When H_1 is the hypothesis that should cause an alarm from data Y=y, it is the common name for \mathbb{P}[D(Y)=0 \quad | \quad H_1]
What is the probability of missed detection?
It is the smallest possible mean-squared error for an estimate of X computed without any data.
What is the variance of X?
It's the name for 1-\alpha when constructing a confidence interval?
What is the confidence level?
When X_is are independent and each X_i has some mean \mu and some variance \sigma^2, it's the mean and variance of the sample mean of \{X_1,X_2,\ldots,X_{100}\}.
What are \mu and \sigma^2/100.
It is limiting probability for a transient state in a Markov chain.
What is 0?
It is the largest possible value for the error probability of the MAP decision rule in a binary hypothesis testing problem.
What is 1/2?
When the conditional distribution of X given Y=y is Uniform(0,y), it is the minimum mean-squared error estimator \hat{x}_{MMSE}(y).
What is y/2?
This number gives the probability of observing data at least as extreme as yours, assuming the null hypothesis.
What is the p value?
It is the justification for treating a sample mean as approximately Gaussian, under very weak (permissive) conditions.
What is the central limit theorem?
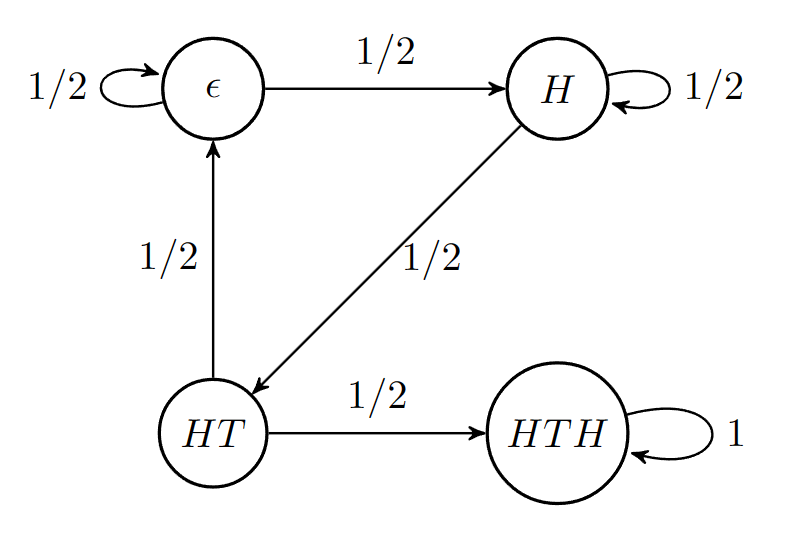
It's the number of communicating classes in the Markov chain above.
What is 2?
With first names of Jerzy and Egon, they gave us a rigorous justification to base decisions on the likelihood ratio.
Who are Neyman and Pearson?
When the conditional distribution of X given Y=y is Uniform(y, y+2), it is the MSE of the MMSE estimator \hat{x}_{MMSE}(y).
What is 1/3?
It's the distribution whose CDF is used to compute a confidence interval for the mean from 20 data samples, when the variance of the underlying distribution is unknown.
What is Student's t distribution with 19 degrees of freedom?
It's the name for getting worse test error rate after adding more parameters to the training of a binary classifier.
What is overfitting?
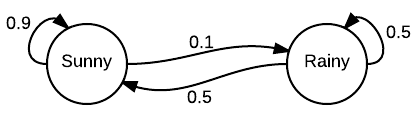 In the Markov chain above, it is the period of the Sunny state.
In the Markov chain above, it is the period of the Sunny state.
What is 1?
When Y is Uniform(0,2) under H_0 and Uniform(0,3) under H_1, it is the maximum likelihood decision from the observation Y=1/2.
What is H_0?
When X ~ Exponential(1/2) and \rho_{XY} = 1/2, it is the MSE of the LLSE estimator of X from Y.
What is 3?
It's the type of test to use when considering the hypothesis that two datasets of size 60 have equal means.
What is the two-sample Z-test?
These two types of binary classifiers have the same shape for their decision regions, though the regions may not be the same.
What are closest average and LDA?
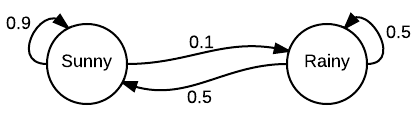 In the Markov chain above, it is the long-term average fraction of sunny days.
In the Markov chain above, it is the long-term average fraction of sunny days.
What is 5/6?
When Y is Uniform(0,2) under H_0 and Uniform(0,3) under H_1, it is smallest value for \mathbb{P}[H_1] for which the MAP decision from the observation Y=1/2 is H_1.
What is 3/5?
When X and Y are jointly Gaussian with mean zero, var[X]=3, var[Y]=2, and cov[X,Y]=2, it is the distribution of the MMSE estimate of X from Y=1.
What is Gaussian with mean 1 and variance 1?
(Mean: observation 2 is scaled by 2/2.
Variance: 3-2^2/2.)
When you have a 100 data samples, it's how much narrower a confidence interval for the mean gets when you collect 300 more data samples.
What is it is halved in length?
It is the condition under which linear discriminant analysis and quadratic discriminant analysis yield the same classifiers.
What are equal covariance matrices for the two classes?
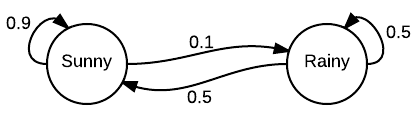 In the Markov chain above, starting with a sunny day, it is the probability that exactly one of the next two days are sunny.
In the Markov chain above, starting with a sunny day, it is the probability that exactly one of the next two days are sunny.
What is 0.14?
(SR has probability (0.9)(0.1)=0.09. RS has probability (0.1)(0.5)=0.05.)