(UE and back)
(UE and back)
(pelvis and LE)
(head and neck)
(wildcards)
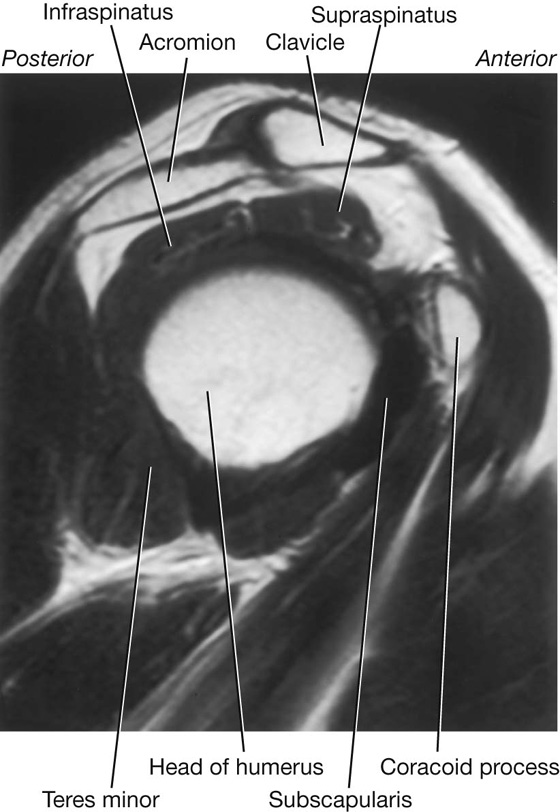
These muscles make up the rotator cuff.
What are supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis?
The coronary artery known as "the widowmaker".
What is the left anterior descending artery?

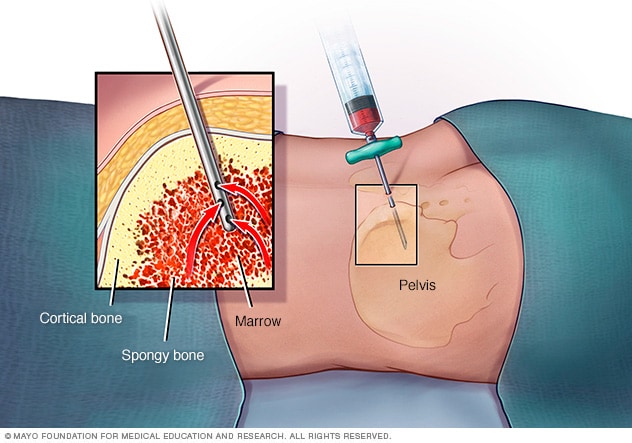
The anatomical landmark used when taking a bone marrow biopsy.
What is the iliac crest?
The 2 nerves involved in the gag reflex.
What are Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX; afferent) and Vagus nerve (CN XII; efferent)?

This spinal cord level supplies the dermatome at the level of the belly button.
What is T10?

If you damage this nerve, you might no longer have opposable thumbs.
What is the recurrent branch of the median nerve?


What is the sigmoid colon?

The nerve blocked by epidural anesthesia.
What is the pudendal nerve?

The names of the cranial nerves in order I-XII.
What are olfactory (I), optic (II), occulomotor (III), trochlear (IV), trigeminal (V), abducens (VI), facial (VII), vestibulocochlear (VIII), glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X), accessory (XI), and hypoglossal (XII) nerves?
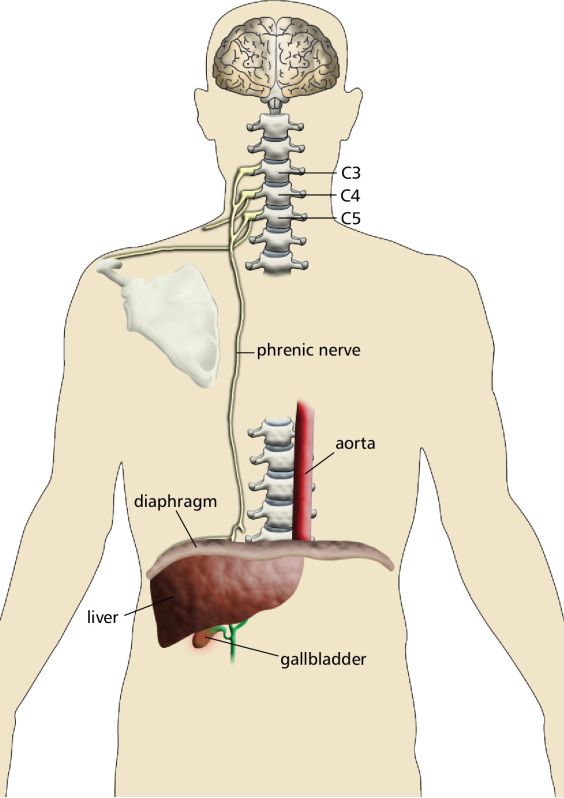
This nerve is responsible for pain from irritation of the peritoneum being referred to the shoulder.
What is the phrenic nerve?
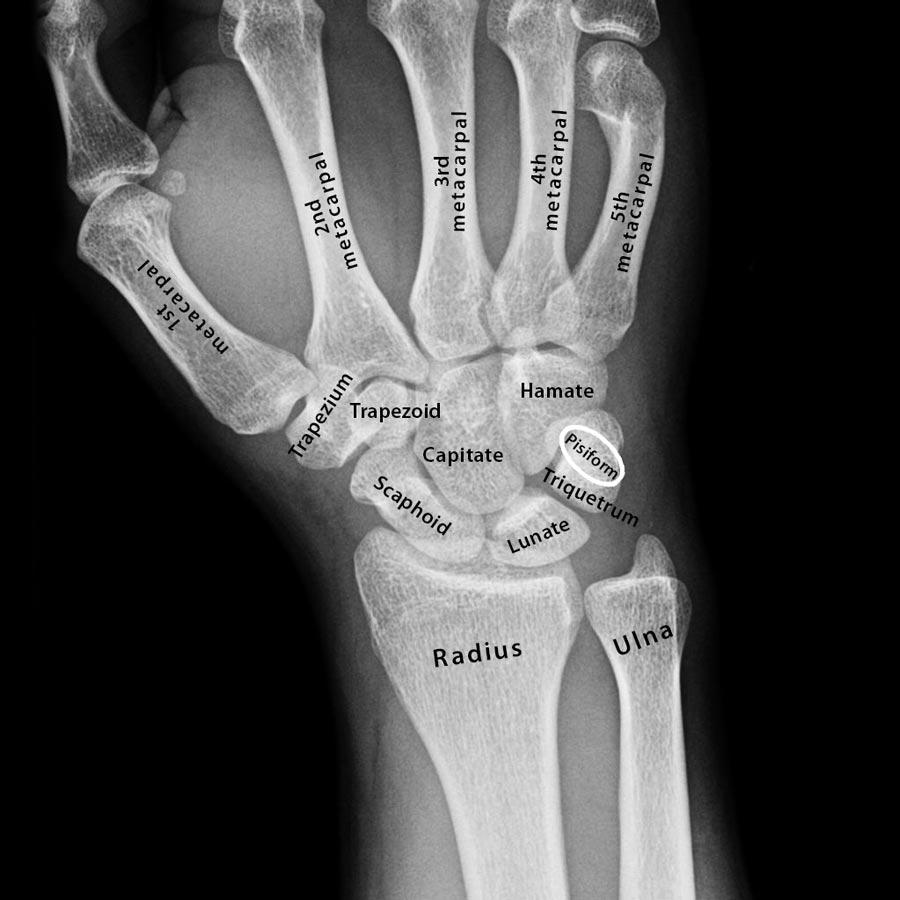
The carpal bones (start on proximal row from lateral to medial then distal row lateral to medial).
What are scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate?
The layers of the abdominal wall from superficial to deep.
What are skin, subcutaneous tissue, Camper's fascia, Scarpa's fascia, external oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis, transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fat, and peritoneum.

The muscles (2) responsible for lateral rotation of the extended hip joint and aBduction of a flexed hip.
What are obterator internus and piriformis? 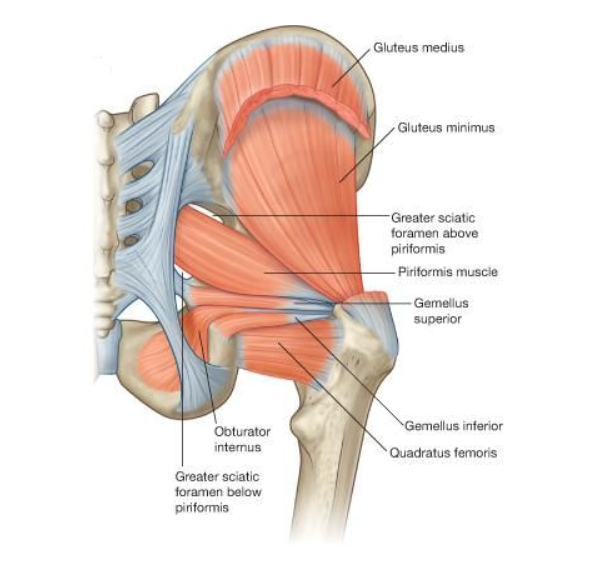
The physical exam finding in the patient with this finding on CT Face.

What is upward gaze palsy?

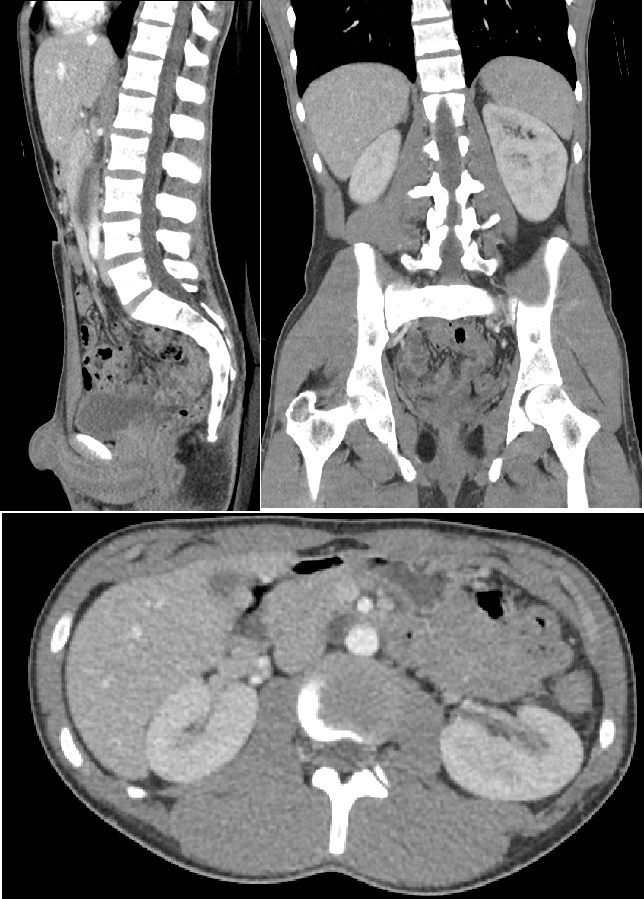
This imaging study results in the highest magnitude of radiation exposure. (be specific!)
What is CT Abdomen Pelvis?
The nerve damaged in this presentation:

Ulnar Nerve. CLAW HAND!

The anatomical boundaries used when treating the diagnosis shown in the CXR below.
What is 5th ICS, anterior axillary line, lateral border of pectoralis major, and lateral border of latissimus dorsi?

The injury seen in this image. 
What is an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear?

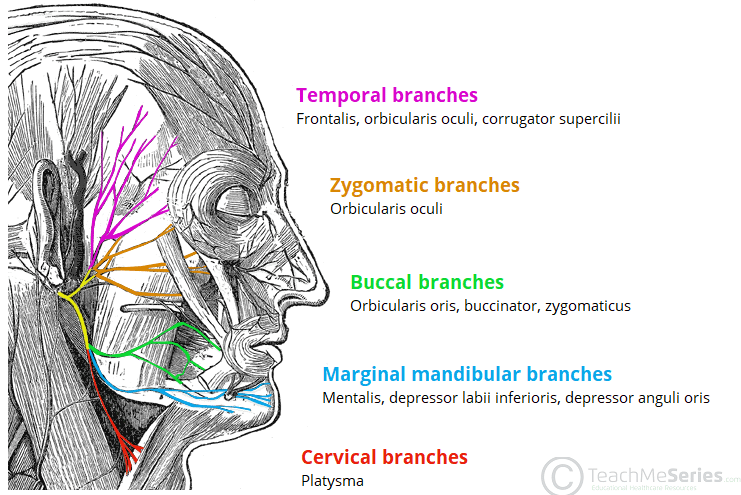
The 5 terminal branches of the facial nerve.
What are the temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular, and cervical branches?
The name of the sign caused by inflating the BP cuff to a pressure higher than a patient's systolic BP for 3 minutes, what you see when this is a positive finding, and what pathology does this sign indicate.
Trousseau sign. Carpal spasms. Hypopathathyroidism/Hypocalcemia.


Draw the brachial plexus on the whiteboard.

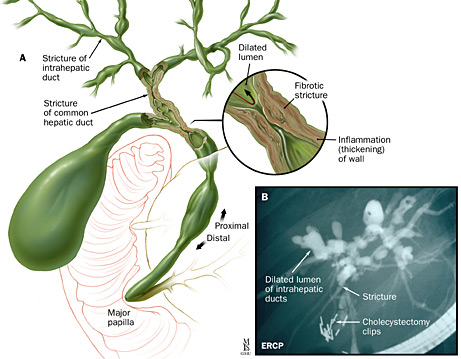
Name the diagnosis:
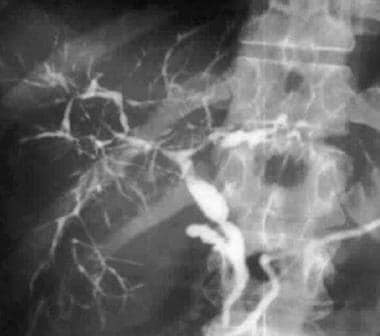
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis.

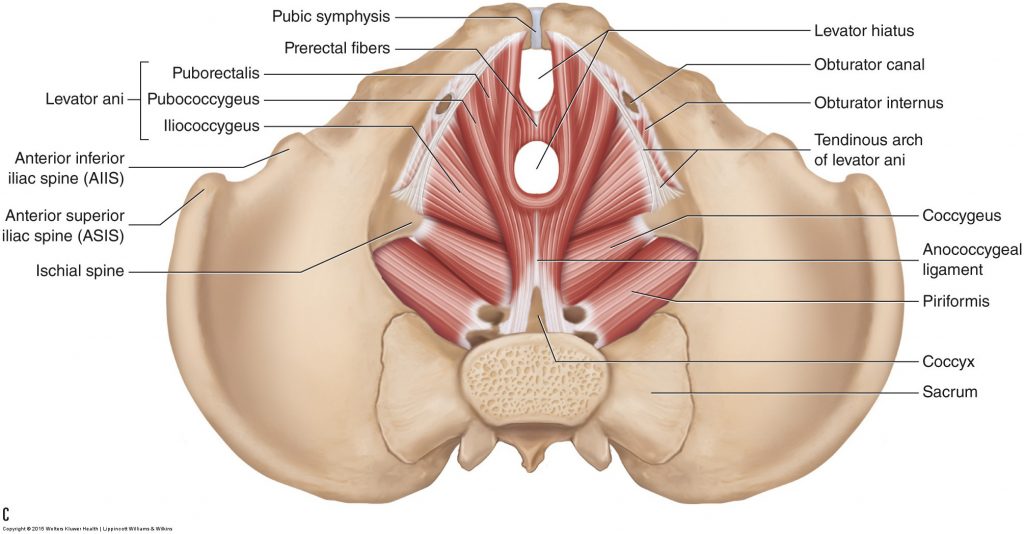
The 4 muscles that make up the pelvic floor.
What are levator ani (pubococcygeus, ileococcygeuys, puborectalis) and coccygeus?
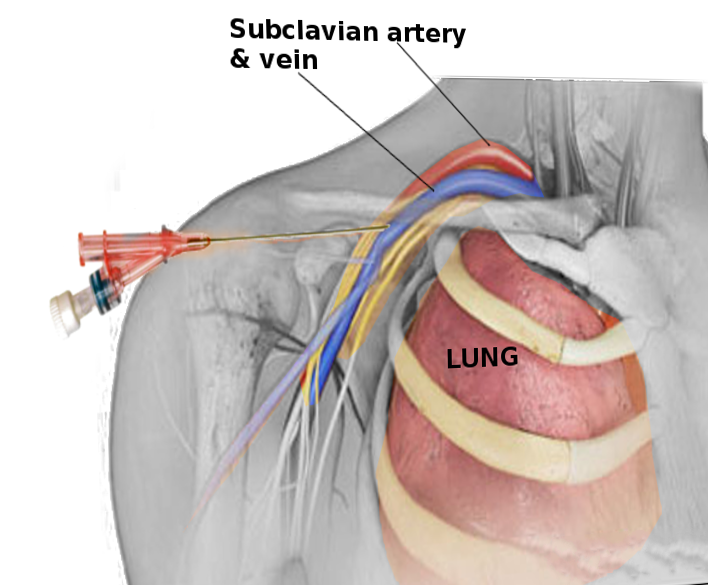
Central venous access used to be obtained by blindly puncturing the central veins. One of these veins is no longer typically used due to a certain complication.
What is the vein that is no longer typically used and what was the complication?
Subclavian vein. The complication is puncturing of the apical pleura producing a pneumothorax.

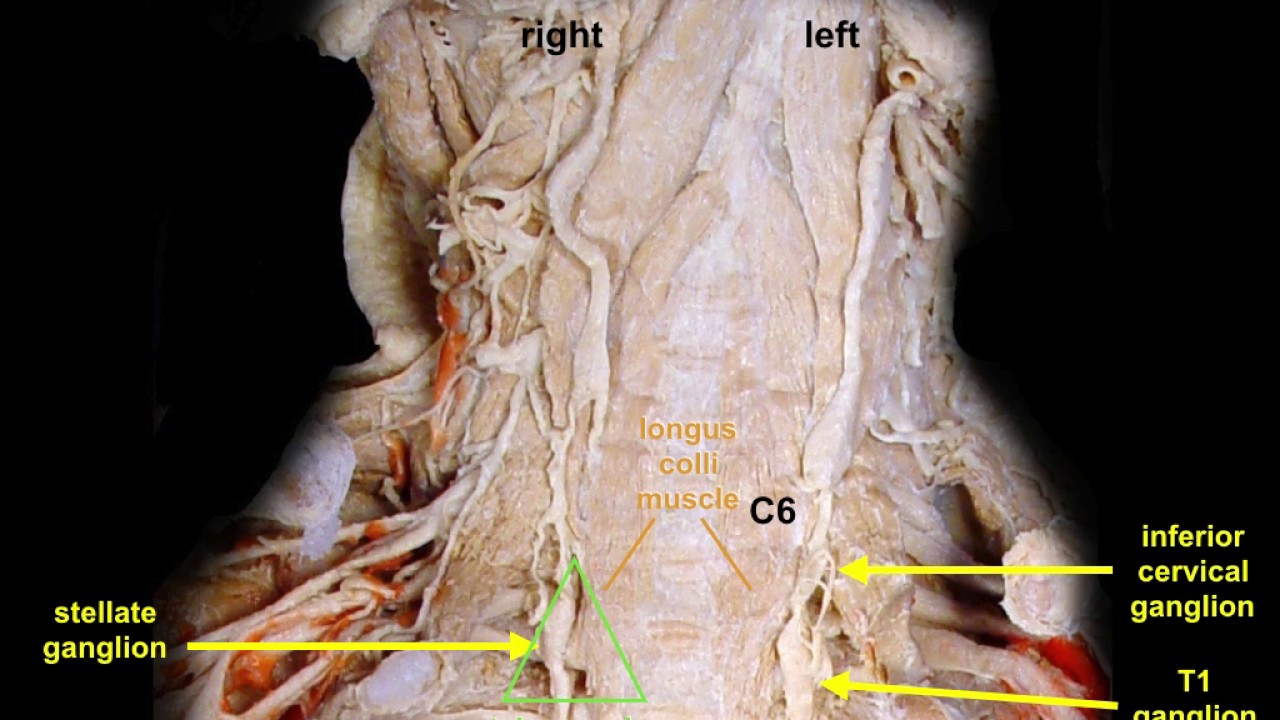
What is this?

Stellate ganglion.