This bond is described as atoms "pooling" valence electrons", which freely move around.
What is a Metallic Bond?
This subatomic particle has a positive charge.
What is the proton?
The Hindenburg exploded in 1937 because it was filled with hydrogen gas, which was highly reactive due to a neutral hydrogen atom having this many number of valence electrons.

What is one valence electron?
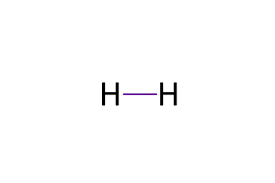
Diatomic Hydrogen (H2)
What is a Single Bond?
NaCl
What are ionic bonds?
This bond is between two nonmetals.
What is a Covalent Bond?
This subatomic particle has a negative charge.
What is the electron?
The halogen family tends to be extremely reactive due its number of valence of electrons. Fluorine, in particular, is the most electronegative element due its limited number of electron shells (2) being pulled extremely close to the nucleus, enabling it to easily "grab" the one extra valence electron it needs. But before that happens, the neutral fluorine atom has this many valence electrons?

Extremely cold fluorine in liquid form
What is seven valence electrons?
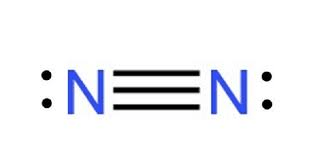
Diatomic Nitrogen (N2)
What is a Triple Bond?
CH4
This bond is between metals and nonmetals.
What is an Ionic Bond?
This subatomic particle determines the identity of the atom. In other words, it is the reason every element has a specific atomic number because every element has a different number of these in the nucleus.
What is the proton?
Spelled "Aluminum" (UH-LOOM-UH-NUM) in the US, and "Aluminium" (OWL-YOO-MIN-EE-UM) elsewhere, this Group 13 metal has how many valence electrons?

What are three valence electrons?
Diatomic Sulfur (S2)
What is a Double Bond?
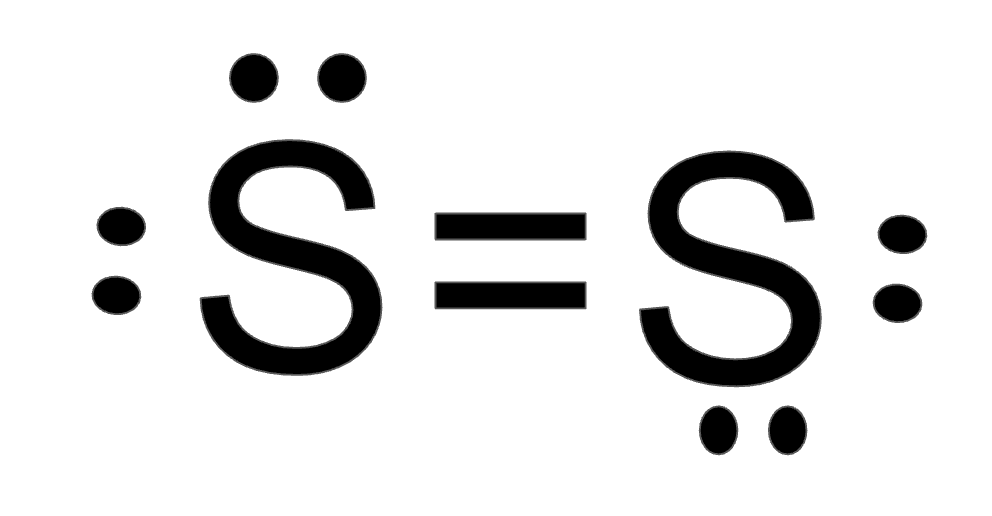
Fe
What are metallic bonds?
This bond is often described as one atom "transferring" valence electrons to another atom. This instructor prefers to describe it as one atom "stealing" valence electrons from another atom.
What is an Ionic Bond?
This subatomic particle determines the chemical reactivity of an element. This is because it is the particle with the least amount of mass, and thus is the easiest to move in between atoms or — in some cases — completely remove from the atom and place on a different atom.
What is the electron?
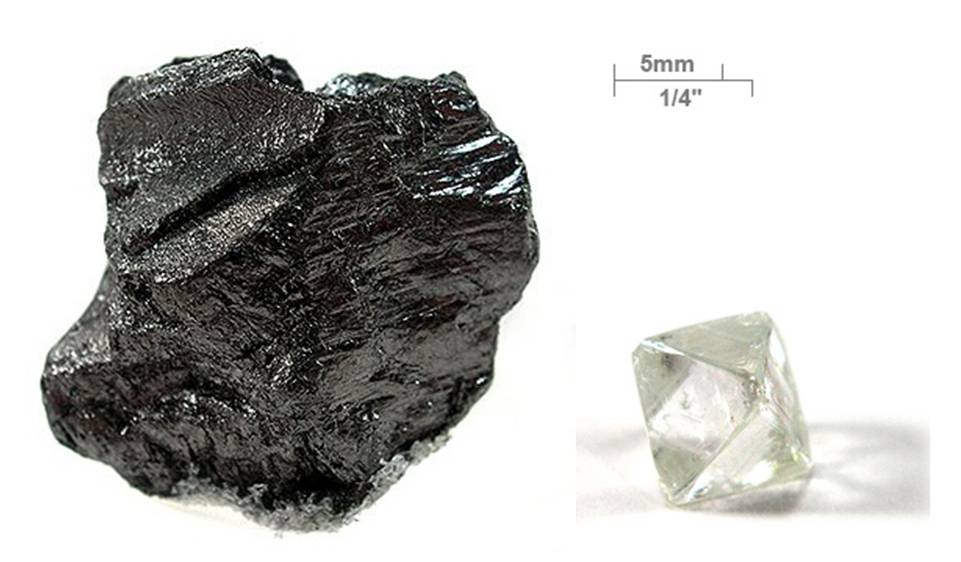


This element is the "backbone" of all organic life, and — as a result —is the main focus of collegiate "Organic Chemistry" class. Depending upon the geometric structure of its bonds, carbon can be a weak material like graphite (pencil "lead") or one of the world's strongest structures (diamond).
How many valence electrons does it have?
What are four valence electrons?
Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2)
What are three single bonds?
MgO
What are ionic bonds?
This bond is often described as atoms "sharing" valence electrons. More accurately, it is when valence electrons find themselves mutually attracted to two nuclei at the same time.
What is a Covalent Bond?
When considering isotopes of the same element — such as Uranium-238 or Uranium-235 — the number of this subatomic particle is what determines the difference in mass number.
What is the neutron?
When we breathe-in oxygen, it is usually in its diatomic molecular form (O2). How many valence electrons altogether do these oxygen atoms have?
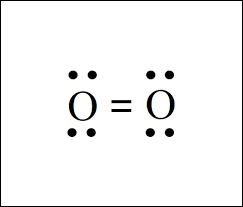
What are twelve valence electrons (six from one oxygen atom and six from the other oxygen atom).
Acetylene (C2H2)
HCl
What is a covalent bond?