What is the function of the Circulatory System?
Transporting blood around the body (to the working tissues)/transporting oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products
What does the word Pulmonary relate to?
The Lungs
What is the Maximum Heart Rate of a 20 year old person?
220 - 20 = 200 bpm (beats per Minute)
Which vocabulary term is described below?
人體的運輸系統,由肺、心臟、血管和血液組成
Circulatory System
TRUE or FALSE - Metacarpals are bones found in the foot.
FALSE - Metatarsals are bones found in the foot. Metacarpals are bones found in the hand.
What are the 3 different types of blood vessels?
Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries
a. State the 4 chambers of the heart
b. identify which side transports oxygenated blood and which side transports deoxygenated blood?
a. Right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
b. LORD
LEFT Side transports OXYGENATED Blood
RIGHT Side transports DEOXYGENATED Blood
a. What is Heart Rate?
b. How is it measured?
a. How many times the heart beats per minute
b. Measured in Beats Per Minute (BPM)
Which vocabulary term is described below?
測量心室收縮時的心臟每分鐘跳動次數(bpm)
Heart Rate
Describe the pathway of air.
1. Nasal Passage (nose)/ Mouth
2. Trachea
3. Bronchus
4. Bronchioles
5. Alveoli
a. Which blood vessels contain valves?
b. What is the function of a valve?
a. Veins
b. Prevent the backflow of blood; ensures blood flows in one direction
a. The vena cava is which type of blood vessel?
b. Which type of blood does the vena cava transport?
c. The aorta is which type of blood vessel?
d. Which type of blood does the aorta transport?
a. Vein
b. Deoxygenated Blood
c. Artery
d. Oxygenated Blood
a. What is stroke volume?
b. How is it measured?
a. The amount of blood ejected from the heart per beat.
b. Measured in milliliters (mL)
What vocabulary term is being described below?
每分鐘從心臟排出的血量;通常以每分鐘升數表示
Cardiac Output
Identify the muscles labeled A-G.
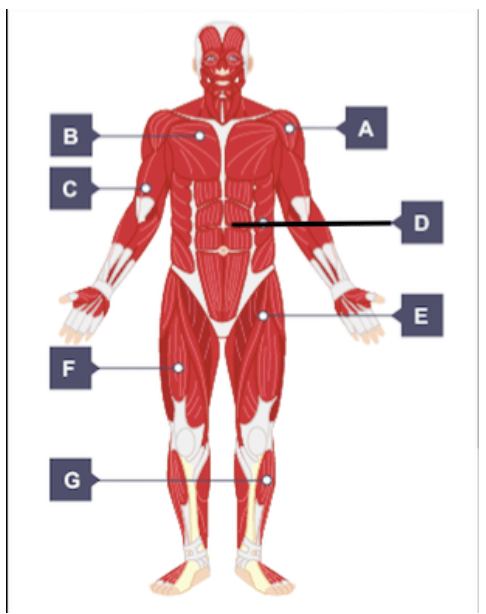
a. deltoid
b. pectorals
c. biceps
d. abdominals
e. hip flexors
f. quadriceps
g. tibialis anterior
State the 4 Components of Blood and their Functions
Plasma - the liquid component of the blood, helps transport nutrients and oxygen/carbon dioxide
Red Blood Cells - contain haemoglobin for transporting oxygen
White Blood Cells - part of the immune system/defends the body against pathogens
Platelets - Helps blood to clot when blood vessels become damaged
What is described below?
Receive blood from the atria. When they contract, blood is forced to the body and lungs. They have thick muscular walls to force blood away from the heart at high pressure
Ventricles
a. What is cardiac output?
b. How is it measured?
c. What is the equation used to find it?
a. The amount of blood expelled from the heart each minute.
b. It is usually expressed in litres per minute (l/min)
c. Cardiac Output = Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
Which vocabulary term is described below?
一種深紅色的化學物質,負責在血液中運輸氧氣
Haemoglobin
a. During diffusion/gaseous exchange, which parts of the respiratory system and circulatory system work together?
b. Explain what happens during gaseous exchange/diffusion?
a. The capillaries of the circulatory system and the alveoli of the respiratory system.
b. the process in the lungs by which oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is removed from it
Describe three differences between arteries and veins.
Arteries - Transports blood under high pressure, Thick Muscular Walls, Narrow Lumen, Pumps Blood Away from the Heart (usually oxygenated), do not contain valves
Veins - Transports blood under low pressure, Thin Walls, Large Lumen, Carries blood to the heart (usually deoxygenated), contain valves to prevent backflow
Describe the pathway of blood through the heart.
Vena cava › right atrium › right ventricle › pulmonary artery › lungs › pulmonary vein > left atrium > left ventricle > pumped back to the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients.
a. What happens to cardiac output during exercise?
b. What causes this to occur?
a. Increases
b. Increase in Heart Rate and Stroke Volume
What vocabulary term is described below?
血管内的通道
Lumen
Identify each part of the synovial joint below

a. Cartilage
b. Bone
c. Synovial Membrane
d. Joint Capsule
e. Synovial Fluid