Mutualism
An interspecific relationship between members of different species where both benefit.
In the mutualistic relationship of pollination, name a benefit AND cost to the flower.
Benefit - gets pollinated.
Cost - has to produce nectar to attract pollinators - wasted energy.
Explain this relationship (i.e., name, costs, benefits)
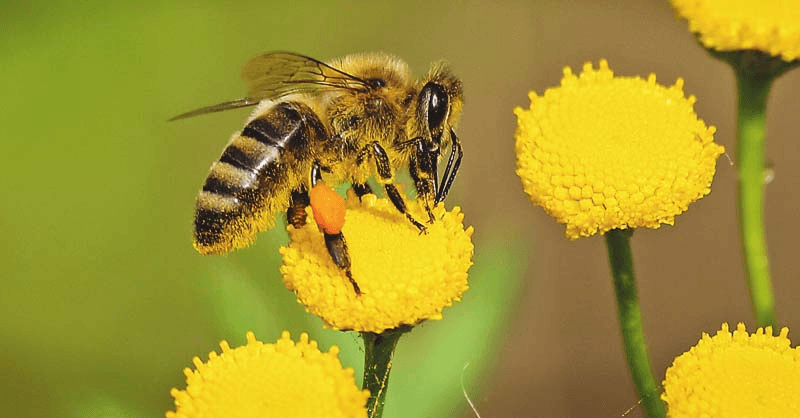

Mutualism
Benefits: Flower gets pollinated, bee gets nectar.
Costs: Flower produces nectar only for pollinator attraction, bee expends energy in finding flowers.
Give an example of a predator-prey relationship.
Benefits predator.
Harms / kills prey.
Predation
An interspecific relationship between members of different species where one species benefits (predator) and the other does not (prey).
In the parasitism relationship of tapeworms, name a benefit AND cost to the tape worm.
Benefit: gets nutrients and safe environment.
Cost: if host dies, tapeworm dies as well.
Explain this relationship (name and benefits).
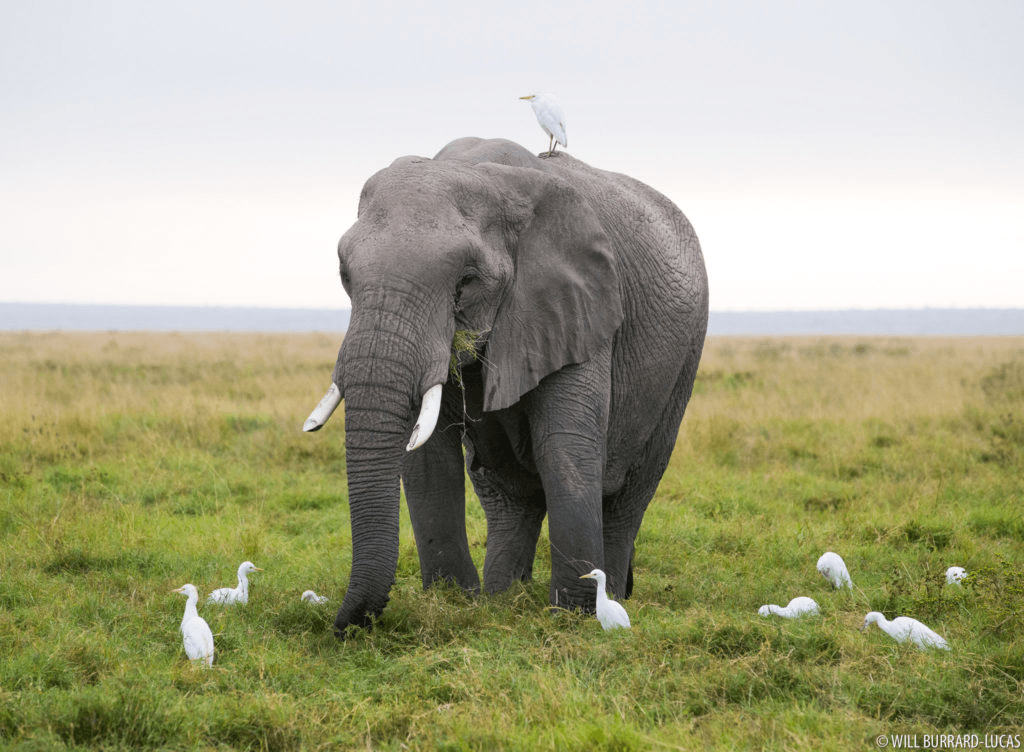

Mutualism.
Benefits: egrets get food from insects that are disturbed as elephant walks. Elephant gets warning about predators.
Give an example of a mutualistic relationship. Explain how it is mutualistic.
Must benefit both.
Commensalism
An interspecific relationship between members of different species where one species benefits and the other is not affected.
In predation, explain the benefits AND cost to the predator. Explain the cost to the prey.
Predator:
Benefit = food for survival and reproduction.
Cost = energy in searching/hunting for food.
Prey:
Cost = death / harmed
Explain this relationship (name and benefits).
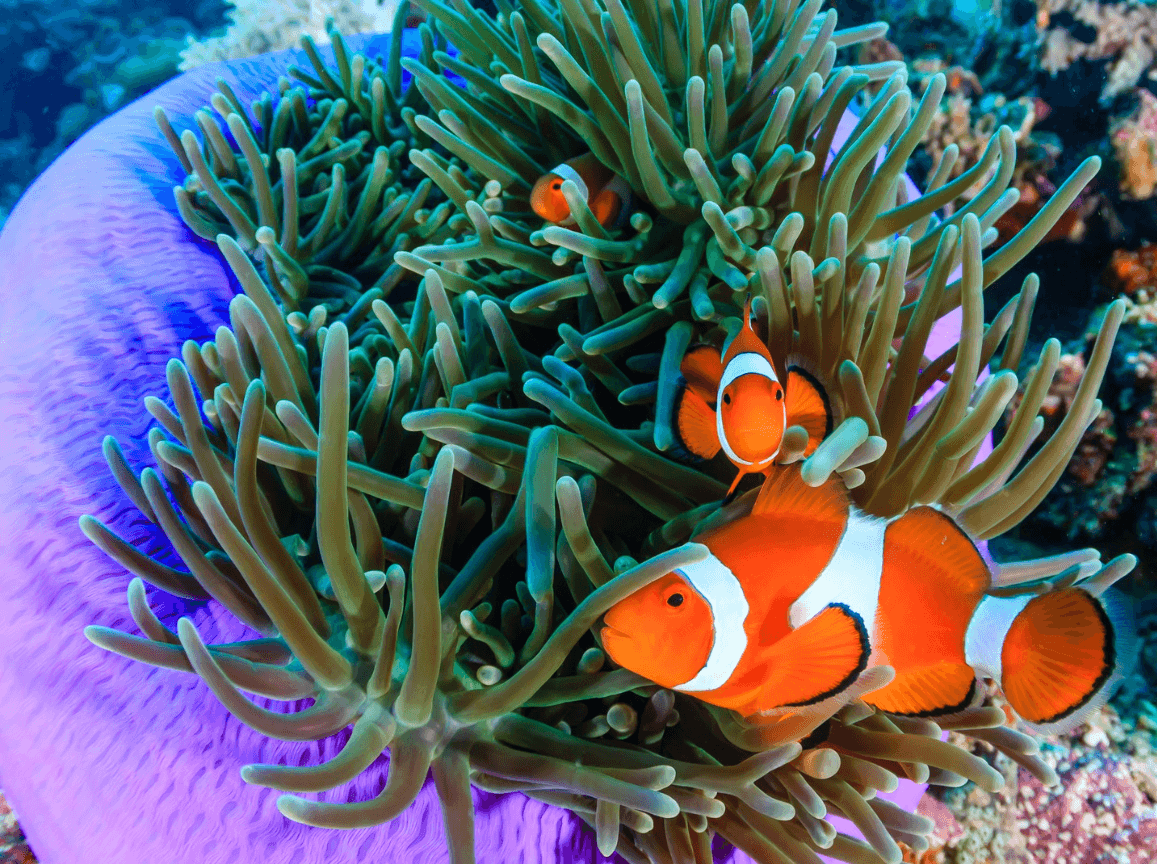

Mutualism.
Benefits: Clownfish gets protection and shelter. Anemone gets food from waste and predators scared off.
Give an example of a commensalism relationship. Explain how it is commensalism.
It benefits one species without affecting the other.
Inquilinism
an association in which one species uses part of the body of another species as a home
In the commensalistic relationship between remora (sucker fish) and sharks, name a cost AND benefit to the remora.
Benefit = gets a free ride, protection, food scraps.
Cost = if dislodged, may die.
Explain this relationship (name, benefits, costs).
Symbiotic.
Benefits: Cow gets food digested, microbes get nutrients and safe place to live.
Costs: Loss of nutrients from cow to microbes, if cow dies, microbes also die.
Give an example of a parasitism relationship. Explain how it is parasitism.
Benefit parasite.
Harm host.