What is absolute advantage?
The ability to produce relatively more output using a given amount of resources
What is a trade barrier?
A means of preventing a foreign product or service from freely entering a nation's territory.
What is World Trade Organization (WTO)?
A worldwide organization whose goal is freer global trade and lower tariffs.
What is protectionism?
The use of trade barriers to protect a nation's industries from foreign competition.
If a nation exports a product, then the price of that product in the nation will _.
rise above the domestic (non-trade) equilibrium price.
What is an example of absolute advantage?
Using same number of workers, the U.S.A. produces 50 tractors a day while China produces 25 tractors a day. In this example, USA has absolute advantage in tractor production.
What are the 3 common forms of trade barriers?
Import quotas, voluntary export restraints, and tariffs.
What is a free-trade zone?
A region where a group of countries agrees to reduce or eliminate trade barriers.
What is an infant industry?
A new industry.
The value of a foreign country's currency in terms of the home country's currency is called ___.
Exchange Rate
What is comparative advantage?
The ability to produce a product most efficiently relative to all the other products that could be produced. (Product that can be produced with lowest opportunity cost).
What is an import quota?
A limit on the amount of a good that can be imported.
What is NAFTA?
The acronym stands for North American Free Trade Agreement. This agreement was meant to eliminate all tariffs and other trade barriers between Canada, Mexico, and the United States.
A difference between money paid to, and received from, other nations in trade is reported in the national income accounts as __.
Balance of payment
An increase in the value of a currency is called _.
appreciation of exchange rate
What is specialization?
A country's productive focus on a product or service that it has comparative advantage in.
What is voluntary export restraint?
A self-imposed limitation on the number of products shipped to a particular country.
What is the EU?
A regional trade organization made up of European Nations.
Limiting imports is supposed to help keep American money in the US instead of allowing in to go abroad to exporting countries.
If the dollar exchange rate changes from $1=100 yen to $1= 80 yen, then this change can be referred to as _.
an example of exchange rate depreciation of dollar against Yen.
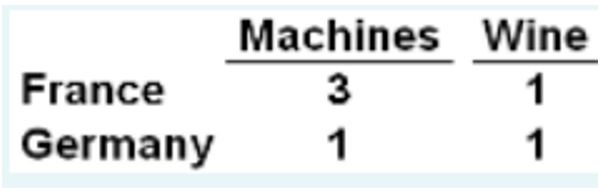
Based on the data table below that shows that each unit of input in France and Germany can product, we see that ____ has a comparative advantage in producing machines.
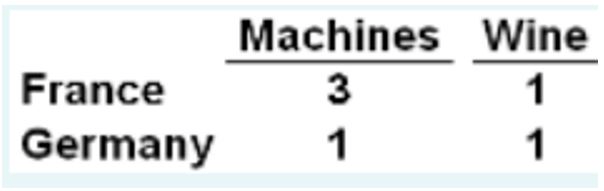
France has a comparative advantage in producing machines according to the given data.
Refer to the table below. The world price is $6/unit. What would be the difference in the total revenue received by foreign producers after a quota of 400 units is imposed, versus the total revenue they (foreign producers) receive when a $1 per unit tariff is paid?
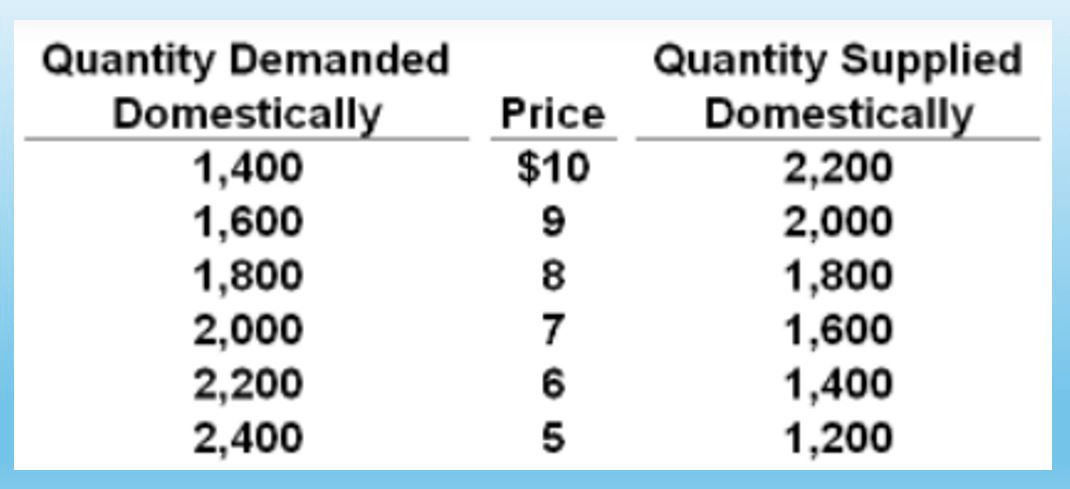
Foreign producers would receive $400 more under quote than under $1 tariff regime.
What is APEC?
A trade agreement including countries that lie along the Pacific Rim.
Mention some of the common arguments supporting and opposing protectionism?
Supporting arguments: Include protecting jobs, protecting infant industries, and safeguarding national security.
Opposing arguments: protectionism can harm consumers, reduce overall economic growth, and can lead to a prolonged trade war which can lead to global recession
Imposition of higher tariff on imported goods and services will usually cause the price of domestic goods and services _.
to increase