Name this compound

2-methyl pentane
What is the general formula of the alkanes?
CnH2n+2
Name three types of addition reaction that alkenes can do (eg. hydrogenation)
halogenation
hydrohalogenation
hydration
polymerization
What is the name of the functional group that all alcohols contain?
hydroxyl group
Name this molecule
Propanone
Balance the combustion reaction for butane
Name the test for unsaturation
The bromine test
What does the term "tertiary alcohol" mean?
An alcohol where the -OH group is attached to a carbon with 3 hydrocarbon constituants.
Name this compound

1-Chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane
What is the name of the type of fission involved in the initiation step of free radical substitution?
homolytic fission
Which part of an alkene is the most electron rich area and why?
The C=C double bond, because of the pi bond (sideways overlap of p orbitals)
Balance the combustion reaction for ethanol
C2H5OH + 3 O2 → 2 CO2 + 3 H2O
Draw 5-bromo-2,4-dimethylhex-1-ene
What is a free radical?
An atom (or molecule) with an unpaired valence electron
Name the conditions needed for hydrogenation
Nickle catalyst and 150 degrees celcius
What is the major product of the reaction of propanoic acid and methanol?
methyl propanoate
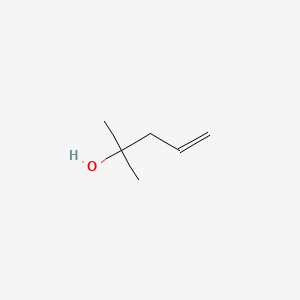
Draw 2-Methyl-4-penten-2-ol
Why does the boiling/melting point of the alkanes increase as the number of carbons increase?
Longer molecules have increased intermolecular (london dispersion) forces between them. This means there are more forces of attraction to break- requiring more energy, and therefore more heat
Describe markovnikovs rule
when an asymmetrical reagent is added to an asymmetrical alkene, then the negative half of the reagent will attach to the carbon atom containing fewer hydrogen atoms (allow equivalent description)
Name the products of the oxidation of each class of alcohol and suggest how to obtain them (including a names oxidizing agent).
Oxidize the alcohol with potassium dichromate/ potassium manganate
Primary- aldehyde (distillation) then carboxylic acid (reflux)
Secondary- ketone
Tertiary- no reaction