Which chemical bonds are the strongest?
Covalent bonds
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The purpose of meiosis is to create gametes (haploid cells)
Which enzyme translated mRNA into a protein?
Ribosome
What technique can you use to determine the size of a DNA fragment?
Gel electrophoresis
What "foreign" sequences make up roughly a half of the human genome?
Transposons
Here is a graph of a typical spontaneous biochemical reaction:
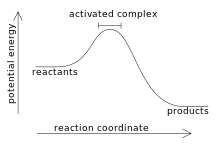
How would this graph change if we add an enzyme?

What's the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype is what kind of genes an organism has, and phenotype is what it looks like (what observable traits it exhibits).
What does DNA polymerase need to start copying the DNA?
A primer
What is special about modified dNTPs that are added to a DNA sequencing reaction?
DNA polymerase gets stuck on them and cannot extend DNA any further past them.
What can you do if you want to try to understand the function of a novel gene in a mouse?
Create a knockout mouse or use other ways to silence that gene
What are the key elements of protein secondary structure?
Alpha helices and beta sheets
In one of his experiments, Mendel studied pea plans with yellow and green peas. The yellow color was dominant over the green color. When Mendel would set up a cross between a heterozygote plant and a recessive homozygote plant, what fraction of plants with green peas would he get?
About 50%
How many DNA polymerases would you expect to find in a replication bubble?
Four
Vectors that are used for cloning always carry a gene of a certain kind. What kind of gene must all cloning vectors carry?
Antibiotic resistance
What would you add to cells to silence a certain gene using RNA interference?
Double-stranded RNA
What is the purpose of the Glycolysis pathway?
Generation fo ATP
What concept or method was used to create the first genetic maps of fruit fly's chromosomes?
Genetic linkage
Give two examples of how a mutation inside a gene would not change a protein that is encoded by this gene.
- A mutation occurs inside an intron
- A mutation is in the third position of a codon
Which two enzymes do you need to clone a piece of DNA into a vector?
Restriction enzyme and a ligase
Would you expect a cell with a gain-of-function mutation in one copy of MEK kinase to be transformed? Why or why not?
Yes, because MEK kinase is a protooncogene.
Suppose a biochemical reaction that converts A to B is unfavorable (delta G > 0). How can it be incorporated into a biochemical pathway?
It can be coupled with a favorable reaction (e.g. with ATP hydrolysis)
Looking at a pedigree of a human disease, how can you suspect X-linked recessive inheritance?
- Most of the sick individuals are males
Additional considerations:
- In a family with a healthy mother (carrier) and a healthy father about 1/2 sons will be sick
- In a family with a sick mother and a healthy father all sons will be sick, and all daughters will be healthy
- In a family with a sick father and a healthy mother all healthy children can be healthy
How can a single gene encode two different proteins?
Alternative splicing
One cycle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has three stages that are performed at very different temperatures. What are those stages?
1. Denature the DNA
2. Anneal the primers
3. Replicate the DNA
Would you expect a cell that lost one copy of a tumor suppressor gene to be transformed? Why or why not?
No, because the remaining copy of that tumor suppressor will guard the cell and protect it against uncontrollable cell division.