Common symptoms to workup for ILD include nonproductive cough and this medical term for shortness of breath
What is dyspnea?
*More characteristic findings include hemoptysis, wheezing, and-if the cough is instead productive-the sputum production
A patient shows signs of dyspnea and coughing black sputum. If were to take their history, the patient would likely say they had this job
What is coal miner?
*Coal workers pneumoconiosis (CWP) is very likely for miners for inhaling coal dust, which will make their lungs (and sputum) black
From cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, you can see this common CT finding of ILDs.

What is ground glass opacities?
*It's the whiter streaks and the hazy regions that are considered ground glass. This is not unique to any disease (e.g. could also be pneumocystis jirovecii)
Interstitial lung diseases almost always show PFT results indicative of this broader category of lung disease
What are restrictive lung diseases?
*Interstitial lung diseases are one subcategory of restrictive lung diseases (square and rectangle argument respectively)
Having a blood test show allergies to bird feathers or microorganisms in moldy hay may signal this disease
What is hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
*Serum precipitins can indicate this disease
Crackles/rales that sound like this commonly used fastener are unique to ILDs, but not necessarily any particular one
What is velcro?
*Exception is sarcoidosis, which is much less common to hear
If a patient with a lung problem has a past medical history of this category of diseases that includes Sjogren's and scleroderma, their ILD is likely a result of that disease
What are connective tissue diseases?
*Such diseases will damage lung interstitium as part of their pathology
This finding on X-Ray shown by the black arrows indicates severely advanced silicosis
What is progressive massive fibrosis (PMF)?
*Formed by smaller nodules combining over time to make huge spots
Because the interstitium is damaged in the lungs, it will directly affect this PFT value
What is DLCO (diffusion capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide)?
*Will be lower than usual for ILDs!
Generally, a biopsy is warranted if you find an abnormality through these category of tests
What is a chest imaging OR X-Ray/CT scan?
*If you see a nodule or mass, you will want to biopsy to determine what exactly it is (malignancy, infection, etc.)
A person with acute onset of dyspnea, chest pain, fevers, chills after inhaling organic antigens may indicate this disease
*It is also called allergic alveolitis
This class III antiarrhythmic that is the drug of choice for stable V tach can lead to interstitial pneumonitis
What is amiodarone?
*Other drugs include some antibiotics and the chemotherapy drug bleomycin
The white plaques on this X-Ray indicate this disease
What is asbestosis?
*Generally these plaques are more present around the diaphragmatic area
While TLC and FVC are lowered in ILDs, this value can remain normal or even be elevated
What is FEV1/FVC?
*They both can drop at the same amount or FVC drops way more than FEV1
This finding is composed of mostly iron and protein and is commonly associated with asbestosis

What are ferruginous bodies?
*They are the brown, translucent bodies
JVD and leg edema can both indicate dysfunction in this heart chamber that indicate advanced ILDs
What is right ventricle?
*This indicates potential pulmonary hypertension! Note this symptom is not specific to any ILD, though
Ceramics, alloys, and electronics all contain this element that has an atomic number of 4 and can lead to a pneumoconiosis
What is beryllium?
*Berylliosis is the associated disease
The arrows on the X-Ray show this finding associated with silicosis
What are eggshell calcifications?
*Often at hilar lymph nodes
ILDs caused by this very common risk factor often shows obstructive lung disease PFTs instead of restrictive ones
What is smoking?
*It's possible for sarcoidosis and hypersensitivity pneumonitis to also be obstructive in nature, but most others are restrictive
A eosinophilic, bloody, exudate from the pleural effusion indicates this disease
What is asbestosis?
*This is a benign asbestos pleural effusion (BAPE)
If your patient has signs of rheumatoid arthritis and you notice symptoms similar to silicosis, you should consider this syndrome as a possible condition
What is Caplan's syndrome?
*Supposedly rheumatoid arthritis alters the immune response of inhaled coal dust, hence why this syndrome must be a combination of RA + CWP
When taking a history for this disease, you often want to know about exposures to sandblasting, quarrying, and ceramics up to 30 years ago
What is silicosis?
*There is generally progressive pulmonary nodules and fibrosis from exposures to silica
Both of these colored arrows indicate the same disease, with the yellow arrow being called this finding
What is traction bronchiectasis (must be specific!)?
*The orange arrows is honeycombing (smaller clusters as opposed to larger/longer tears), both representing idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
If the red/green loop represents a normal flow volume loop, the blue loop can suggest this broad category of lung disease
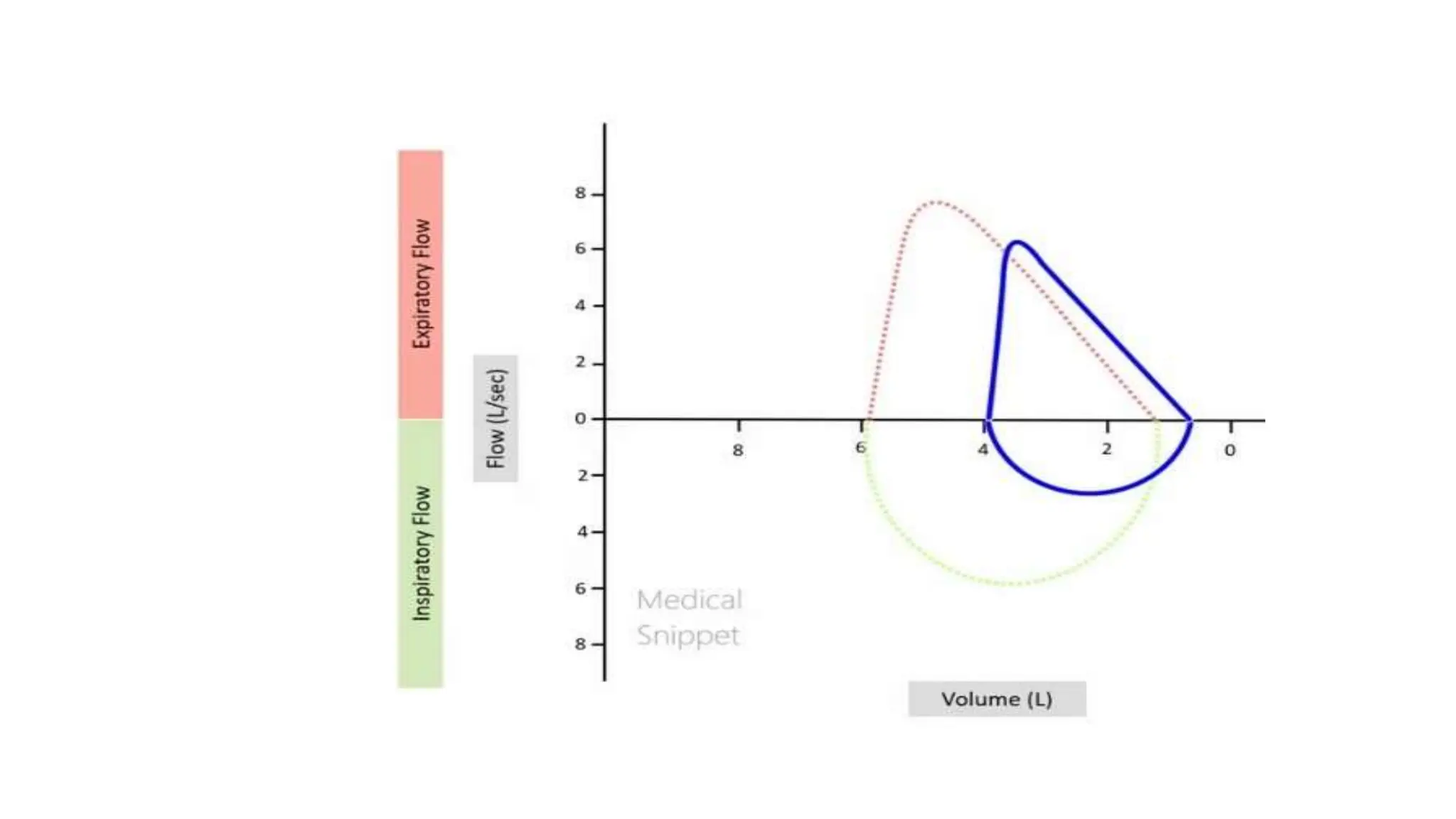
What is restrictive lung disease?
*The big factor is decreased TLC (leftmost point) and right-shifted curve for restrictive lung disease
This disease is commonly associated with the finding below, along with other labs of high TGF-beta
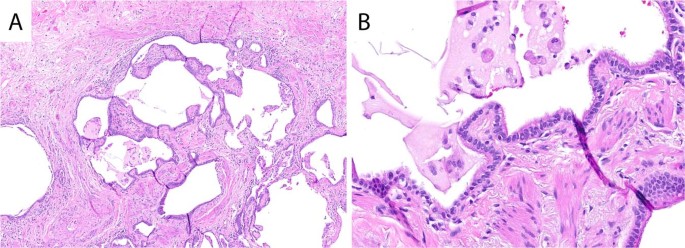
What is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
*The histology shows honeycombing, which helps confirm IPF!
