This is known as the pacemaker of the heart.
What is SA node?
PVCs that look alike are called.
What is unifocal PVCs?
The type of heart block in which the PR interval is longer thatn 0.20 seconds, but it remains consistent.
What is 1st degree heart block?
Treatment of symptomatic bradycardia.
What is atropine?
The EKG pattern/complex we see during ventricular depolarization.
What is the QRS complex?
What is 60 to 100?
Rhythm that occurs from a single ectopic foci in the atria, a classical "sawtooth" pattern is seen.
What is Atrial Flutter?
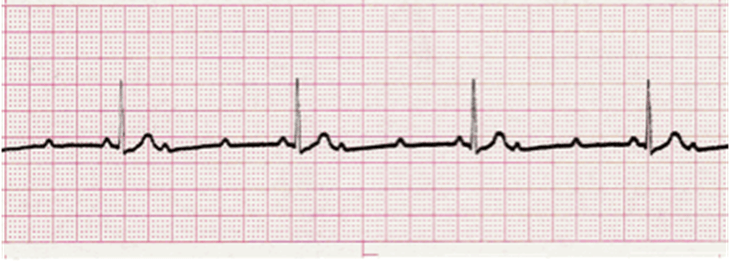
What is 2nd Degree Type II?
The 2 rhythms that require immediate defibrillation.
What is V-fib or V-Tach?
A complete heartbeat from its generation to the beginning of the next beat.
What is a cardiac cycle?
The intrinsic rate of AV node and junctional tissues.
What is 40 to 60 beats per minute?
Sinus rhythm caused by failure of the SA node to create an impulse and complete failure of all impulses.
What is asystole?
The type of heart block that is represented on EKG as a progressive lengthening of the PR interval until there is a P wave without a QRS complex.
What is Second Degree Type 1 heart block, also called Mobitz 1 or Wenckeback?
First line treatment for asymptomatic SVT.
What is Vagal Maneuvers?
Represents repolarization of the ventircles.
What is the T wave?
The structures of the electrical conduction system that only beats at 20 to 40 beats per minute.
What is Purkinje Fibers?
A type of v-tach that is caused by prolonged QT intervals and/or a severe magnesium deficiency.
What is torsades de pointes?
The type of heart block in which the atria and ventricles beat independently of each other.
What is 3rd degree or complete heart block?
The first line treatment for symptomatic PSVT.
What is adenosine or Synchronized Cardioversion?
This is the normal duration of the QRS complex.
What is less than 0.12 seconds?
Same characteristics as a Junctional rhythm with a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute
What is Accelerated Junctional?
An arrhythmia in which there are multiple erratic impulses i the atria. There is no identifiable P wave, an irregular ventricular rate, and there is loss in atrial kick.
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
It looks organized electrically but there is no mechanical output.
What is Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)?
The electrolyte abnormality associated with tall "peaked" T waves.
What is hyperkalemia?
These 2 EKG changes are seen in all junctional rhythms.
What is P wave abnormalities and PR interval changes?