What are the three main types of logic used for truth tables and their symbols?
AND: ∧
OR: ∨
NOT: ¬
How are or, if, & and gates represented?
What is the difference between the = and == operators?
= is to assign a value to a variable
== is used to compare the value of two variables
What does "elif" mean?
"else if" -- used when you need another if statement
Write a program that asks the user to enter their name and print how many letters are in their name
name = input("What's your name? ")
print(len(name))
Write a truth table for the following:
What are the definitions of gates and circuits?
Gate - performs a Boolean logic operation on one or more binary inputs and then outputs a single binary output
Circuit - a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function.
What is the definition of modulus?
The remainder of a number after division of a certain number.
What are the two types of logic we've talked about for Python statements? Hint: we've practiced one for a few weeks but one is newer
Conditional and Iterative
Write a program that gives the user an item in the list corresponding to whatever index they ask for. Assume that they don't know how to index in Python, so the first item in the list is 1, second is 2, etc.
def func(lis=[34, 56, 21, 79])
ind = int(input("What list item do you want? ")
print(lis[ind-1])
Fill in the following truth table, with ~ meaning not.
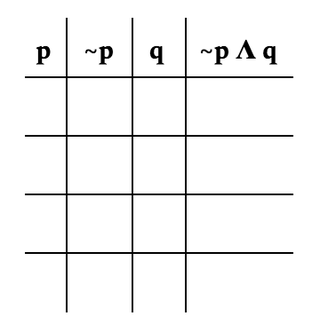
p ~p q ~p∧q
0 1 0 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 0
1 0 1 0
Create a circuit from the following:
A ∧ (B ∨ C)
You got it
What is the result of this command? print ("5" + "3")
A) 8
B) "8"
C) "5" + "3"
D) 53
D) 53
What is the result of the following code, given an input of -1?
number = int(input("Enter an integer number: "))
if number >= 1:
print("Your number is greater than 10")
elif number ==0:
print("Your number is 0")
There would be no output.
Write a function divisible_by_five() that asks a user to input a number. If it is divisible by 5, return the number. If not, print no output.
def divisible_by_five():
number = int(input("Please enter a number"))
if number%5 == 0:
print("Your number,", number, "is divisible by five")
divisible_by_five()
Write a truth table for the following:
(¬A) ∧ (B ∨ C)
A B C ¬A B ∨ C Output
0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 1
0 1 0 1 1 1
0 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 1 0 1 0
1 1 0 0 1 0
1 1 1 0 1 0
Create a circuit for the following sequence:
(A ∧ B) ∨ (¬B ∧ C)
You got it
What is the difference between return and print()? Answer must include where values are sent.
str(input(
float(input(
int(input(
How would we index list_example to get the first ten values?
list_example[:11]
Write a program that checks if "dog" is in the following list:
pets = ['cat', 'hamster', 'dog', 'bird', 'guinea pig']
pets = ['cat', 'hamster', 'dog', 'bird', 'guinea pig']
if 'dog' in pets:
print("Yes, a dog is a pet")
Write a truth table for the following circuit:

A B ¬A A∨B ¬A∧B (¬A∧B) ∨ (A)
0 0 1 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0 1
1 0 0 1 0 1
1 1 0 1 0 1
Write a truth table for the circuit below:
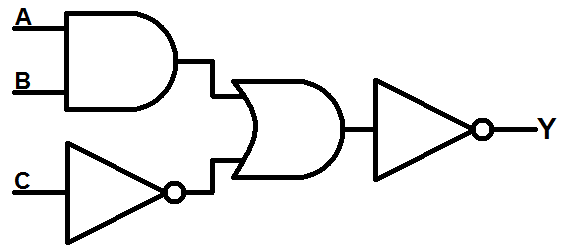
A B C A ∧ B ¬C (A∧B) ∨ (¬C) Output
0 0 0 0 1 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 1 1 0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1
1 0 0 0 1 0 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 1
1 1 0 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 1 0 1 0
What would the result of (x // 2) % 3 be if x=35?
2
(35 // 2) = 17, 17 % 3 = 2
Consider the following example:
lst = [1, 2, 3]
print(1 in lst)
What would the output be?
True
Write a program that asks a user for the time, rounded to the nearest hour. Then, calculate and print what time it will be in four hours using a 12-hour clock (e.g, 1 pm instead of 13:00)
time = int(input("What time is it currently, rounded to the nearest hour? "))
in_four_hours = (time+4)%12
print(in_four_hours)