___________ can bind all biomolecules, _____________ can only bind protein peptides
BCRs, TCRs
autoimmune hemolytic anemia is an example of a _____________ HS reaction
What is type II?
absent B cells in peripheral blood, low/absent Ig of all classes leads to recurent bacterial infections and enteroviral infections after 6 mons
What is X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA)?
these are the cells from the myeloid progenitor line
What are
1. RBCs
2. granulocytes
3. phagocytes
4. megakaryocytes?
What is hereditary sideroblastic anemia?
porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common porphyria that is caused by a defective ______________________ enzyme
What is uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase?
NK cells = CD___
CD16
What is CD28?
BONUS: How does CD80/86 interact with CD28?
heterogenous immune disorer characterized by recurrent sinopulmonary infections that occurs due to defective B cell differentiation into plasma cells
What is CVID?
hematopoiesis is highest in the ________ & ________ in the prenatal period
What are yolk sac and liver?
lead poisoning interferes with _________ and ____________ (enzymes)
What are ALA-dehydratase and ferrochelatase?
these are the two most common symptoms seen in porphyria cutanea tarda
What are cutaneous blistering and photosensitivity?
CD4+ cells are induced by __________ to become Th1 cells which secrete ___________
IL-12, IFN-y
IL-4
IL-4, 5, 13
What is AIRE?
_________ is responsible for the production and differentiation of megakaryocyte precursors and regulation of platelet production
What is TPO?
_______ activates CD8+ cells, induces Ig secretion, and stimulaties eosinophils
What is IL-5?
acute intermittent porphyria is due to a defective ________________ enzyme
What is porphobilogen deaminase?
CD4+ T cells are induced by ____________ to become Th17 cells which secrete ______________
TGF-B, IL-6, IL-23
IL-17, 21, 22
________ present endogenous antigens from inside the cell whereas ________present exogenous antigens
MHCI, MCHII
low levels of low-affinity Ig due to presence of some abnormal B cells that survive development; no other Ab classes present and antigen specific antibodies cannot be made
What is SCID?
____________ facilitates B-cell differentiation, promotes Ig secretion, acts as growth factor for malignancy plasma cells, works with other ILs
What is IL-6?
difference in shape of erythrocytes
What is poililocytosis?
these are the treatments for PCT
What is phlebotomy and low dose hydroxychloroquine?
special type of rejection where donor T cells damage host tissues
What is GvHD?
BONUS: What type of HS is this?
activates MACs and CD8+ T cells to kill phagocytosed intracellular microbes
What are Th1 cells?
defect in PIGA gene preventing formation of GPi anchors for complement inhibitors?
What is PNH?
these are the 3 phases that occur in the developmental pathway of RBCs
1. ribosome synthesis
2. Hb accumulation
3. ejection of nucleus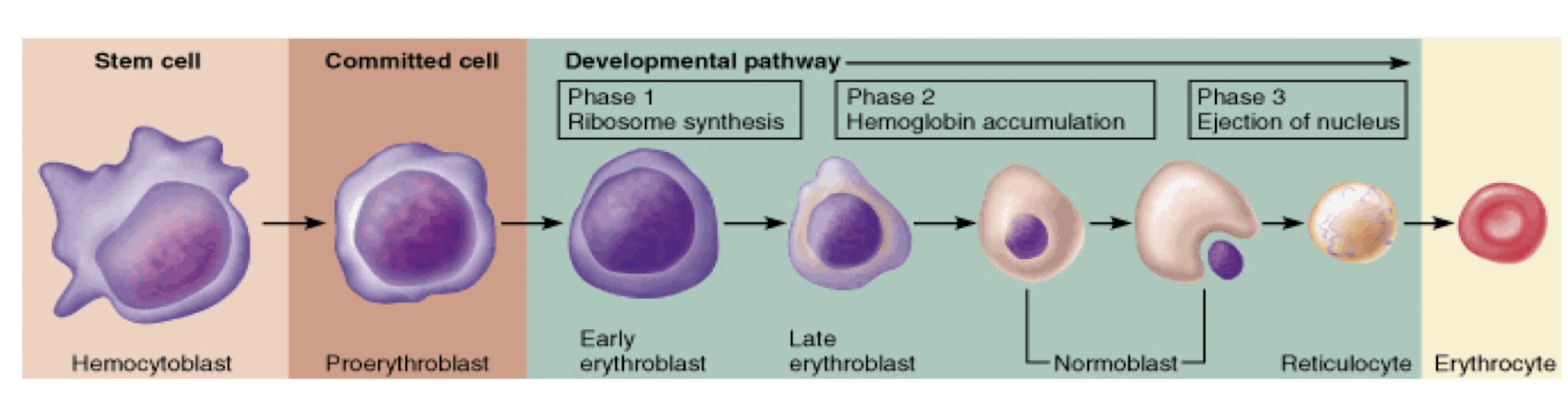
these are the 5 P's of acute intermittent porphyria
What are
1. painful abdomen
2. port wine-colored urine
3. polyneuropathy
4. psychological disturbances
5. precipitated by drugs (CYP P450 inducers, alcohol, starvation)
these are the therapies/treatments for lead poisoning
What are
1. oral succimer w/ or w/o IV EDTA
2. IM dimercaprol ?