The numbers on the back of football jerseys represent.
What is nominal?
A method of sampling where every individual in the population has an equal chance of being selected.
What is Simple Random Sampling?
A developmental psychologist visits a preschool and records how often children share toys without interacting with them.
What is Observational?
Consistency of participants' scores on a measurement over time.
Variance that is unaccounted for by the study variables.
Error Variance
Movie ratings (e.g., 1 star, 2 stars, 3 stars) are measured on this scale, which reflects rank order but not equal intervals between values.
What is ordinal?
The type of sampling where researchers select every nth person in a population list.
What is Systematic Sampling?
A psychologist asks participants to complete a questionnaire about their daily stress levels
What is Self-Report?
Degree to which two independent raters agree.
What is interrater reliability?
Researchers erroneously generalize results to a population that differs from the one which the sample was drawn.
What is misgeneralization?
What is interval data?
This type of sampling divides a population into subgroups before randomly selecting participants.
What is Stratified Sampling?
Researchers studying stress levels use a device to measure participants' heart rate and cortisol levels in response to a stressful task.
What is Physiological?
A test item appears to measure what it is supposed to measure.
What is Face Validity?
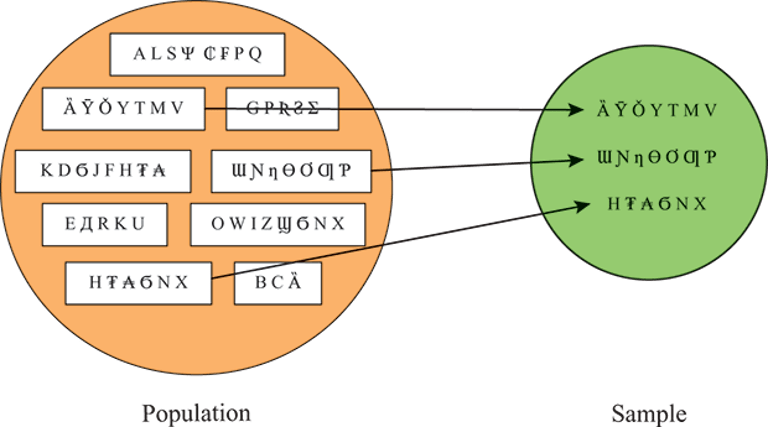
What is Cluster Sampling?
A scientist measures temperature in Kelvin
What is ratio?
This broad category of sampling does not give all individuals an equal chance of being selected.
A researcher uses fMRI scans to examine brain activity while participants watch emotional videos.
What is Physiological?
Items are not assumed to measure a single underlying construct.
What are Formative Measures?
This type of nonprobability sampling is the most commonly used in behavioral science research.
What is Convenience Sampling?
A team of scientists measures the weight of newborns in grams. Later, they divide each baby’s weight by the heaviest baby’s weight to express weight as a percentage of the maximum recorded value.
What is ratio?
This issue occurs when a sample does not accurately reflect the population from which it was drawn.
What is Sampling Error?
Using different methods to measure on variable.
What is Converging Operations?
Sample Size, Population Size, Variance - this term is a function of all three of these things.
What is Error of Estimate?