What are the three states of matter?
Solid, liquid, gas.
What are the three subatomic particles in an atom?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons.
How do you interpret a mass spectrum to find the relative abundance of isotopes?
The height of the peaks in a mass spectrum corresponds to the relative abundance of each isotope.
What is the maximum number of electrons in the first energy level (n = 1)?
2
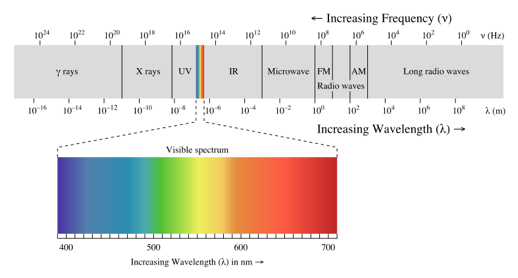
What are the two variables that change across the electromagnetic spectrum?
Wavelength and frequency.
What is the difference between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous mixture?
A homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition, while a heterogeneous mixture has visibly different components.
What does the number of protons in an atom represent?
The atomic number (Z), which determines the element.
Why do isotopes of the same element have similar chemical properties?
Because they have the same number of electrons and protons, which determine chemical behavior.
Which atomic orbitals are present in the second energy level?
The 2s and 2p orbitals.

Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum has the highest energy?
Gamma rays.
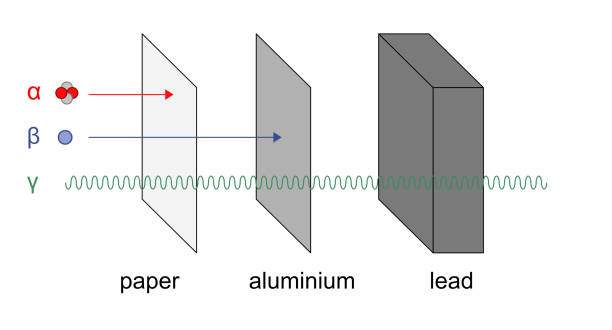
How do changes in temperature affect the state of matter?
Adding or removing heat changes the kinetic energy of particles, causing changes in state (solid to liquid to gas)
How can you calculate the number of neutrons in an atom?
By subtracting the atomic number (Z) from the mass number (A)
How is the relative atomic mass of an element calculated?
By taking the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes, based on their natural abundance.
What is the electron configuration of carbon (Z = 6)?
1s² 2s² 2p²
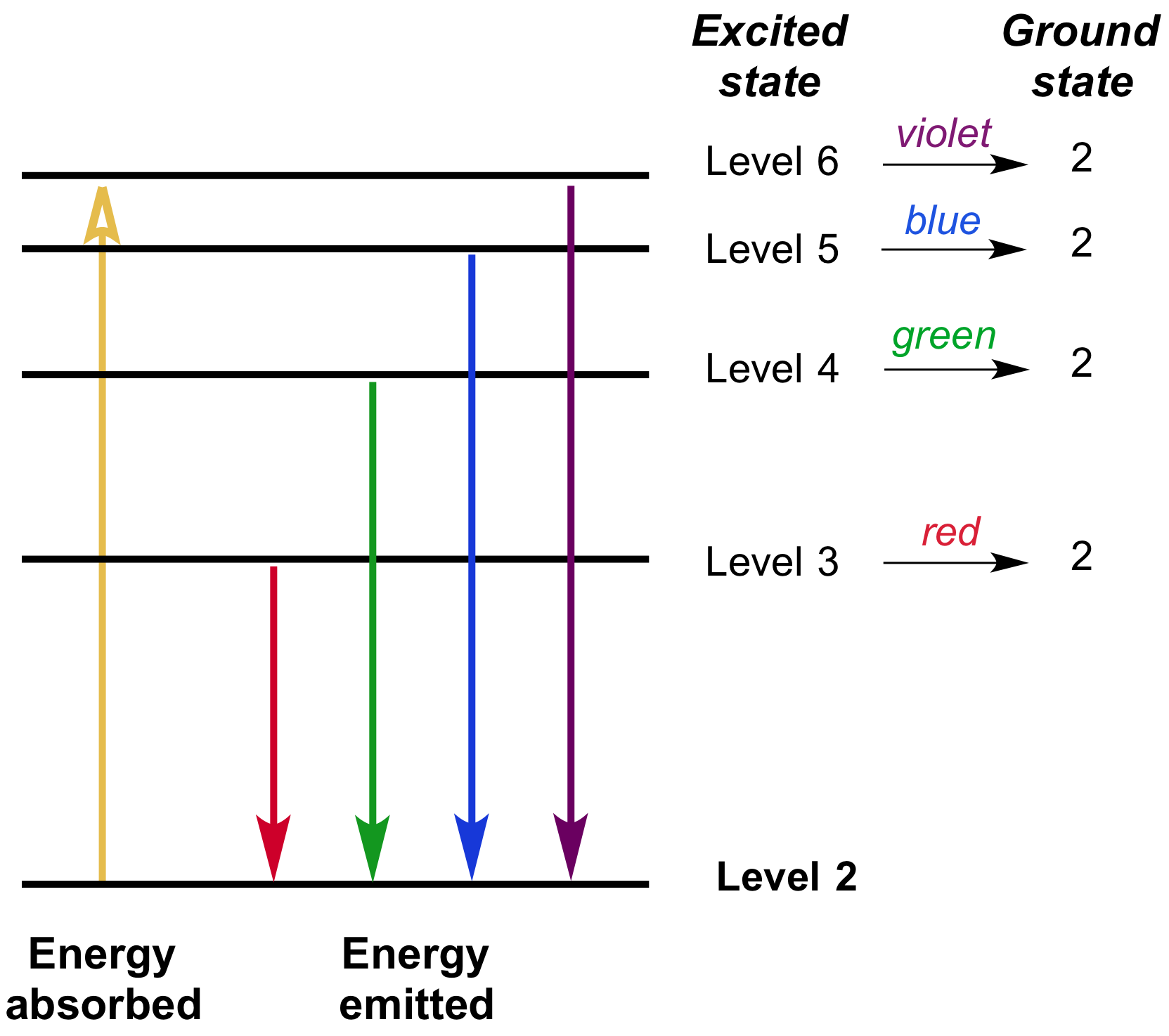
What happens to an electron when it falls from a higher to a lower energy level in an atom?
It releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
Convert 25°C to Kelvin.
298 K
Define an isotope.
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
Explain why the relative atomic mass of chlorine is not a whole number.
Chlorine exists as two main isotopes, and the atomic mass is a weighted average of these isotopes.
Sketch the orbital diagram for oxygen (Z = 8).

What is the difference between a continuous spectrum and an emission line spectrum?
A continuous spectrum shows all wavelengths, while an emission line spectrum only shows specific wavelengths emitted by electrons transitioning between energy levels.

What separation technique would you use to separate a saltwater solution, and why?
Distillation, because it separates based on different boiling points.
How would you deduce the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons for an ion of oxygen, O²⁻, with mass number 16?
Protons = 8 (Z = 8), Neutrons = 8 (16 - 8), Electrons = 10 (8 + 2)
How does the concept of isotopes play a role in the development of the hydrogen bomb?

The hydrogen bomb uses isotopes of hydrogen, like deuterium (²H) and tritium (³H). When these isotopes fuse together, they release a huge amount of energy, which causes the explosion.

Explain (shortly) how the trends in electron configuration across Period 3 influence the ionisation energy of these elements.
1. As you move across Period 3, the number of protons increases.
2. Electrons stay in the same energy level (n=3), but the nuclear charge increases.
3. This makes the electrons harder to remove, so ionisation energy increases across the period.
Which element spectrum you observe?

Sodium (Na - natrium)
