Multiple Sclerosis patients may experience exacerbations in their symptoms during the course of the disease. What do the potential causes of these episodes have in common?
Increase Body Temperature (Hot tub, Bath, Sauna, Exercise etc)
This descending tract, often affected in MS, explains why patients may develop spasticity and hyperreflexia.
What is the corticospinal tract?
Palsy of this cranial nerve can occur in patients with multiple sclerosis. Patients present with facial pain that becomes achy
Trigeminal nerve (CN V1-3)
This is the gold standard for diagnosing cases of multiple sclerosis.
MRI
The first line treatment for exacerbations of multiple sclerosis.
IV or PO glucocorticoids
People aged 20-40 and females are at higher risk for Multiple sclerosis. What are two other risk factors?
Growing up farther from the equator and low Vitamin D levels (smoking, obesity in early life, EBV, HHV-6 accepted too)
Relevant afferent pupillary defect aka Marcus Gunn Pupil has the affected eye do this in response to illumination.
Dilates
This physical exam finding is most commonly the first to develop in multiple sclerosis patients. It is often unilateral and painful.
optic neuritis
CSF from a patient with multiple sclerosis is likely to reveal elevated levels of both of these.
IgG and myelin basic protein
Absolute contraindication for female patients with multiple sclerosis planning to receive monoclonal antibody treatment.
Pregnancy or breast feeding
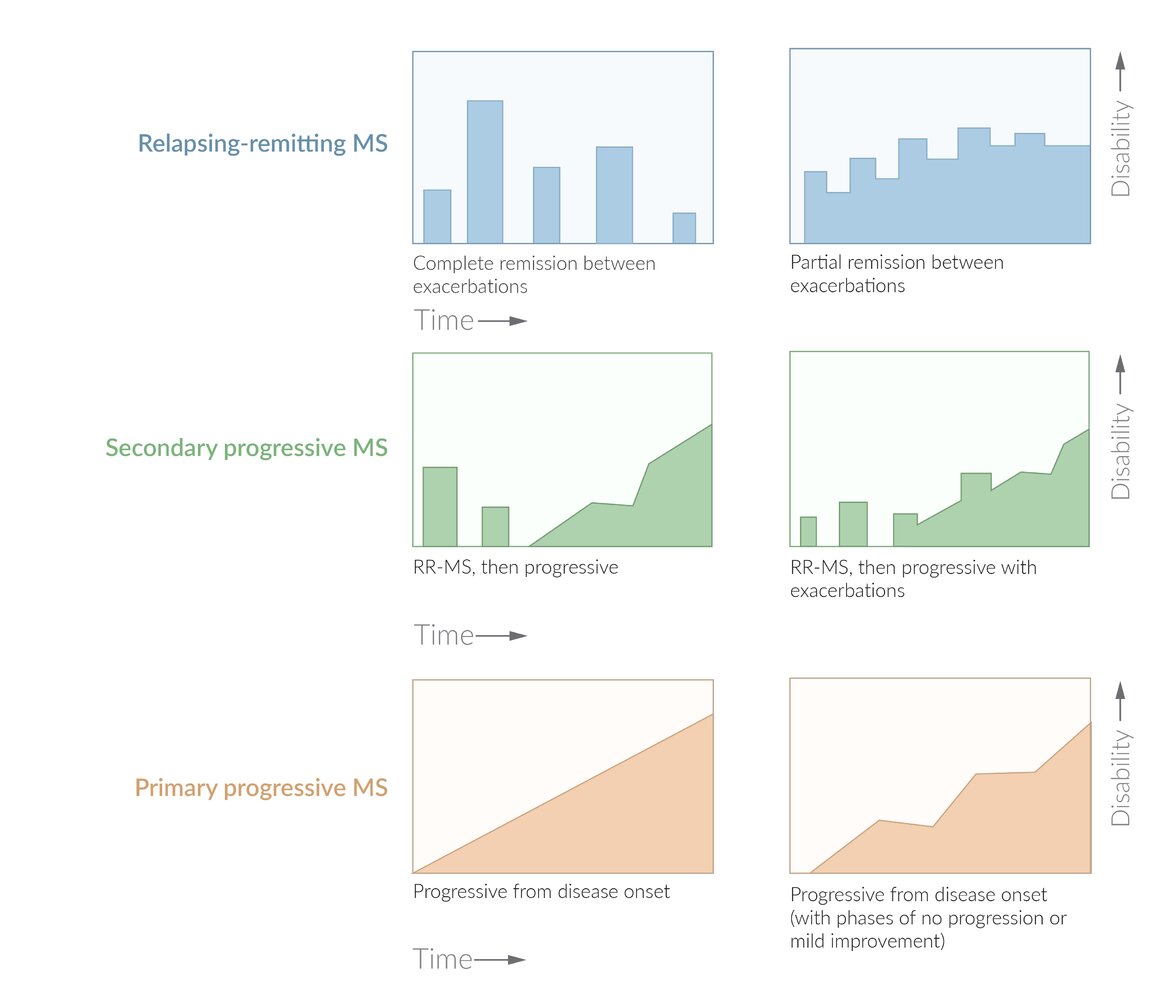
This pattern of Multiple Sclerosis is the most common phenotype seen in 90% of patients.
Relapse-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RR-MS)
A collection of nerve fibers that encompasses the corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts. Consists of upper motor neurons that originate in the cerebral cortex and terminate in either the brainstem (corticobulbar tract) or spinal cord (corticospinal tract).
Pyramidal Tract
Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system in patients with multiple sclerosis can lead to these two "below the belt" findings.
Urinary incontinence and sexual dysfunction
These are sites of oligodendrocyte loss and reactive gliosis commonly found on imaging in the periventricular region or in the cervical region of the spinal cord.
demyelinating plaque(s)
These two medications could be given for multiple sclerosis patients who are experiencing spasticity.
Baclofen (centrally acting GABA B agonist) and Tizanidine (α2-receptor agonist)
The underlying pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis is not fully understood/clear. What is the current understanding of this disease process?
Activation of autoreactive T-lymphocytes → inflammatory processes → focal demyelination with partial preservation of axons (acute plaques) → loss of axons and atrophy of oligodendrocytes (chronic plaques) → gliosis → inadequate remyelination
These are the 7 steps of the Optic Tract.
Retina --> optic nerves --> optic chiasm --> optic tracts--> lateral geniculate nucleus --> optic radiation--> primary visual cortex
A shooting electric sensation that travels down the spine upon flexion of the neck. Typical in multiple sclerosis and may occur in other demyelinating diseases.
Lhermitte sign
What finding on the imaging below is strongly indicative of multiple sclerosis?
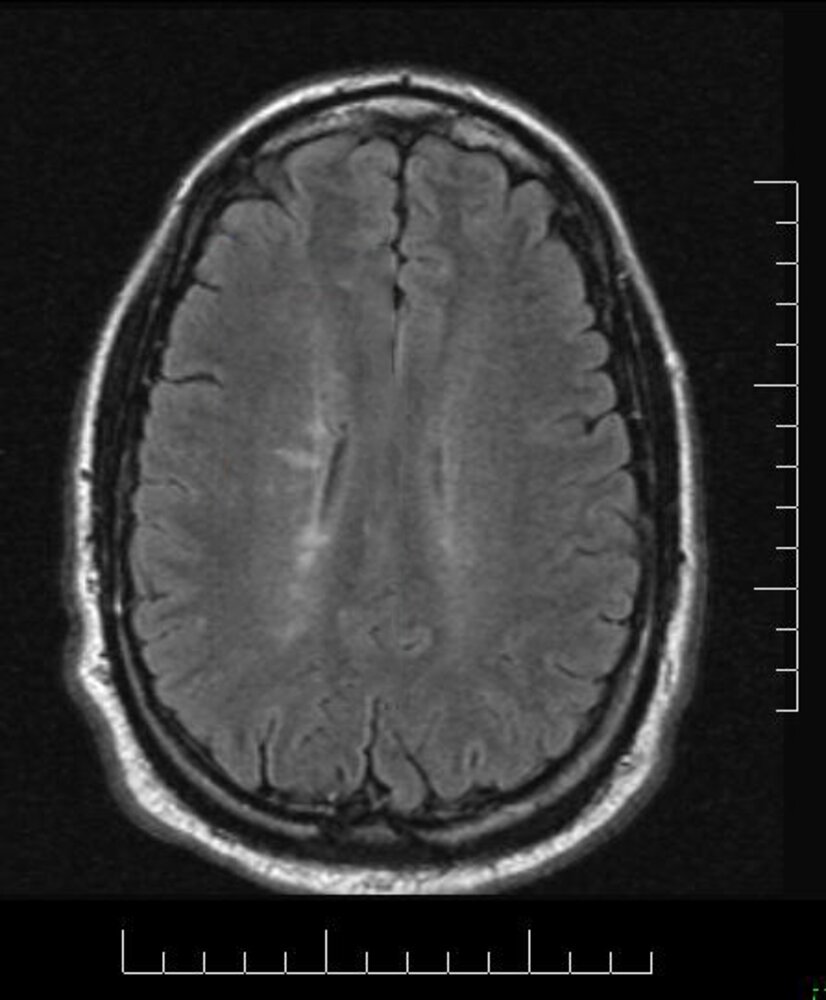
Dawson Fingers
These two classes of medications can be given to treat the central neuropathic pain seen in multiple sclerosis patients.
tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline)
anticonvulsants (e.g., carbamazepine, gabapentin)
Which HLA allele is protective for multiple sclerosis?
HLA-A*02
Patients with internuclear ophthalmoplegia can successfully look straight ahead, demonstrate convergence, and gaze ipsilateral to the lesion that is found here.
medial longitudinal fasciculus
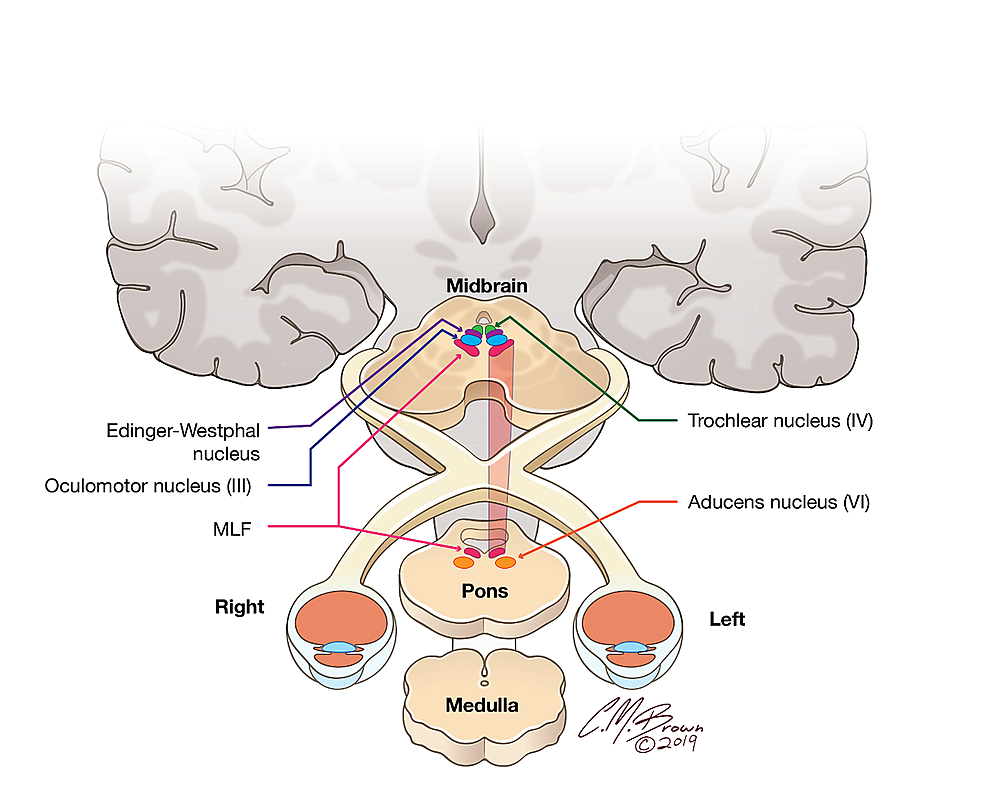
The reversible worsening of symptoms in patients with multiple sclerosis that is thought to be due to worsened impulse conduction of demyelinated nerves.
Uhthoff phenomenon
Lesions for multiple sclerosis are disseminated in time and space. This is the official criteria used to diagnose MS based on the clinical presentation, CSF analysis, and imaging findings that suggest the presence of lesions.
McDonald's criteria
Patients with multiple sclerosis should be screened and treated for this condition that can occur alongside MS in some people.
Depression