This is advantageous in photon detection because it allows the discrimination of photoelectric events from scattered events.
A. Temporal Resolution
B. Energy Resolution
C. Spatial Resolution
What is energy resolution?
This is used to verify that the dose calibrator is measuring radioactivity precisely.
A. Linearity Test
B. Accuracy Test
C. Constancy Test
D. Geometry Test
What is constancy test? done daily.
True or False.
Collimators can stay on for extrinsic uniformity QC
True
Name the electronic components of a gamma camera that are required to produce and analyze the event pulses. (100 points for each answer)
Photon transducer (PMT), a preamplifier, amplifier, pulse height analyzer, scalars, or rate meters
Name a PET detector (4 answers)
BGO, LSO, LYSO, GSO
The precise time determination of when an event has occurred.
A. Temporal Resolution
B. Energy Resolution
C. Spatial Resolution
What is temporal resolution?
This test checks that the calibrator is able to accurately assay over the entire range of radioactivity used in the laboratory.
A. Linearity Test
B. Accuracy Test
C. Constancy Test
D. Geometry Test
What is Linearity Test? Done quarterly.
Name one way to do spatial resolution QC (Two answers)
Bar Pattern or SPECT Phantom
Converts visible light into an electronic pulse.
Photomultiplier tube
PET projections are obtained from ______ lines of response.
Coincidence
FMHM (KeV) / Photon Energy (KeV) X 100%
A. Temporal Resolution
B. Energy Resolution
C. Spatial Resolution
What is equation for Energy Resolution?
The ______ of the dose calibrator must be validated annually using calibrated radioactive sources traceable to the NIST.
A. Linearity Test
B. Accuracy Test
C. Constancy Test
D. Geometry Test
What is the accuracy test?
DAILY DOUBLE
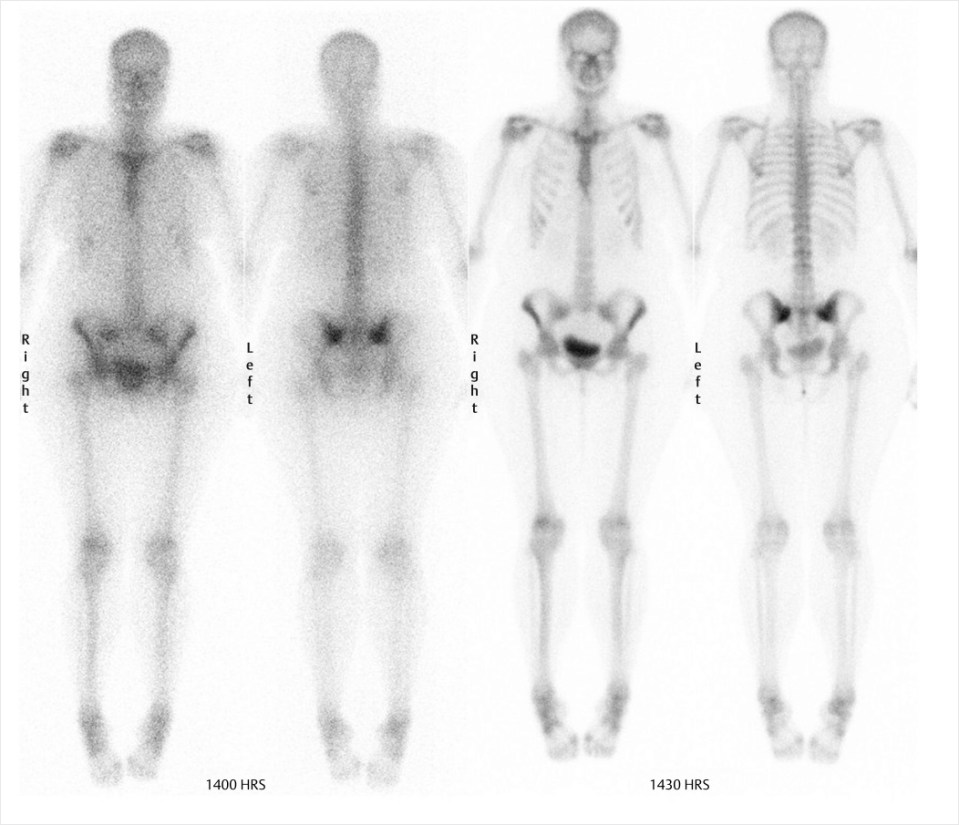
What is the problem with the picture on the left regarding QC.
Photopeak setting Problem. Study on the left is using Co-57 peak and not Tc-99m
This type of collimator is generally avoided because they have the lowest sensitivity of any collimator design for a given spatial resolution.
What is a diverging colimator?
Falsely hot activity on body surfaces and falsely low activity within deep structures is demonstrated without what type of correction?
Attenuation Correction
DAILY DOUBLE
When an event happens too rapidly, it cannot be properly analyzed, and information is lost.
What is Deadtime?
This checks to determine whether activity measurements change with sample volume or configuration.
A. Linearity Test
B. Accuracy Test
C. Constancy Test
D. Geometry Test
What is geometry test?
What would pictures look like if the PMTs have gone bad?
False Cold Spots
Name 5 types of collimators. (All or Nothing)
Parallel hole, slant, converging, diverging, pinhole
A display technique that uses reprojections of the volume information back into a series of projections around the body is called?
A MIP, maximum-intensity projection
This describes the ability of an imaging system to display detail.
A. Temporal Resolution
B. Energy Resolution
C. Spatial Resolution
What is Spatial Resolution?
What are the two methods that are used to evaluate linearity.
The decay of a test source or by attenuation shields.
Why is energy peaking or photopeak verification performed daily in gamma camera QC?
What's correctly identifying and centering the energy window over the radionuclide's photopeak
You're imaging a tiny baby's kidneys and zoom isn't an option for your parallel hole collimator, what collimator would be best for this study?
Converging collimator.
What's a disadvantage to filtered back-projections
Created severe streak or star artifacts, thus increasing image noise and reducing contrast.
Low spatial frequencies tend to be recorded accurately whereas high spatial frequencies are ________.
A. Attenuated
B. Absorbed
What is Attenuated?
What should be used if any of the measured activities exceed a 10% error from the expected activity? (Part of geometry testing)
A correction factor.
Characterized by a large number of hot spots at the periphery of the field of view.
What is Crystal Hydration (Measles)
Name 2 parameters that determine collimator sensitivity (total of 4 answers)
Hole length, hole diameter, hole geometry, septal thickness
What QC scan must be done each morning to be used as a reference uniformity measure for the transmission scan used in attenuation correction.
Blank Scan
The blurring effect of spatial resolution.
What is convolution?
What sources are used for accuracy test?
Co-57, Ba-133, Cs-137, Ge-68
Why is resolution and contrast testing important in SPECT QC, and how is it assessed?
What is Resolution and contrast testing evaluates the gamma camera’s ability to distinguish small, closely spaced structures (resolution) and detect differences in activity concentrations (contrast). These characteristics are assessed using a SPECT phantom (e.g., Jaszczak phantom) that contains cold and hot rods, spheres, and inserts.
Name 3 parameters that determine collimator spatial resolution. (All or nothing)
Hole length, hole diameter, the distance between source and collimator
What is the purpose of a transmission scan, and how can it be done? (double points by answering both questions)
To provide attenuation correction by using an external rotating radioactive source (Ge-68) or by a low-dose CT.