This type of tremor, characteristic of PD, is often described as "pill-rolling" and is maximal when the patient's hands are supported in their lap.
What is a resting tremor?
This neurotransmitter is synthesized by neurons in the __________ and is deficient in Parkinson Disease.
What is the substantia nigra pars compacta?
This clinical feature, defined as slowness of movement, is an important sign required for the clinical diagnosis of Parkinson's disease.
What is bradykinesia?
Which first-line treatment is often considered for patients under 70 due to decreased risk of dyskinesias?
What are dopamine agonists? (pramipexole or ropinorole)
"Levodopa sparing"
What occupation is associated with a higher risk for Parkinson Disease?
What are farmers?
Farmers are frequently exposed to specific chemicals that lab studies have shown can directly harm the neurons lost in Parkinson's disease.
Rotenone (Insecticide): This is widely used in labs to create a PD model in animals because it specifically damages the mitochondria (the cell's powerhouses) in the dopamine neurons.
Paraquat (Herbicide): This chemical is known to induce high levels of oxidative stress
These chemicals are selectively toxic to the dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra!!
This tremor worsens with movement but often improves dramatically with the consumption of alcohol.
What is an essential tremor?
What is the major dopaminergic pathway affected in PD?
What is the nigrostriatal pathway?
This physical exam finding is characterized by jerky resistance when passively moving a limb, due to an underlying tremor superimposed on rigidity.
What is cogwheel rigidity?
What is the MOA of entacapone/talcapone?
What is inhibition of catechol-o-methyltransferase (COMT)?
Bonus: what is the normal reaction that COMT catalyzes?
This protective environmental factor, whose mechanism is debated but may involve MAO-B inhibition, is associated with a significantly decreased risk of developing PD.
This key medication is the primary pharmacologic agent used to treat an essential tremor.
What is propranolol? (non-selective beta blockers)
Which of the following is the most likely pathophysiological mechanism responsible for the decline in hearing seen in PD patients?
What is loss of dopaminergic innervation to the cochlear efferent (olivocochlear) system, impairing auditory signal modulation.
-----------------------------------------------------------
Auditory dysfunction in PD (often subtle sensorineural loss or difficulty filtering background noise) is linked to central and efferent pathway involvement. The olivocochlear bundle is a key efferent system that uses dopamine as a neurotransmitter to fine-tune cochlear function, helping to enhance signals in noise. The degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the brainstem disrupts this system.
This cognitive assessment tool includes drawing a cube and a clock, making it more sensitive to mild executive dysfunction in PD than the mini mental state examination (MMSE).
What is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment? (MoCA)
What is bromocriptine?
By what mechanism do drugs induce parkinsonism?
What is inhibition of dopaminergic neurotransmission?
A tremor that is absent at rest but increases as the limb nears a target during a directed movement.
What is an intention tremor?
What would be seen on a DaT scan of a patient with PD?
What is reduced uptake of the radioactive tracer?
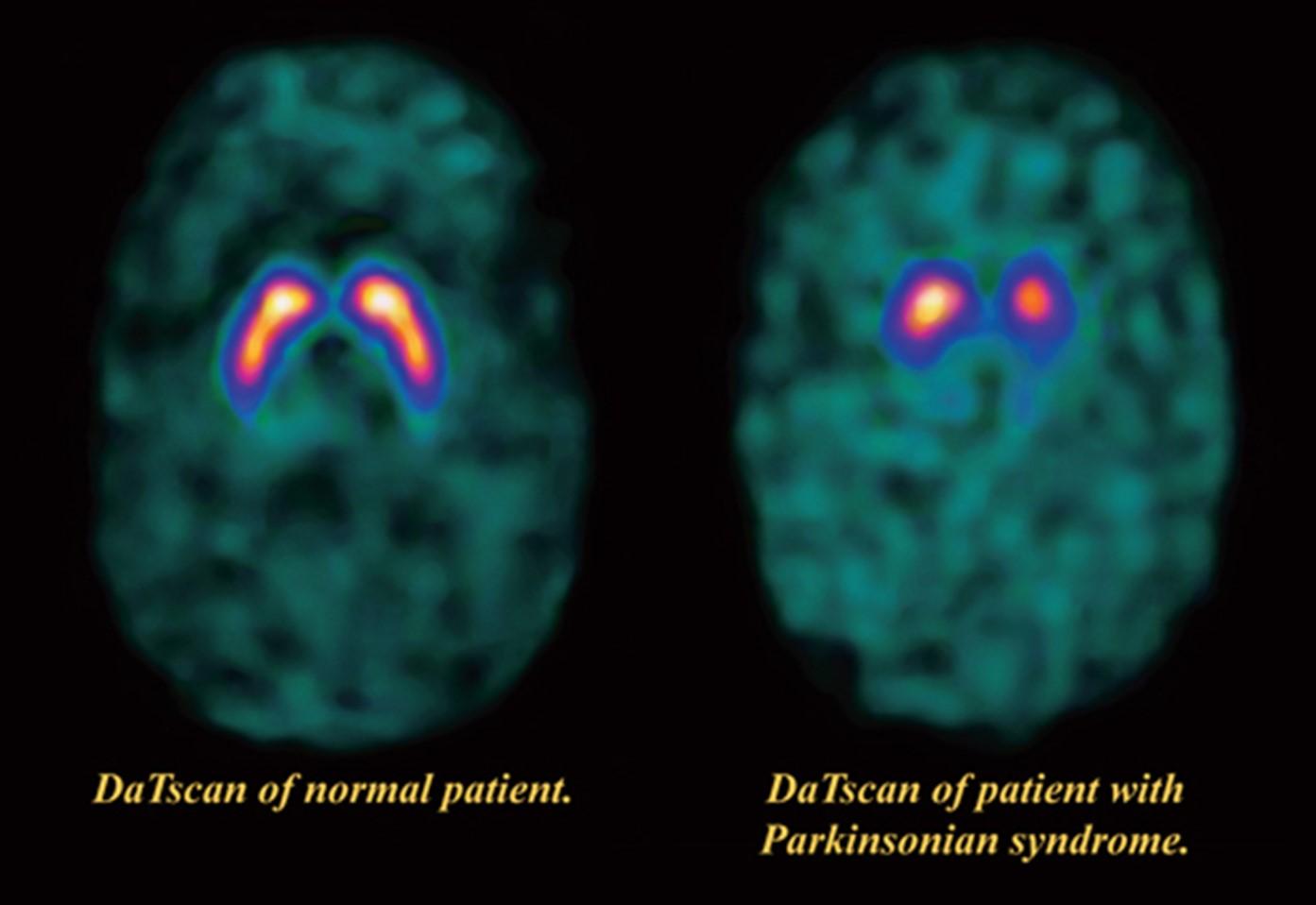
Normally, Parkinson's disease is characterized by the breakdown and death of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, which leads to a decrease in the chemical dopamine. These neurons have special proteins on their surface called Dopamine Transporters (DAT), which are responsible for recycling dopamine.
The classical pathologic finding in PD, consisting of cytoplasmic inclusions of aggregated α-synuclein protein.
What is a lewy body?

Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical treatment for Parkinson's disease that uses electrodes to modulate activity in the motor circuit. Which of the following is the most frequently chosen primary target for DBS implantation?
A. Subthalamic Nucleus
B. Substantia Nigra pars compacta
C. Red Nucleus
D. Cerebral Cortex
A. Subthalamic Nucleus
The STN is the most common target because stimulating it provides control over the entire motor circuit and allows patients to significantly reduce their need for Levodopa.
This environmental neurotoxin, which can be found in illicitly synthesized street drugs, causes immediate and severe parkinsonism by destroying dopaminergic neurons.
What is MPTP? (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine)
What is dysmetria?
Dysmetria is caused by damage to the cerebellum. It means an inability to accurately judge the distance required for a movement. This causes an intention tremor because you try to quickly fine tune your movements - this is best seen when performing the finger-to-nose test.
What is the fundamental functional imbalance within the basal ganglia motor circuit that directly causes the slowed movement (bradykinesia) characteristic of Parkinson's disease?
What is the over-inhibition of the thalamus by the basal ganglia's output structure, the Globus Pallidus Interna (GPi).
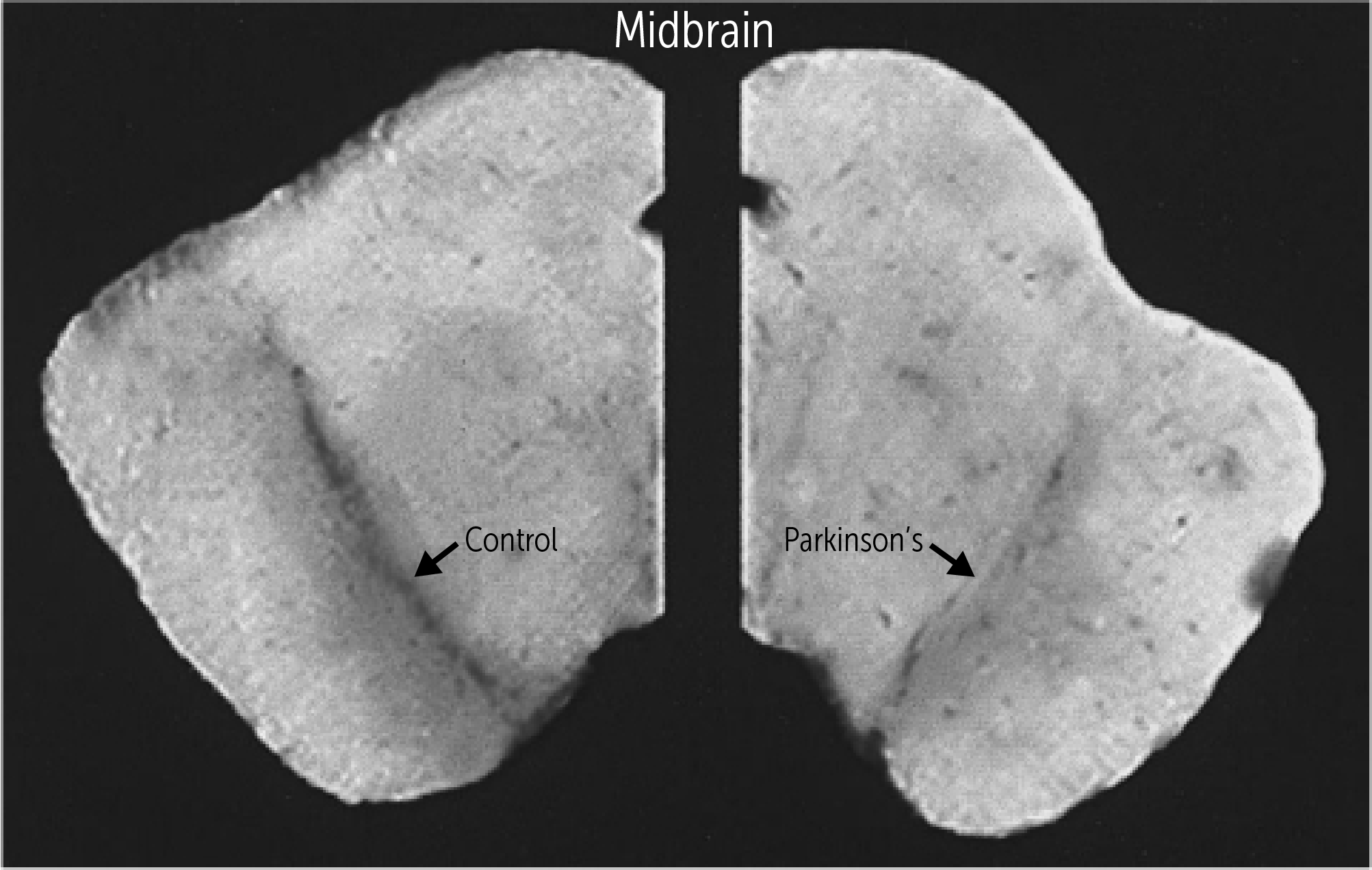
What gross change is seen on a brain cross-section in PD?
What is depigmentation of the substantia nigra?
DBS is highly effective in improving the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. In addition to treating tremor and rigidity, which major side effect of long-term Levodopa therapy is DBS most consistently used to minimize and control?
What is dyskinesia?
Name 3 drug classes that may cause drug induced parkinsonism.
What are
- Antipsychotic drugs (eg, trifluoperazine, fluphenazine, haloperidol)
- Anti-emetics that block dopamine (metoclopramide and prochlorperazine)
- Valproic acid (epilepsy and bipolar disorder)