Accumulation of knowledge and skills over time. Allows the nurse to analyze and synthesize the patient's presentation, objective, and subjective data to provide evidence-based nursing interventions to improve patient outcomes.
What is clinical judgement?
The scientific name that describes the drug's chemical structure.
What is the chemical name?
Movement of the drug into the bloodstream after administration.
What is absorption?
Expected action of drug therapy. Can have more than one.
What is the therapeutic effect?
What is black box warning?
Age
Age significantly impacts medication administration due to physiological changes that alter how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates drugs. These changes can affect drug efficacy and increase the risk of side effects in older adults.
It considers the interconnectedness of physical, emotional, social, spiritual, and environmental factors that influence a person's health and well-being.
What is holistic nursing care?
The official, nonproprietary name of a drug; universal name.
What is the generic name?
Movement of the drug from the circulation to the body tissues.
What is distribution?
Itching, headache, GI upset.
What is a side effect?
Requires strict recordkeeping and monitoring of narcotics, stimulants, depressants, hallucinogens, and anabolic sterioids.
What is the Controlled Substances Act?
Patient history
To help avoid preventable errors in prescribing, since an inaccurate history on admission to hospital may lead to unwanted duplication of drugs, drug interactions, discontinuation of long-term medications, and failure to detect drug-related problems
Wrong dose, wrong medication, wrong time, wrong indication.
What is a medication error?
The name of a medication is the proprietary name given by the drug company that makes the drug and is usually easy to say for sales and marketing purposes.
What is the brand (trade) name?
Also known as biotransformation. This is the process by which the body chemically changes the drugs into a form that can be excreted.
What is metabolism?
diarrhea, shortness of breath, anaphylaxis
What is adverse drug reactions?
Helps to protect the consumer from medication harm.
What are the FDA, DEA, TJC, CMS, State Nurse Practice Act, and State Board of Nursing?
Body weight
The effect of body weight on drug action may vary in extent. In some cases, weight can primarily determine the dosage; in other cases, the weight effect may be minimal or dosage can be affected only when weight is combined with other factors
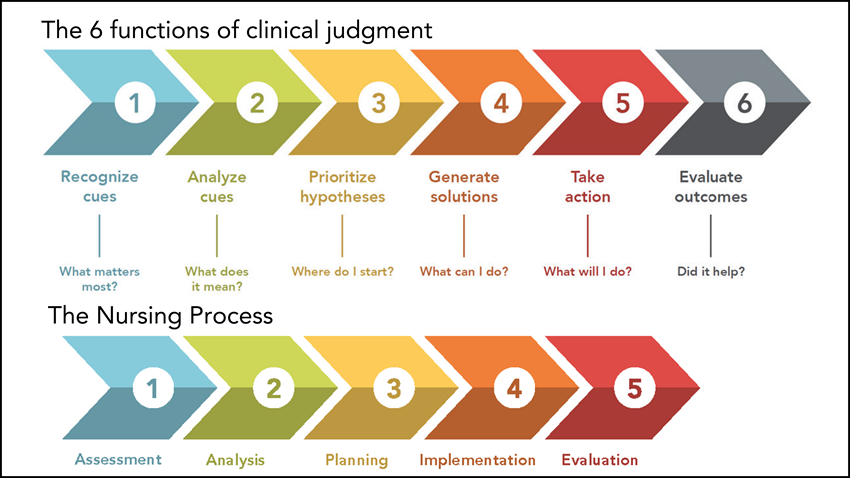
What is the clinical judgement model?
Categories of their therapeutic use or medical conditions they treat, e.g., antibiotics, analgesics, etc
What is drug classification?
Elimination of the drug from the body?
What is excretion?
The drug level exceeds the therapeutic range.
What is drug toxicity?
Requires a written order by a provider.
What is a prescription?
Pregnancy/Breastfeeding
Medication safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding is a complex topic, as medications can affect both the developing fetus and the breastfeeding infant. While a medication may be safe for a pregnant person, it doesn't automatically mean it's safe for a breastfeeding mother and their infant. The transfer of medications into breast milk can vary based on factors like the drug's properties and the infant's metabolism.
What will the nurse perform to help prevent a medication error?
What are the rights of medication administration?
An individual drug that represents a drug class.
What is a prototype?
What happens to the level of a medication in the body for a patient with renal dysfunction?
What is the level increases due to decreased excretion?
Examples of how a nurse can improve medication administration safety.
What is: Appropriate prescribing, risk assessment, medication review, dispensing, preparation and administration, communication, and patient engagement, and medication reconcilliation?
What are herbal and supplements?
Culture
Cultural beliefs and practices can significantly impact how individuals perceive and respond to medications, influencing their adherence and overall treatment outcomes. These cultural factors can affect medication administration in several ways, including beliefs about illness and treatment, adherence to medication regimens, and even physical responses to medications.