What does viscus mean
How thick something is.
What is a volcano
A mountain with molten rock below the surface that can open.
Define what an earthquake is
What is a Tectonic Earthquake
When tectonic plates move around and cause the earth to shake.
What was Pangea
A supercontinent that held all the continents together like a puzzle.
What are tectonic plates
Tectonic plates are large slabs of Earth's lithosphere that move and interact on the semi-molten asthenosphere beneath them.
What type of volcano is this? Describe it.

Cinder cone volcano- cone-shaped and magma comes out slowly
What is the Ring of Fire
The boundary of the Pacific plate there are a lot of earthquakes and volcanoes that occur.
A Volcanic Earthquake
What other natural disaster can an earthquake cause. Define it.
A Tsunami. Title wave.
What is the name of the famous Volcano located in Washington State
Mt. St. Helens Volcano
Name three places in the US where active volcanoes can be found
Hawaii, Alaska, Washington, Oregon, and California
What are fault lines?
fracture lines that occur between areas of the rocks in the crust due to plate movement.
When an underground mine or cavern falls in due to pressure, what kind of earthquake is produced?
A Collapse Earthquake
Give three out of the five "W's" about Haiti's Earthquake.
Who:
The people of Haiti, especially those living in and around Port-au-Prince. Over 3 million people were affected.
What:
A powerful earthquake measuring 7.0 magnitude that caused massive destruction of homes, schools, hospitals, and government buildings.
When:
January 12, 2010, at 4:53 p.m. local time.
Where:
Near Port-au-Prince, Haiti’s capital city, with the epicenter about 15 miles southwest of the city.
Why:
The earthquake happened because of movement along the Enriquillo–Plantain Garden fault, where two tectonic plates (the Caribbean Plate and North American Plate) slide past each other.
Where are volcanoes located on Earth
It's crust
What is the difference between magma and lava
Lava is molten rock ON the earth's surfact. (Magma turns into lava)
What is an earthquakes epicenter?
The location on the surface of the crust that is directly above where the earthquake has taken place.
The type of earthquake caused by a nuclear blast or chemical explosion
Explosion earthquake
Label the parts of an earthquake-
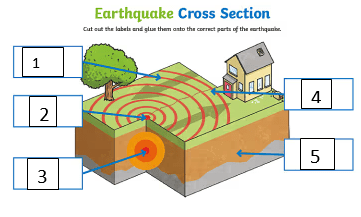
1. Tatonic Plate
2. Epicenter
3. Hypocenter
4. Seismic Waves
5. The Earth's Crust
Extinct - a volcano that erupted a long time ago and will not erupt again.
Dormant- a volcano that has not erupted in a long time, and there is a chance it will.
Active- a volcano that is erupting, or has recently erupted and will erupt again.
Give 3 out of the 5 "W's" on Mt. St. Helen
Who:
People living in and around Washington State,What:
A major volcanic eruption occurred, causing an explosion, landslides, ash fall, and destruction of forests and buildings.When:
May 18, 1980 (the most famous eruption).Where:
Mount St. Helens, in Washington State, USA, part of the Cascade Range.Why:
Pressure built up when magma rose beneath the volcano, causing the mountain to become unstable and erupt after an earthquake triggered a landslide.
What device is used to measure earthquakes? What is the name of the strength of the earthquake measured with , and how high does it go?
How should you prepare for an earthquake? Name 1 thing you should do before, during, and after the shaking.
Before - have an emergency kit, have a family meeting place, and conduct a practice drill.
During - stay calm, move away from windows, drop/cover/hold
After- be alert and cautious, expect aftershocks, check yourself for injuries, and check for information.
Name the parts of the volcano
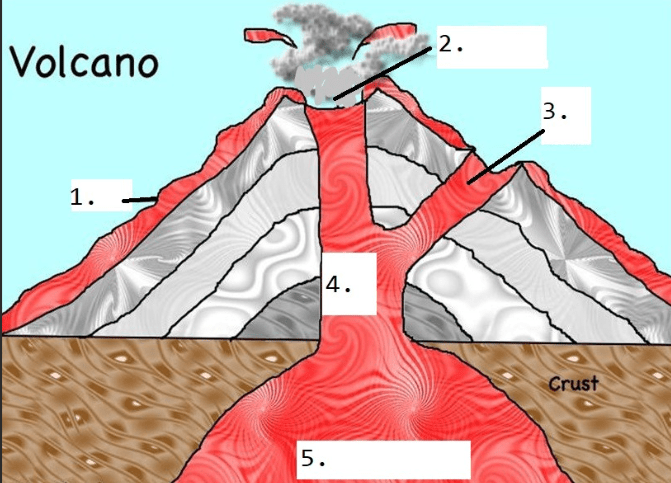
1. Lava flow
2. creator
3. Side vent
4. Main vent
5. Magma Chamber (reserve)