指骨英文怎么说?
Phalanges
滑膜英文怎么说?
Synovial Membrane
屈曲英文怎么说?
Flexion
大腿后肌英文怎么说?
Hamstrings
等张收缩英文怎么说和解释?
Isotonic Muscle Contraction - Where muscles change length as they contract
快缩肌纤维英文怎么说?
Fast Twitch Muscle Fibre
True or False - The centre of some large bones contains red blood marrow, which creates red blood cells.
TRUE
The pelvis and femur are both important in blood production
True or False - The cranium is a fixed or immoveable joint
TRUE
These bones cannot move or bend.
Identify the movement labeled B & C.
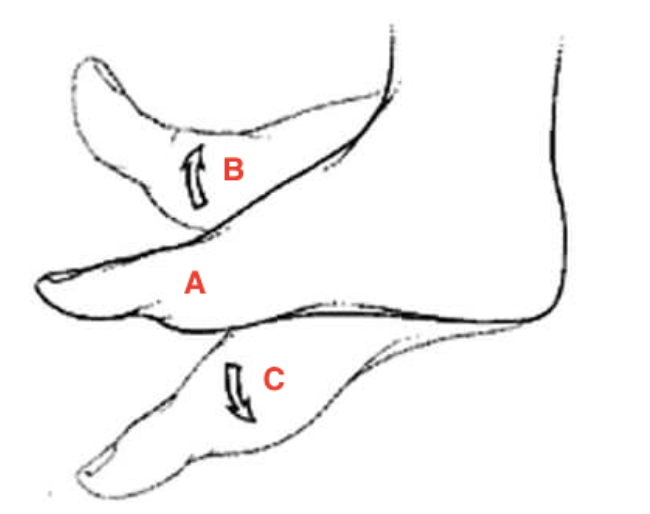
B. Dorsiflexion
C. Plantar Flexion
True or False - A tough band of fibrous tissue that anchors muscles to a bone and allows movement is known as a Ligament
FALSE
A tough band of fibrous tissue that anchors muscles to a bone and allows movement is known as a TENDON
A. The muscle that contracts to create movement is known as the...
B. The muscle that relaxes to allow movement is known as the...
A. Agonist/Prime Mover
B. Antagonist
Provide one example of an exercise/sport that uses slow twitch muscle fibres and an example of a sport/exercise that uses fast twitch muscle fibres.
Many possible answers
Which type of bones provide a large surface area for muscles to attach to? They also provide protection to organs.
Answer - Flat Bones
Examples - Pelvis, Cranium, Scapula, Ribs
State two names for each of the three joint types.
1. Fixed/ Immoveable AKA Fibrous Joints
2. Slightly Moveable AKA Cartilaginous Joints
3. Freely Moveable AKA Synovial Joints
Which movement, in the knee joint of the kicking leg, was executed from phase 1 to phase 2 in this illustration?
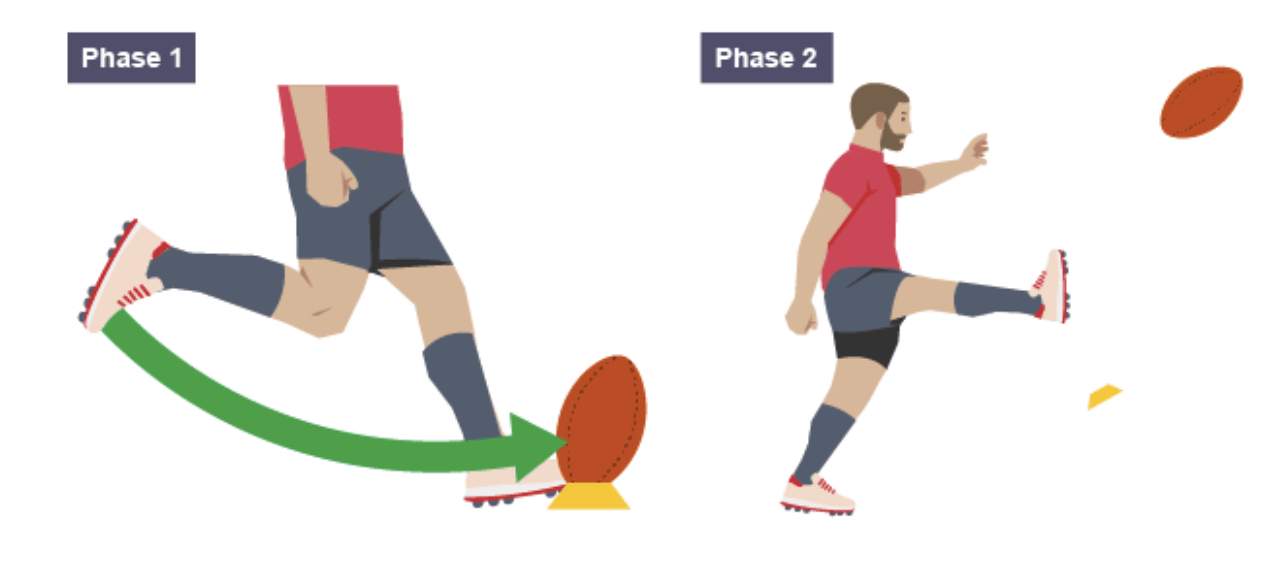
Flexion to Extension
What movement best represents the main action of the bicep muscle?
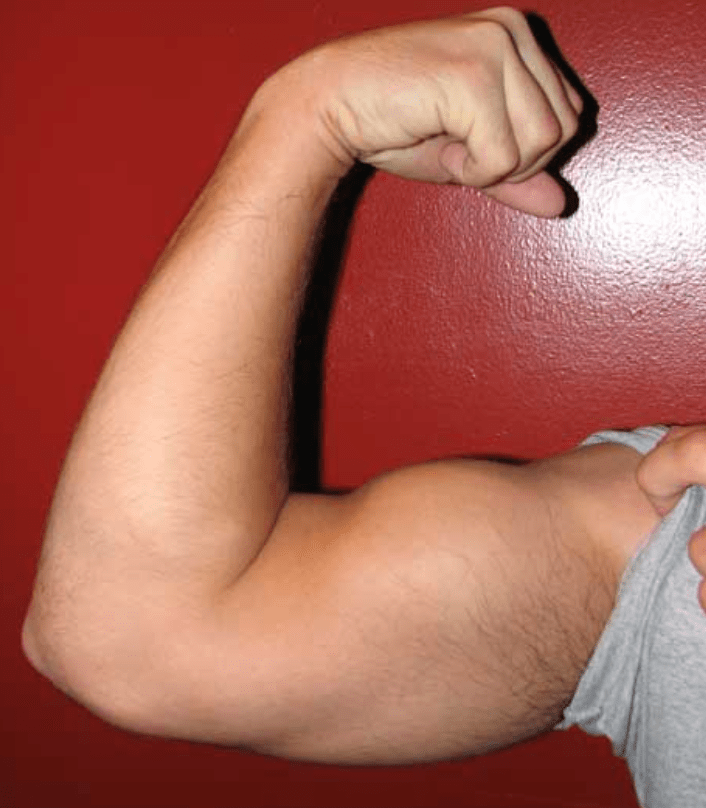

Flexion - flexes/bends your arm at the elbow
In this photo which muscle is the agonist and which is the antagonist?
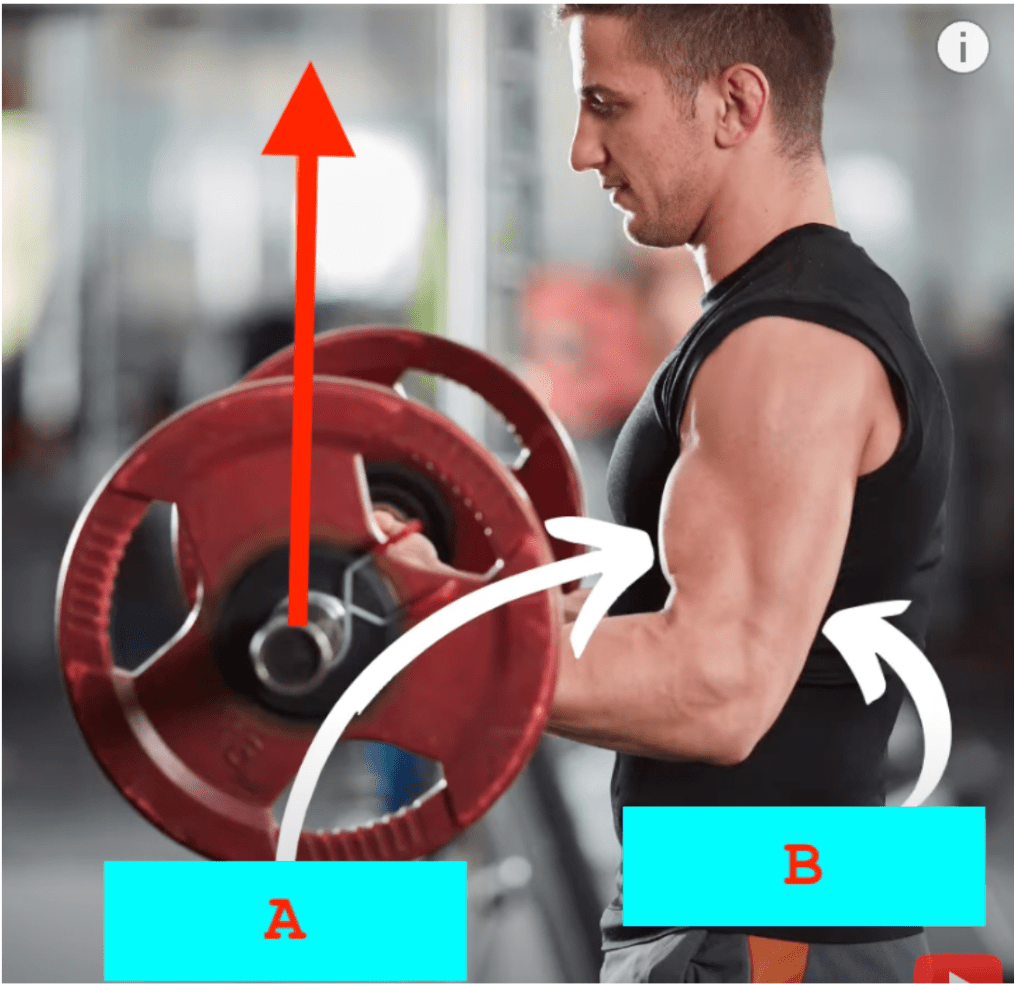
A. Bicep - Agonist
B. Tricep - Antagonist
TRUE or FALSE - Increasing muscle mass and improving strength uses slow twitch muscle fibres and is the focus point of aerobic exercise.
FALSE
Increasing muscle mass and improving strength uses FAST twitch muscle fibres and is the focus point of ANAEROBIC exercise.
5 part question
1. The skull is also known as...
2. The shoulder blade is also known as...
3. The collarbone is also known as...
4. The kneecap is also known as...
5. The ankle bone is also known as...
1. Cranium
2. Scapula
3. Clavicle
4. Patella
5. Talus
Provide one example for each of the three joint types
1. Fixed/Immoveable AKA Fibrous Joints - Found between the flat bones of the Cranium
2. Slightly Moveable AKA Cartilaginous Joints - Found between the vertebrae of the spine
3. Freely Moveable AKA Synovial Joints - Ball & Socket (Shoulders & Hips), Hinge (Elbow & Knee)
1. A sideways movement away from the centre of the body is known as...
2. Provide a sporting example of this movement
1. Abduction
2. A football goaltender moving their arm to the side to stop the ball (other answers also acceptable)
Which muscle pulls your arm down at the shoulder and draws it behind your back? (Extension)
Latissimus Dorsi
State the antagonistic muscle pair for the following muscles.
1. Triceps
2. Gastrocnemius
3. Hamstrings
1. Biceps
2. Tibialis Anterior
3. Quadriceps
Identify the which muscle fibre is described in #1 & #2.
1. uses oxygen to fire; they take longer to get going, but they can go for longer without getting tired
2. thicker and quicker to contract, but they wear out quickly. They are more powerful but lower in endurance.
1. Slow Twitch Muscle Fibre
2. Fast Twitch Muscle Fibre
Identify the four main functions of the skeleton.
1. Shape & Support
2. Muscle Attachment for Movement
3. Protection of Vital Organs
4. Blood Production
Identify the parts (A-G) of the synovial joint below.
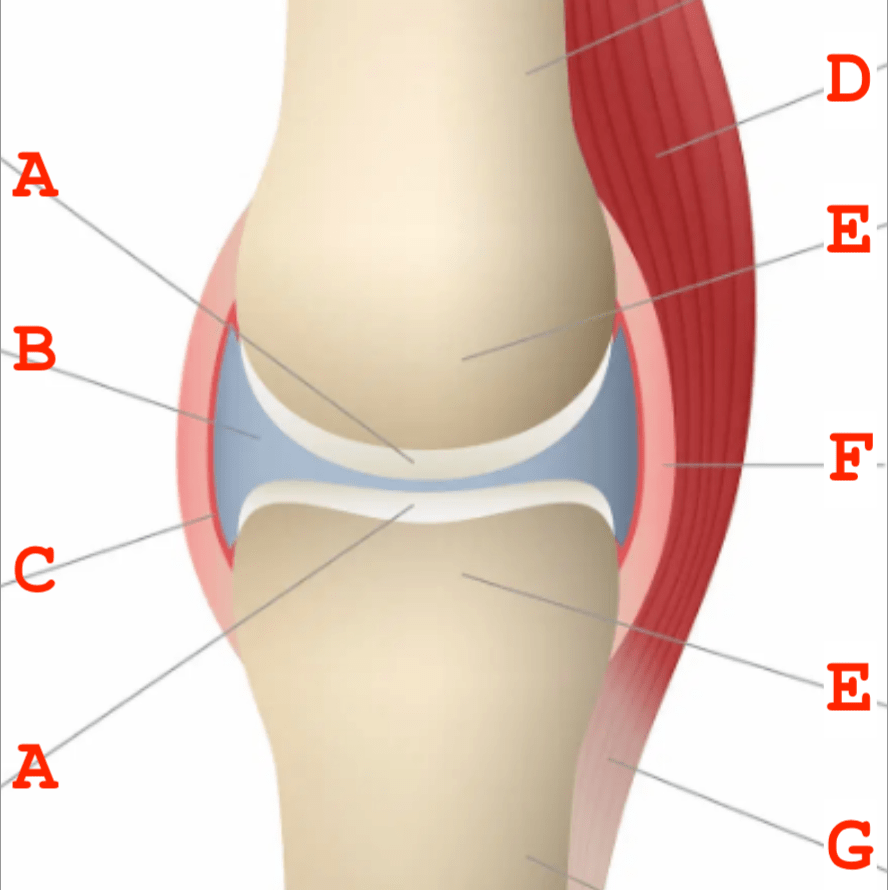
A - Cartilage
B - Synovial Fluid
C - Synovial Membrane
D - Muscle
E - Bone
F - Joint Capsule
G - Tendon
Identify the movements at 1, 2, & 3.
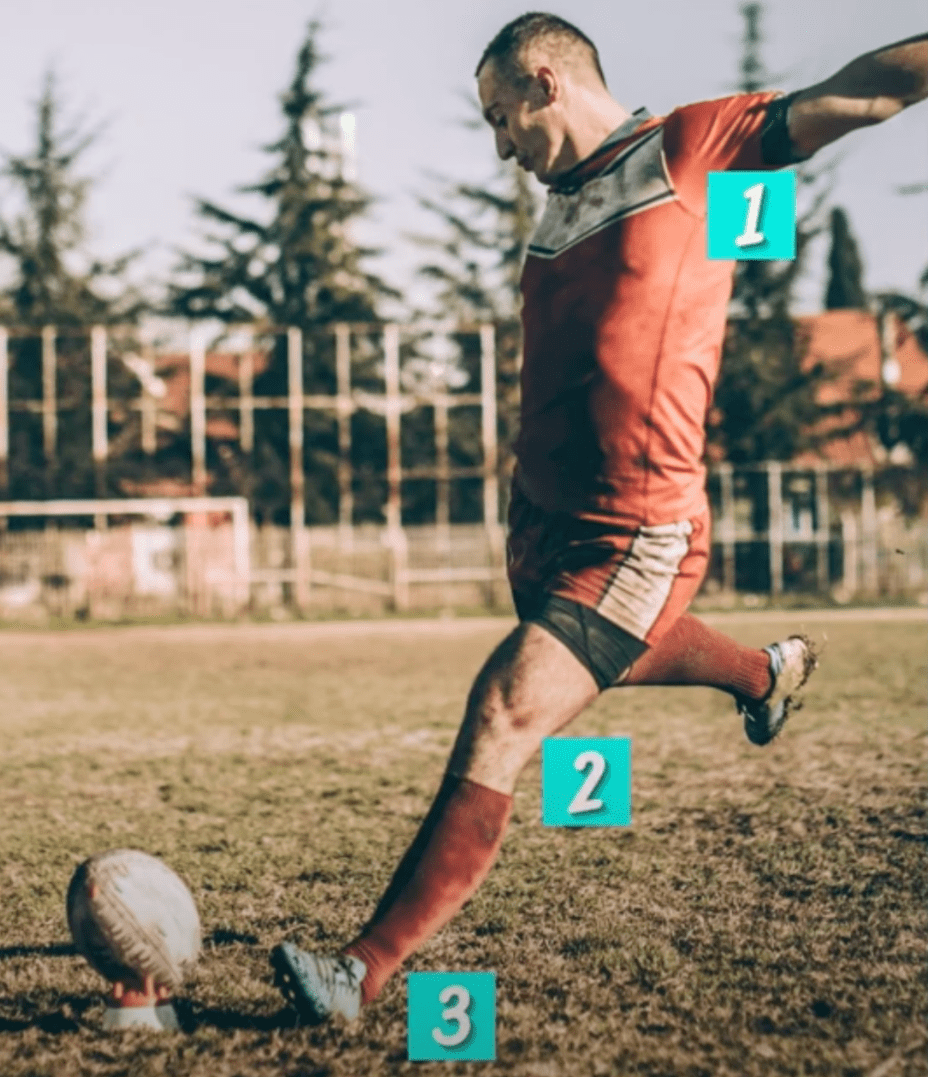

1. Abduction
2. Extension
3. Dorsiflexion
Which muscle holds & rotates your shoulders, and moves your head back and sideways (Rotation). For example, a swimmer turning their head to breathe.
Trapezius
State two isotonic muscle contractions and explain what happens when they contract.
1. Concentric Contraction - Muscle contraction where the muscle shortens
2. Eccentric Contraction - Muscle Contraction where the muscle lengthens
Identify a sport/activity that uses both Fast & Slow Twitch Muscle Fibres and explain when each are used.
Example - Basketball
Slow Twitch Muscle Fibre - Jogging back on defense after a made basket
Fast Twitch Muscle Fibre - Jumping to slam dunk the ball
List one example of each of the four main bones types.
Possible Answers
Long Bones - Femur, Tibia, Fibula, Humerus, Ulna, Radius, Phalanges, Clavicle, Metatarsals, & Metacarpals
Short Bones - Carpals, Tarsals, Talus
Flat Bones - Pelvis, Cranium, Scapula, & Ribs
Irregular Bones - Vertebrae
Identify 5 parts of a synovial joint and describe their role.
1. Synovial Membrane - lines the inside of joint capsule, secretes synovial fluid
2. Synovial Fluid - lubricates and reduces friction in the joint, allows for smooth movement
3. Joint Capsule - the structure that protects the joint, holds bones together
5. Cartilage - found at the end of bones and acts as a cushion to prevent bones from knocking together
5. Tendon - connects muscle to bone
State the four main pairs of movements and demonstrate each one
1. Flexion & Extension
2. Abduction & Adduction
3. Plantar Flexion & Dorsiflexion
4. Rotation & Circumduction
Must correctly demonstrate each movement
Name and point to the location on the body of 10 different muscles.
When squatting down, which muscle contractions happen in the:
A: Hamstrings
B: Quadriceps
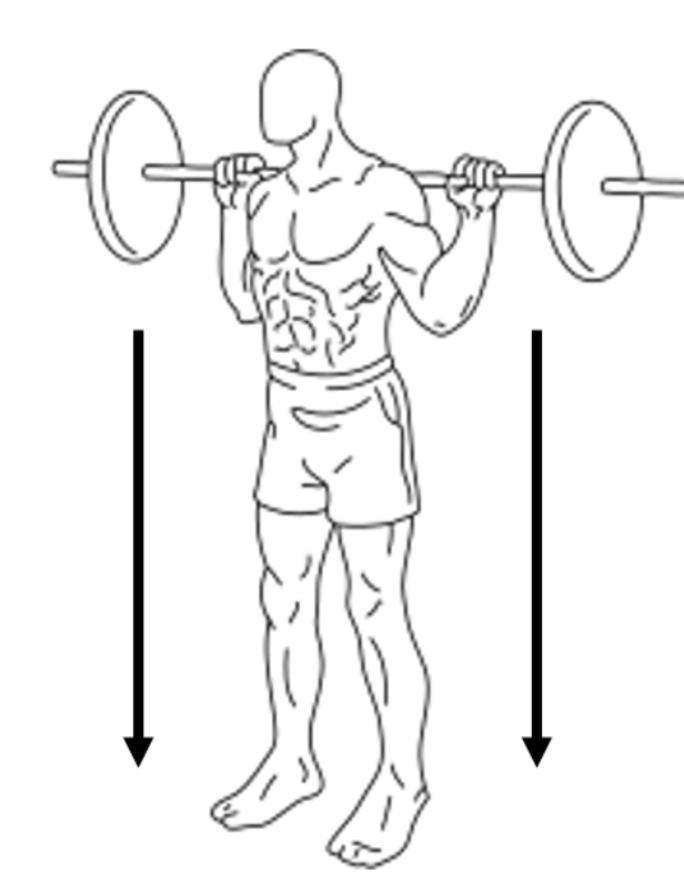
A: Concentric (Shortening)
B: Eccentric (Lengthening)
Describe 4 characteristics on Slow Twitch & Fast Twitch Muscle Fibres.
Slow Twitch Muscle Fibres
1. Contracts Slowly
2. Produces a little force
3. Do not tire easily/Tires slowly
4. Good for endurance activities
5. Small fibre size
Fast Twitch Muscle Fibres
1. Contract Quickly
2. Produce a lot of force
3 Good for strength & power activities
4. Tires Quickly
5. Large fibre size