the passing of traits from parent to offspring
heredity
two genetically identical cells created as a result of mitosis
daughter cells 
distinguishing quality or characteristics of a person
trait
How many chromosomes does the offspring have after meiosis?
23 chromosomes
How many chromosomes do the offspring have after mitosis?
46 chromosomes
A molecule of DNA that is wrapped tightly around structural proteins called histonines
Chromosome
structure that holds the sister chromatids together; point where chromosomes attach to spindle fibers during mitosis
centromere 
chromosomes that have the similar size and same genes.
homologous chromosomes 
microtubules that guide the movement of chromosomes during cell division
spindle fibers
What type of cells are made during mitosis?
two body cells
A long molecule that stores the genetic code with instructions needed to produce proteins for an organism to develop and function.
Deoxyribonucleic acid 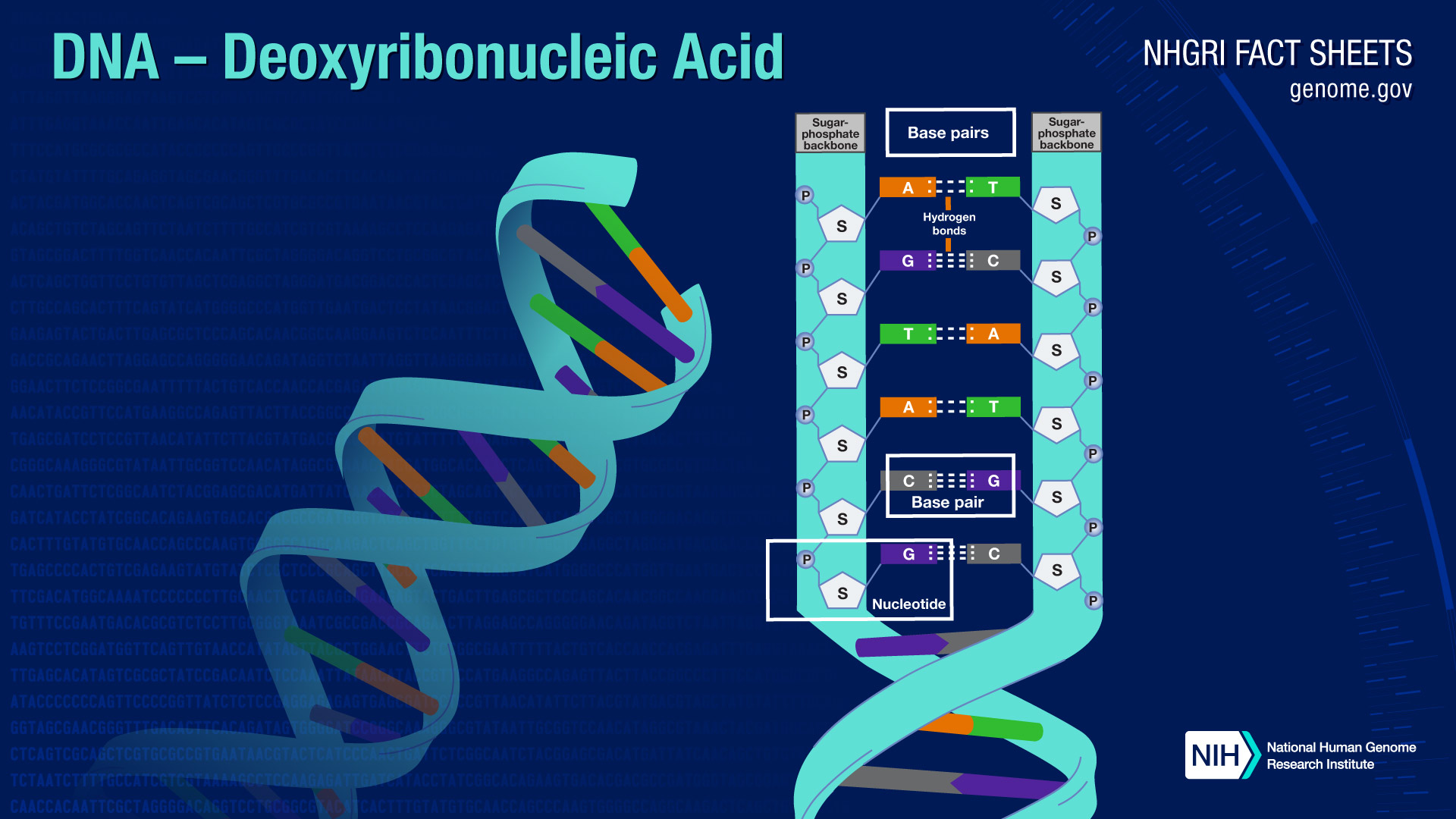
process in which DNA makes copy of itself
DNA replication

phase of the cell cycle during which a cell is not dividing
interphase
![]()
having two sets of chromosomes (2n)
diploid

What type of cells are made during meiosis?
four gamete cells
A segment of DNA located on a chromosome that is a set of directions for certain kinds of proteins
Gene 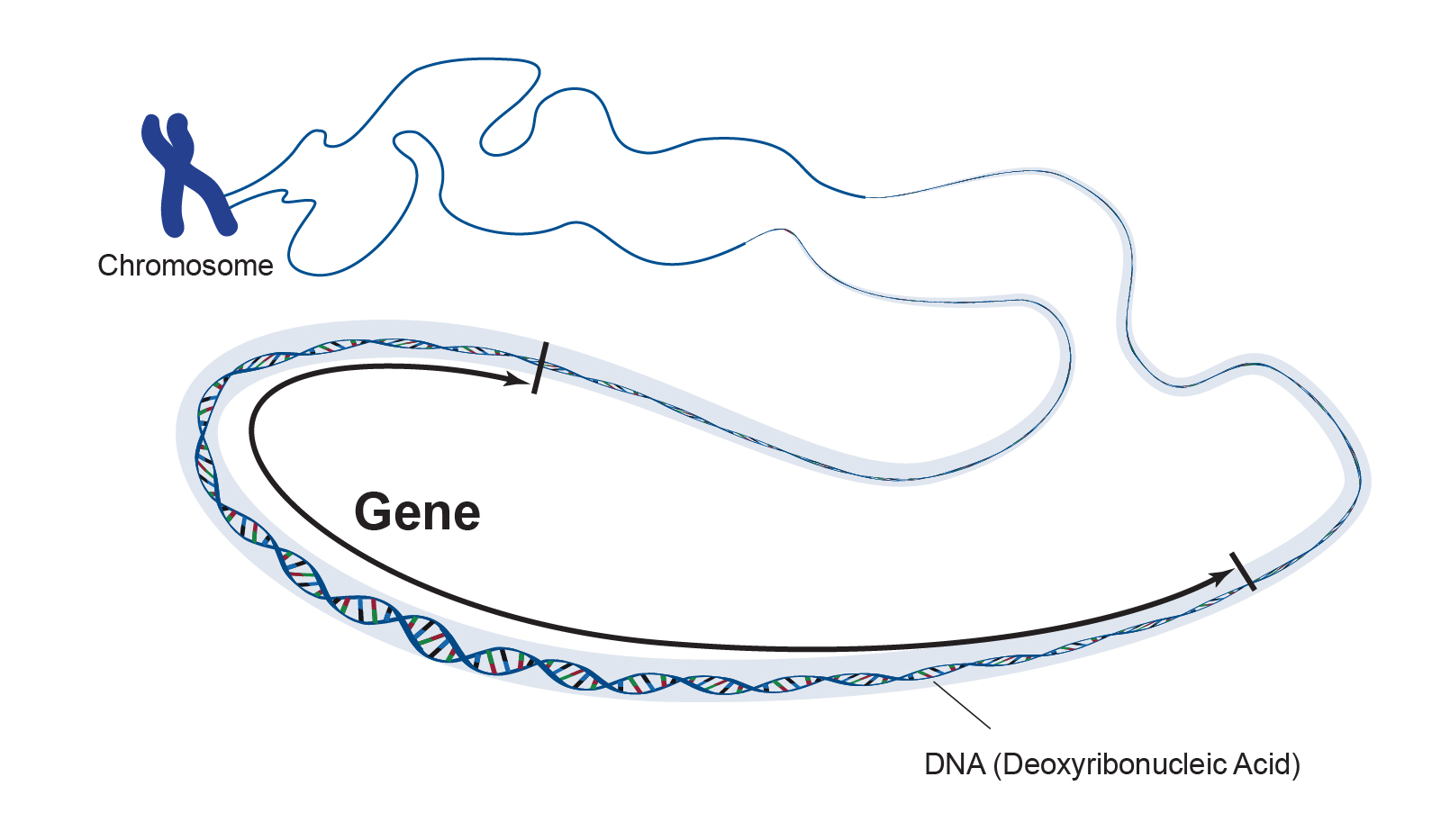
cylindral structure made up of microtubule that makes spindle fibers for cell division
centriole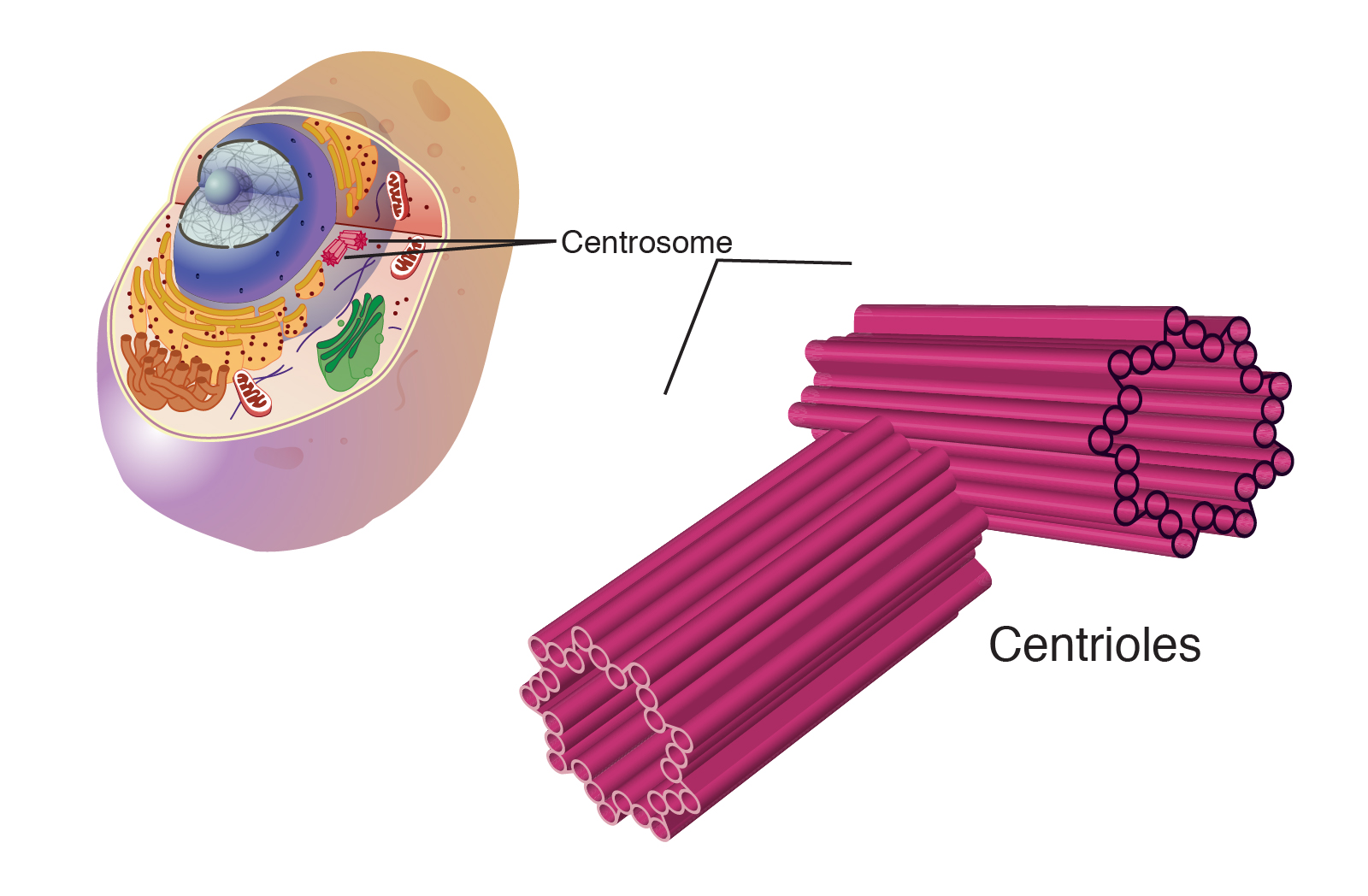
four cells as a result of meiosis, which are genetically different from each other and the parent cells
haploid cells 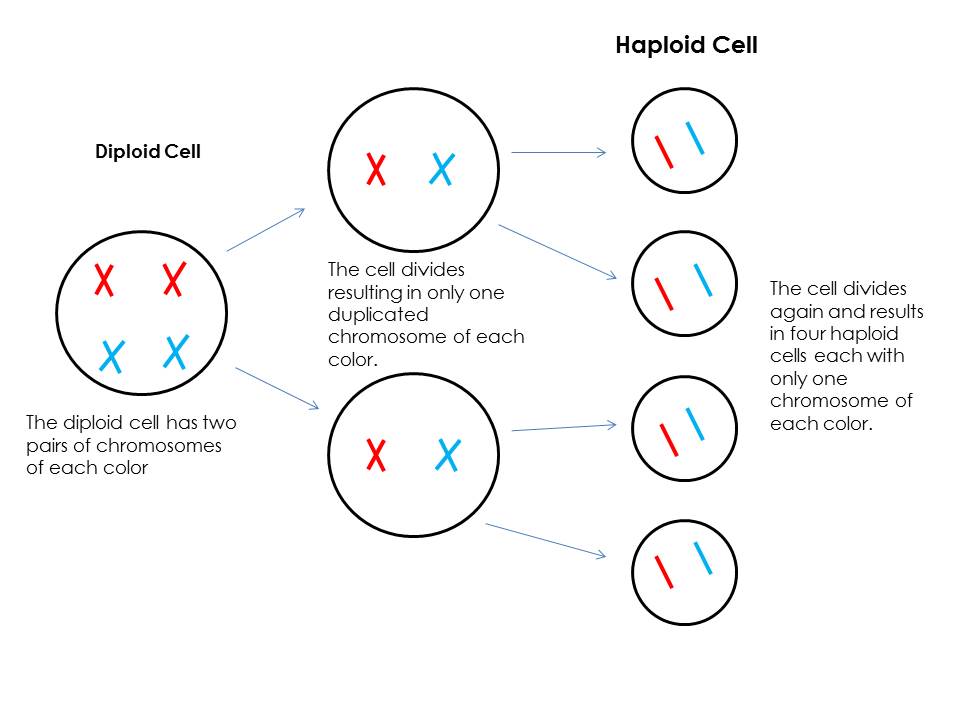
What is a nucleotide made up of?
nitrogen base, phosphate group, and deoxyribose (a sugar molecule)
What are the steps, or rungs, of the ladder made up of?
A sequence of paired nitrogen bases
each genes come in different forms called _____
alleles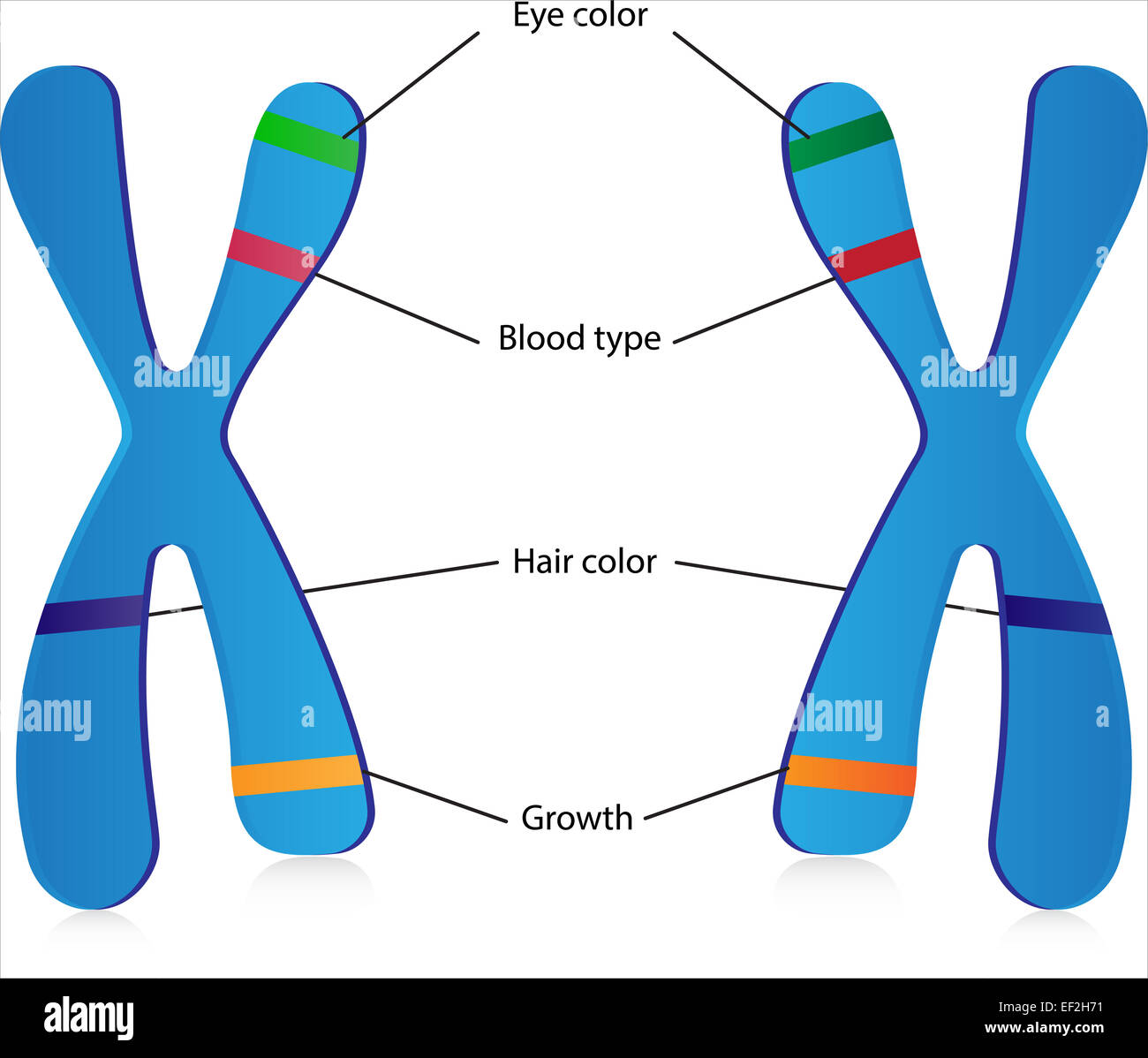
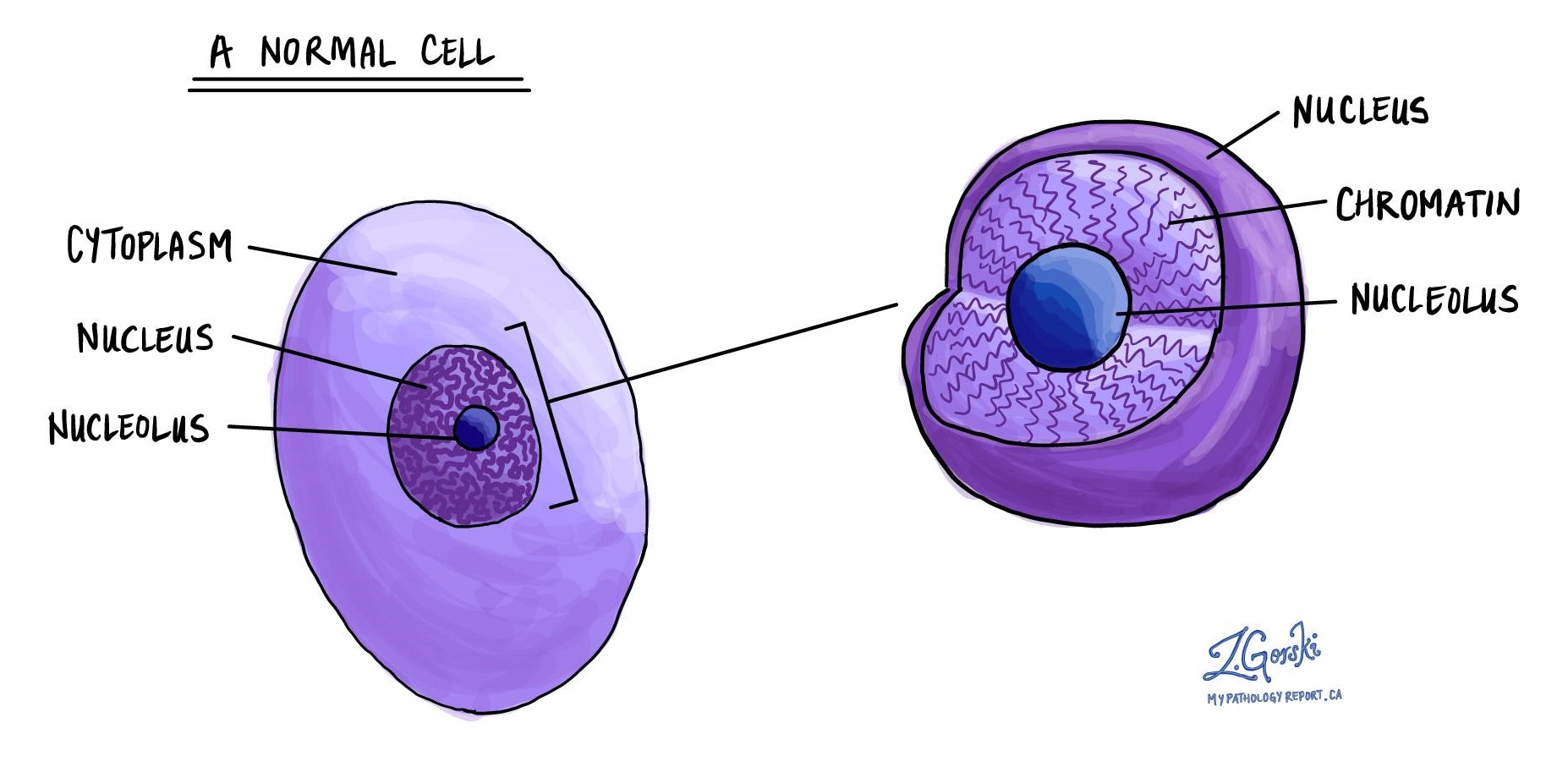
thread-like form of DNA in the nucleus of the cell interphase and cytokines
chromatin
the process where homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material to form new chromosomes
crossing over 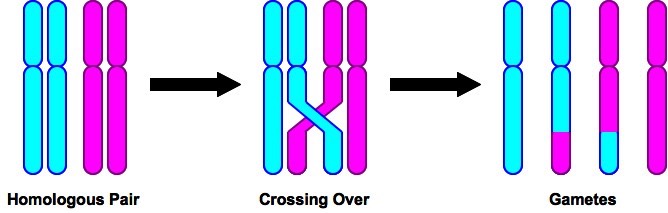
What is the backbone (both sides of the ladder) of DNA made up of?
deoxyribose (a sugar molecule) and a phosphate group

What type of acid is DNA?
DNA is a nucleic acid
