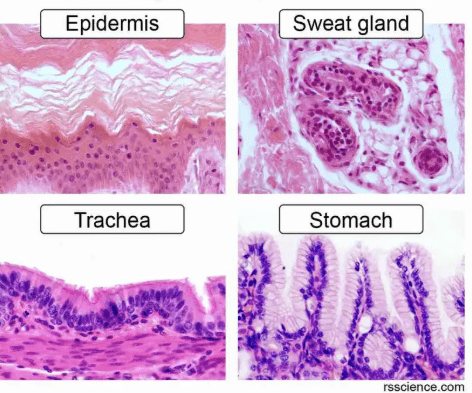
What is epithelial tissue?
Two systems that work with the skin to maintain homeostasis
What are muscular, nervous, immune, cardiovascular?
An example of a negative feedback loop in the body
What is sweating, shivering, or anything else that is accurate?
The vitamin produced by the skin
What is Vitamin D?
4 functions of the skeletal system
What are: Support
Allows movement
Mineral storage (reservoir)
Blood production (bone marrow)
Protects organs
Two involuntary muscle tissue types
What are cardiac and smooth muscle?
The difference between a tissue, an organ, and an organ system
What is: tissue - group of cells working for a job
organ - different tissues doing a job
system - multiple organs working together
Three systems that work together to deliver oxygen to all cells in the body
What are the cardiovascular/circulatory, respiratory, and muscular systems?
An example of a positive feedback mechanism
What is a baby's head pushing against the cervix, triggering oxytocin release from mom's brain leading to uterine contractions?