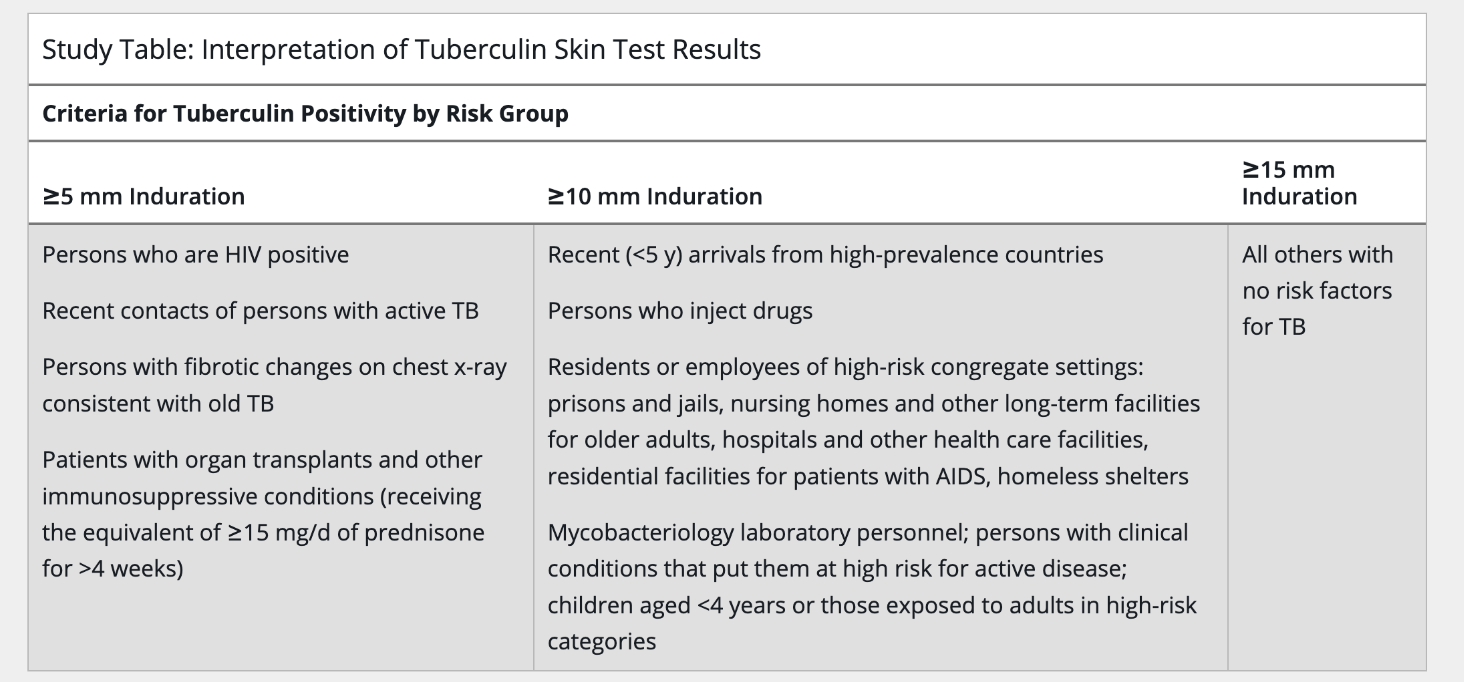
Which of the following patients would be considered to have a positive tuberculin skin test with an induration of >5 mm?
A. A 25-year-old healthcare worker
B. A recent immigrant from TB-endemic country who arrived 2 weeks ago
C. A 40-year-old man with HIV
D. A 60-year-old nursing home resident
C. A 40-year-old man with HIV
An 18-year-old college student presents with fever, sore throat, and posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. She develops a diffuse morbilliform rash after starting amoxicillin. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Ampicillin allergy
B. Infectious mononucleosis
C. CMV infection
D. Early HIV infection
B. Infectious mononucleosis

A 28-year-old woman with asthma has worsening shortness of breath, cough with brownish sputum, and recurrent pulmonary infiltrates. Labs show elevated IgE and peripheral eosinophilia. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
B. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
C. Aspergilloma
D. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA)
B. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
A 32-year-old woman presents with vaginal discharge. NAAT is positive for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Which of the following is the correct treatment if concurrent Chlamydia trachomatis infection has not been excluded?
A. Ceftriaxone alone
B. Ceftriaxone plus doxycycline
C. Ceftriaxone plus azithromycin and levofloxacin
D. Fluoroquinolone monotherapy
B. Ceftriaxone plus doxycycline

A patient presents with fever, photophobia, and nuchal rigidity. CSF analysis reveals WBC 1500 with 90% neutrophils, glucose 25, protein 300. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Viral meningitis
B. Fungal meningitis
C. Bacterial meningitis
D. Tuberculous meningitis
C. Bacterial meningitis
Which of the following statements about toxic shock syndrome is false?
A. Corticosteroids are first-line therapy to reduce inflammation
B. Clindamycin is used to inhibit toxin production
C. Staphylococcal TSS can occur without positive blood cultures
D. Streptococcal TSS often presents with soft tissue necrosis
A. Corticosteroids are first-line therapy to reduce inflammation

A 35-year-old kidney transplant recipient presents with fever, malaise, and rising creatinine. A blood PCR test detects viral DNA. Which of the following viruses is most likely responsible for this patient’s presentation?
A. Epstein-Barr virus
B. Cytomegalovirus
C. BK virus
D. JC virus
C. BK virus

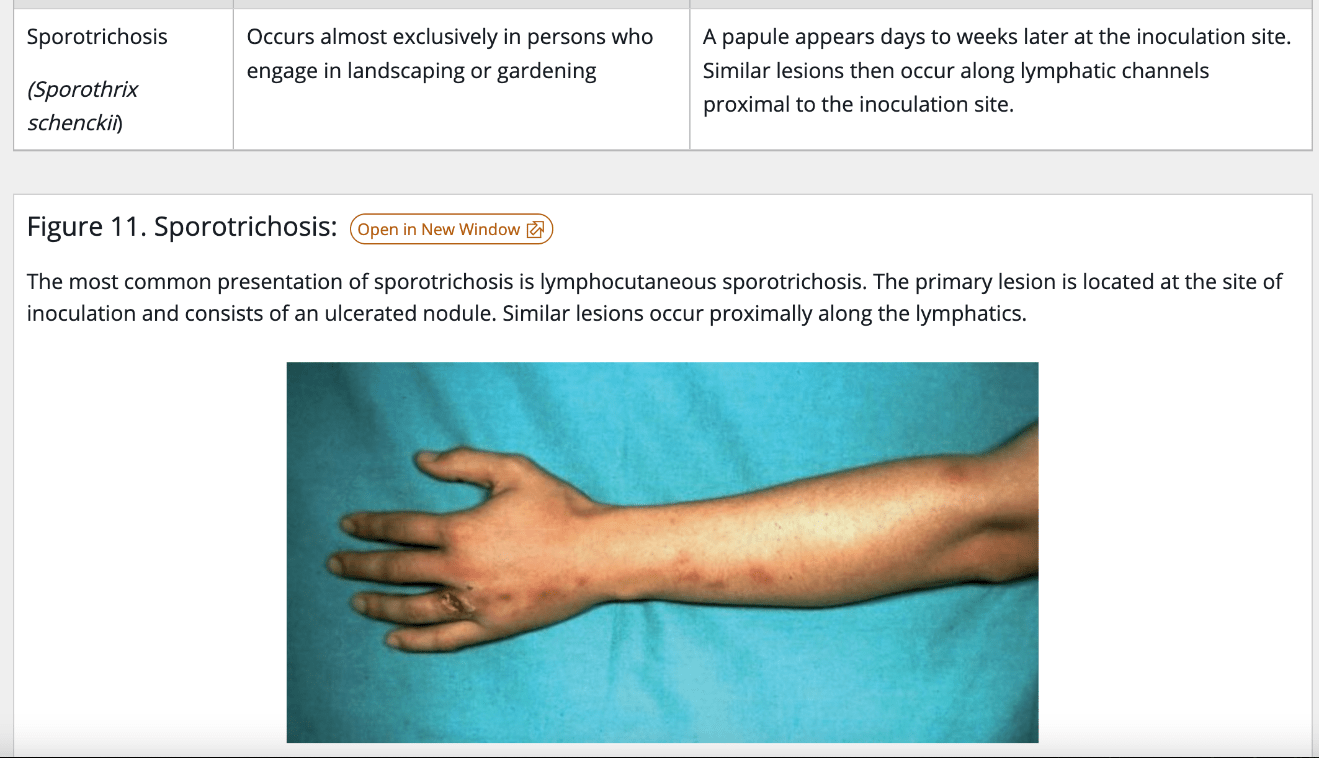
A 40-year-old landscaper, who recently trimmed a rose garden presents with an ulcerated nodule on his hand and several similar nodules along his forearm in a linear pattern shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
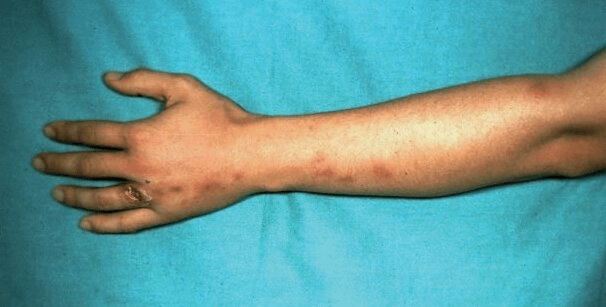
A. Nocardia asteroides
B. Mycobacterium marinum
C. Sporothrix schenckii
D. Histoplasma capsulatum
C. Sporothrix schenckii
A 25-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents to clinic requesting HIV preexposure prophylaxis. Which of the following is an appropriate option for this patient?
A. Lamivudine and efavirenz
B. Emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate
C. Zidovudine and lopinavir
D. Darunavir and ritonavir
B. Emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate

A 65-year-old hospitalized woman develops watery diarrhea after receiving ceftriaxone for pneumonia. Her stool tests are positive for GDH and negative for toxin EIA. What is the most appropriate next diagnostic step?
A. Repeat toxin EIA in 24 hours
B. Send C. difficile stool culture
C. Perform NAAT test for toxin genes
D. Treat with oral vancomycin
C. Perform NAAT test for toxin genes

A 29-year-old man with recurrent disseminated gonococcal infections is found to have tenosynovitis and pustular skin lesions. Blood cultures are negative. What additional test should be ordered to evaluate the underlying cause?
A. ANA
B. HIV viral load
C. Terminal complement pathway assay (CH50)
D. HLA-B27
C. Terminal complement pathway assay (CH50)

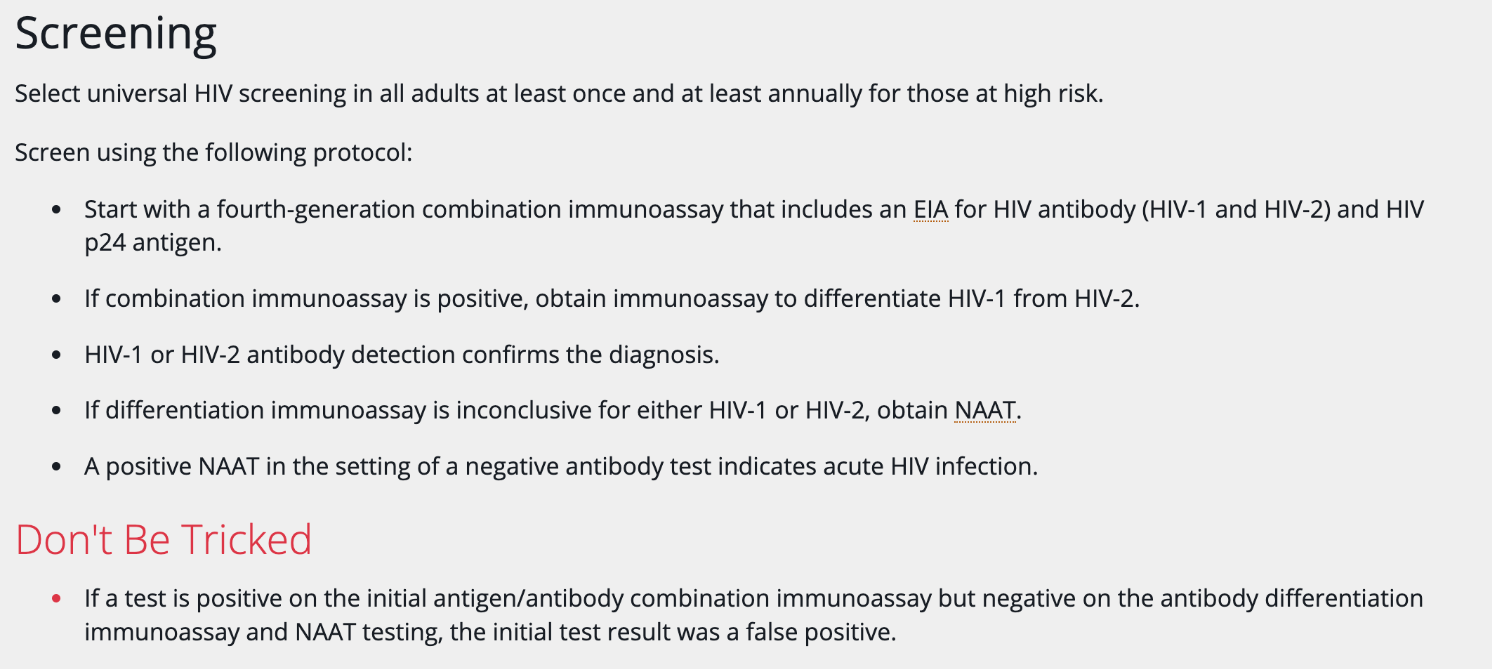
In a 31-year-old male HIV antigen/antibody immunoassay is positive. An HIV-1/2 differentiation test is negative, and a confirmatory NAAT is also negative. What is the most likely explanation?
A. Acute HIV infection
B. Early HIV-2 infection
C. False-positive initial test
D. Window period of HIV-1 infection
C. False-positive initial test
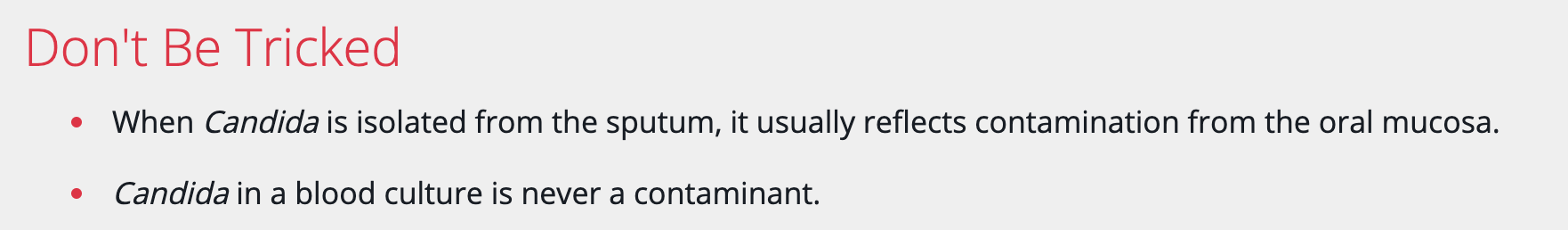
Which of the following statements about Candida is correct?
A. Candida in sputum cultures should be treated with systemic antifungals in ventilated patients
B. Candiduria should always be treated, regardless of symptoms
C. Candida in blood cultures is never considered a contaminant
D. Oral candidiasis in HIV patients is best treated with topical corticosteroids
C. Candida in blood cultures is never considered a contaminant
A 60-year-old man with a central venous catheter develops fever and chills. Blood cultures grow Candida albicans. What is the most appropriate initial treatment?
A. Fluconazole and remove central line
B. Amphotericin B and remove central line
C. Echinocandin and remove central line
D. No treatment, this is likely contamination
C. Echinocandin and remove central line

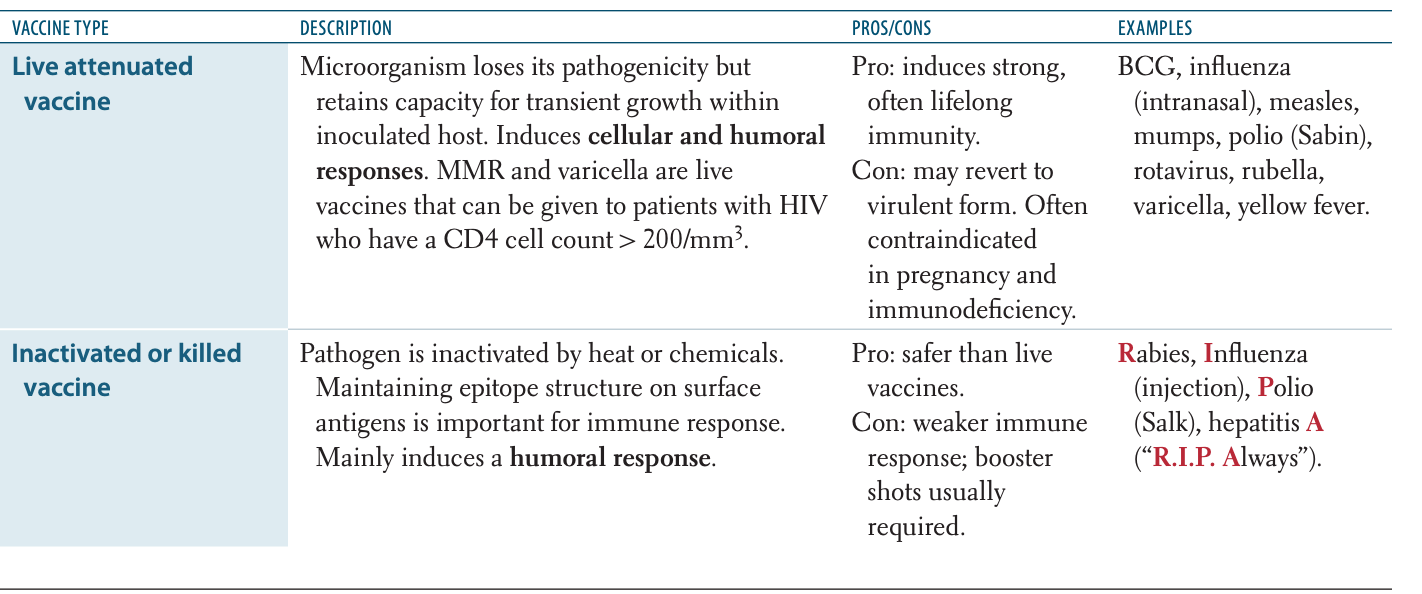
Which of the following vaccines is a live attenuated vaccine?
A. Influenza IM
B. Rabies
C. Hepatitis A
D. Influenza intranasal
D. Influenza intranasal
A 25-year-old male presents for routine follow-up. He states that a couple of weeks ago he had a painless ulcer in the genital region that resolved spontaneously. What is your diagnosis?
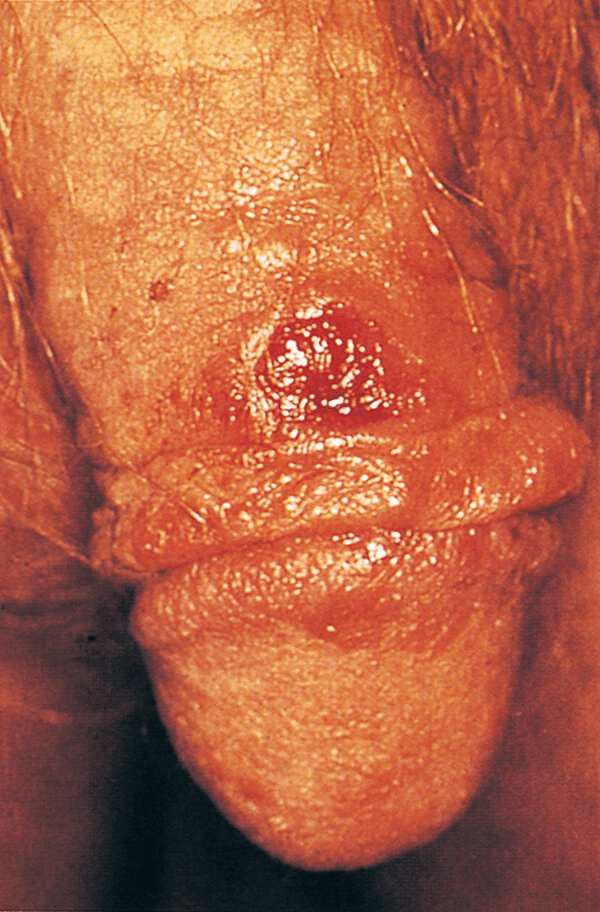
A. Primary syphilis
B. Secondary syphilis
C. HSV-2
D. Haemophilus ducreyi
A. Primary syphilis

Which of the following diagnostic tests is most appropriate for confirming active genital herpes infection in a patient with vesicular lesions?
A. HSV-2 IgG serology
B. Tzanck smear
C. Bacterial swab culture
D. PCR of lesion sample
D. PCR of lesion sample

A 30-year-old woman recently returned from a hiking trip in Arizona. She presents with fever, cough, and joint pain. Physical exam reveals erythema nodosum on her shins. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Coccidioidomycosis
B. Blastomycosis
C. Histoplasmosis
D. Sarcoidosis
A. Coccidioidomycosis

A 36-year-old man with HIV and CD4 count of 42/μL is not yet on ART. He has no known allergies. What combination of prophylactic agents is most appropriate?
A. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole alone
B. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and azithromycin
C. Clarithromycin and isoniazid
D. Dapsone and rifampin
B. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and azithromycin
A 45-year-old man presents with fevers, new-onset seizures and severe headache. He has a history of chronic sinusitis. CT shows a 3.5 cm brain lesion in the frontal lobe. MRI pending. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Lumbar puncture for CSF analysis
B. Start empiric IV vancomycin, metronidazole, and ceftriaxone
C. Start dexamethasone and repeat MRI in 48 hours
D. Begin acyclovir and await viral PCR results
B. Start empiric IV vancomycin, metronidazole, and ceftriaxone

A 48-year-old man presents with heel pain and swelling 3 days after stepping on a nail while wearing sneakers. He has no systemic symptoms. Which organism is most likely responsible?
A. Staphylococcus aureus
B. Streptococcus pyogenes
C. Salmonella species
D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
27-year-old male presents with a recurrence of the rash shown below. What is your diagnosis?
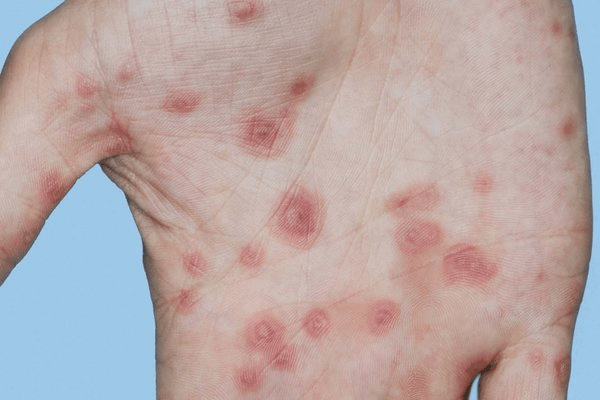
A. HSV recurrences
B. CMV infection
C. EBV infection
D. Recent influenza vaccination
A. HSV recurrences

A 55-year-old man from Missouri presents with a chronic cough, weight loss, and skin nodules. Chest imaging reveals a lung mass. Biopsy shows broad-based budding yeast. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Histoplasmosis
B. Coccidioidomycosis
C. Blastomycosis
D. Sporotrichosis
C. Blastomycosis
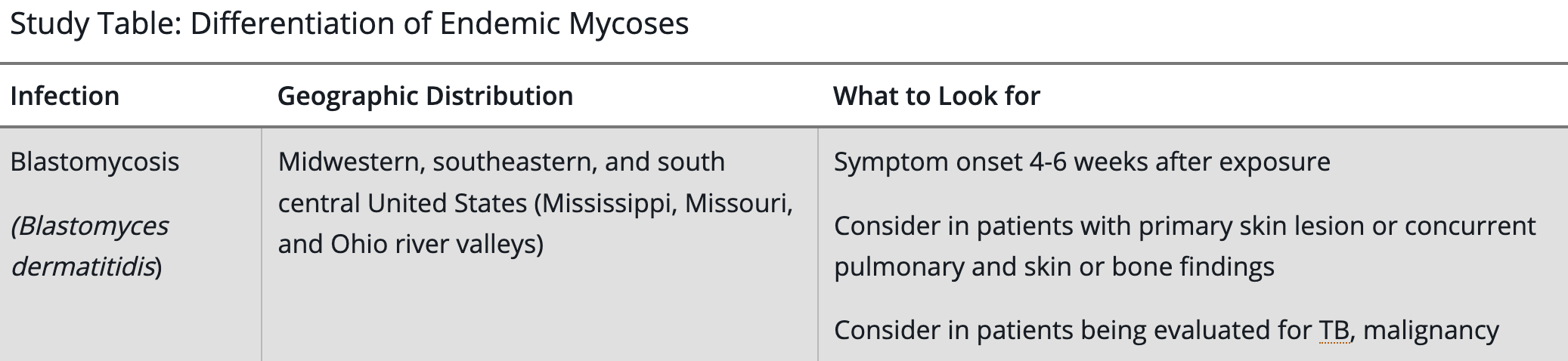
Which of the following patients must be desensitized to penicillin and cannot be treated with alternatives like doxycycline?
A. A nonpregnant man with early latent syphilis and penicillin allergy
B. A pregnant woman with secondary syphilis and penicillin allergy
C. A man with neurosyphilis and mild penicillin rash
D. A woman with latent syphilis of unknown duration who is HIV positive
B. A pregnant woman with secondary syphilis and penicillin allergy

A 30-year-old woman from Conneticut presents 2 days after a tick bite. The tick was removed 48 hours after attachment. She is not pregnant. What is the best next step?
A. Observe; no prophylaxis needed
B. Start amoxicillin for 10 days
C. Give a single dose of doxycycline
D. Start doxycycline for 14 days
C. Give a single dose of doxycycline

40-year-old asymptomatic hospital employee, originally from Vietnam, has a 10-mm induration on a tuberculin skin test (TST) during routine screening. She received BCG vaccine as a child. Chest x-ray is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. False-positive TST due to BCG vaccination
B. Latent tuberculosis infection
C. Active pulmonary tuberculosis
D. Negative TST requiring no further evaluation
B. Latent tuberculosis infection
During an influenza outbreak at a long-term care facility, which of the following is the most appropriate strategy to control spread?
A. Administer amantadine to all exposed staff and residents
B. Provide live attenuated influenza vaccine to all unimmunized staff
C. Begin oseltamivir chemoprophylaxis for all residents and staff for at least 2 weeks
D. Wait until cases are confirmed by PCR before intervening
C. Begin oseltamivir chemoprophylaxis for all residents and staff for at least 2 weeks

Which of the following statements about Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is most accurate?
A. PCP typically presents with acute pleuritic chest pain and productive cough in HIV patients
B. Fluconazole is preferred over TMP-SMX in sulfa-allergic patients
C. PCP is the most common cause of spontaneous pneumothorax in AIDS
D. Blood cultures are needed to confirm diagnosis of PCP
C. PCP is the most common cause of spontaneous pneumothorax in AIDS

A 40-year-old man with HIV and a CD4 count of 38 presents with fever, weight loss, night sweats, and chronic diarrhea. All stool studies are negative and CT shows non-specific lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment regimen?
A. Azithromycin and rifampin
B. Azithromycin, ethambutol, and rifabutin
C. Clarithromycin and rifampin only
D. Rifampin and pyrazinamide
B. Azithromycin, ethambutol, and rifabutin

Which of the following findings is most characteristic of HSV encephalitis?
A. Basilar meningeal enhancement on MRI
B. Periodic lateralizing epileptiform discharges on EEG
C. Tonic-clonic seizures
D. Frontal lobe enhancement and hypodensities
B. Periodic lateralizing epileptiform discharges on EEG
