In 1964 this was the first person to describe the use of "tympanometry"
Who was Knut Terkildsen?
EHDI
What is Early Hearing Detection and Intervention?
ABR
What is the Auditory Brainstem Response?
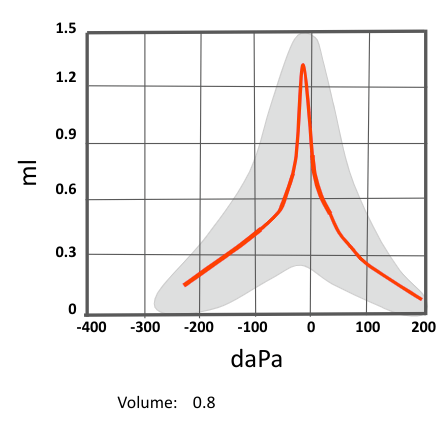
What is a Type A tympanogram
This term is used to indicate that a condition was present at birth.
What is congenital?
This is the process to separate a group of people who are well from those who are at risk for an undiagnosed disease or defect.
What is a screening?
This northwestern graduate developed the PBK50 Word list used in testing WRS on pediatric patients.
Who was Harriet L. Haskins?
1-2/1000
What is the incidence of children born with with hearing loss?
OAE
What are Otoacoustic Emissions?
This is an involuntary muscle contraction that occurs in the middle ear in response to loud sound stimuli. It results in a stiffening of the Middle ear system and serves to protect the ears from loud sounds.
What is an acoustic reflex?
This is a disorder that results from a collection of tympanic membrane debris/skin that can erode the ossicles and cause a conductive hearing loss. They can further progress to damage other critical structures near the ear.
What is a Cholesteatoma?
This federal regulation mandates the provision of interpreter services (including American Sign Language) for the both the patient and their families in acute care facilities.
What is the ADA or American's with Disabilities Act?
This audiometric pattern that is commonly found in otosclerosis demonstrates a conductive hearing loss where the air-bone gap closes at 2000 Hz.
What is a Carhart notch?
The goals of an EHDI program
1-3-6 Hearing screen by 1 month, diagnosis by 3 months, and Intervention by 6 months.
What are Wave I, III and V?
This type of tympanogram would be found in a patient with open pressure equalization tubes or a Tympanic membrane perfortion
This common viral disorder makes up the "C" in T.O.R.C.H and is one of the in utero infections that can result in congenital hearing loss and other issues.
What is Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
This disability questionnaire is designed to screen for patients self-perceived handicap resulting from a hearing loss.
What is the hearing handicap inventory screening (HHI-S)
This disorder associated with rotary vertigo, low-frequency fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss was named after this French physical.
Prosper Ménière
These the three possible outcomes from a newborn hearing screening (EHDI screening).
What are Pass, Pass with Risk factors, Referral for more testing.
This physiologic test evaluates the sounds generated by of the outer hair cells in the cochlea and is interpreted as being either "present' or "absent"
What are Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE)
A machine that can perform tympanometry, acoustic Reflexes, and reflex decay.
What is an immittance bridge.
Audiology Emergency
What is a sudden sensorineural hearing loss?
What is 1 in 3?
Her research provided support to the concept of early intervention for hearing loss and when on to champion newborn hearing screening programs around the world.
Christine Yoshinaga-Itano
These are the two tests can can be used in a newborn hearing screening programs.
What are Automated Auditory Brainstem Response (AABR) and Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE)
This electrophysiology tests can obtain hearing thresholds by analyzing a person's EEG and detecting brainwave activity that synchronizes with modulations added to the sound wave for the pitch you are testing.
What is Auditory Steady State Response (ASSR)
The acoustic reflex threshold displayed on this image: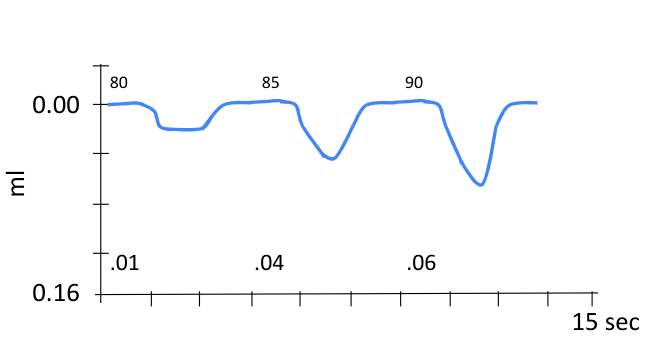
What is 85 dB?
This is a common genetic hearing loss
What is connexin 26 or GJB2?
These are the core frequencies tested on a pure-tone hearing screening (children and adults)
What are 1000, 2000, 4000 Hz?
This audiologist championed early intervention in children with hearing loss and is considered the "mother" of pediatric Audiology.
Who was Marion Downs?
The benefit of early detection and intervention in children born with hearing loss.
Baring other issues, children who receive early intervention will catch up to their normal hearing peer's speech and language skills; those who do not get early intervention fall irrevocably behind.
Auditory Neuropathy and a Vestibular Schwannoma can be detected by this physiologic test.
What is the Auditory Brainstem Response?
This tympanogram pattern type demonstrates negative pressure suggesting that the patient may have Eustachian tube dysfunction.
What is a type C tympanogram.
Thee are both exogenous inner ear pathologies.
What are noise-induced hearing loss, ototoxic drugs or any of the infections diseases (any two)
This is the proportion of a population who have a specific characteristic in a given time period, regardless of when they first developed the characteristic.
What is prevalence?