System
After traveling down the esophagus via Peristaltic Movement, food stops here and is mixed with strong acids that break down proteins.
What is: The stomach!
What's the function of the Respiratory System?
What is: To absorb Oxygen and remove Carbon Dioxide!
This transports oxygen around the body and contains hemoglobin.
What is: Red Blood Cell!
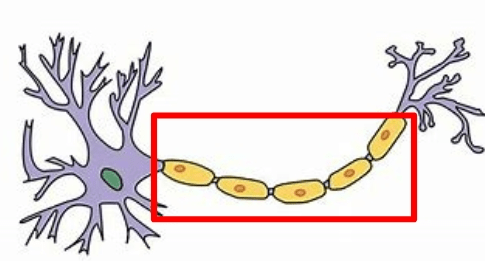
This is the part of the neuron that transmits an impulse to the Presynaptic Terminal.
What is the Axon! (Myelin sheaths also accepted)
What is the purpose of the skeletal system?
What is: Provides structure, support, and protection to the body
This part is responsible for the absorption of water back into the body.
What is: The Large Intestine!
This is known as the voice box which contains vocal cords.
What is: The Larynx!
Veins carry blood to the heart. What carries blood away from the heart?
What are: Arteries
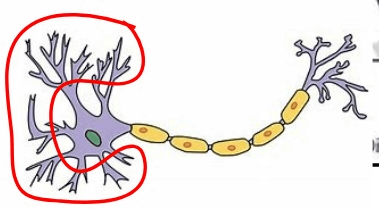
This is the part of the neuron that receives an impulse and transmits the signal to the nerve cell body.
What are the Dendrites!
This produces white and red blood cells.
This part contains enzymes produced by the Pancreas that break down carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Nutrients are also absorbed into the bloodstream via villi
What is: The Small Intestine!
This is located at the back of the throat. It connects the nasal cavity and the oral cavity to the trachea.
What is: The Pharynx!
This circuit transports blood to the lungs to pick up O2 and drops off CO2.
What is: Pulmonary circuit!
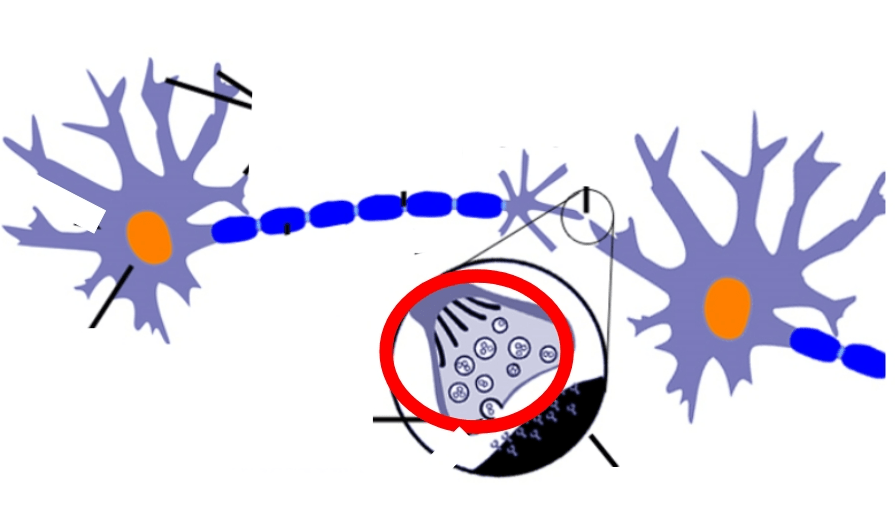
When this part receives an impulse, neurotransmitters are released into the cleft and transmit the signal to the postsynaptic terminal.
What is the Presynaptic Terminal!
Osteoclasts break down bone, what aids in building bone?
What is: Osteoblasts!
These two organs work together. One produces bile, while the other stores it and delivers it to the small intestine to emulsify lipids.
What is: The Liver and Gallbladder!
The Trachea connects the pharynx to the Bronchi, but what does the Bronchi do?
What is: channels air into and out of the lungs!
This circuit transports blood to the body to pick up CO2 and give O2.
What is: Systemic Circuit!
What is the Central Nervous System comprised of? (Two Parts)
What is the Brain and Spinal Cord!
This is the part of the skeleton that includes the arms and legs.
What is: The Appendicular Skeleton
What causes the mechanical breakdown of food while also enzymatically breaking down carbohydrates via amylase? (Two Parts)
What is: The Teeth and Salivary Glands
These are tiny air sacs that allow for air exchange. O2 moves from (this) into blood capillaries while CO2 moves from blood capillaries to (this).
What is: The Alveoli!
Which part of the heart recieves blood and which part pumps blood.
What is: The Atria recieves the blood and the Ventricles pump the blood.
This part of the nervous system comprises of the nerve cell network that spreads throughout the rest of the body.
The Peripheral Nervous System
This flexible connective tissue helps with joint movement and is mainly the bone composition of a newborn.
What is: Cartillage!
Suppose a person develops a condition that damages the villi, such as celiac disease or a chronic infection. Explain how this would affect the individual.
What is: The individual would experience reduced nutrient absorption because the Villi are responsible for absorbing nutrients into the bloodstream.
Suppose a person develops a condition, such as chronic bronchitis or asthma, that causes inflammation and narrowing of the Bronchi. Explain how this would affect the individual.
What is: Less air will reach the alveoli, where oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream. The body will also struggle to remove CO2 from the body as well.
Suppose a person develops a condition such as pulmonary embolism (a blood clot in the lungs). Explain how this would affect the individual.
What is: Less blood reaches the lungs, reducing the amount of oxygen absorbed and carbon dioxide removed.
Suppose a person has a disorder that causes the myelin sheath around their neurons to deteriorate (such as in multiple sclerosis). Explain how this condition would affect the individual.
What is: Normally, impulses "jump" in between each myelin sheath (Nodes of Ranvier) making our signals incredibly fast. However, without the sheaths, the impulses must travel continuously down the axon, making them much slower and sometimes unable to reach their destination at full strength.
Suppose a person develops a condition such as leukemia (cancer of the bone marrow). Explain how this would affect the individual.
What is: The person would experince decreased Red and White Blood Cell production, bone pain, and other complications.