This scoring system is used to assess levels of Hirsutism in PCOS.
What is the FERRIMAN-GALLWEY SCALE
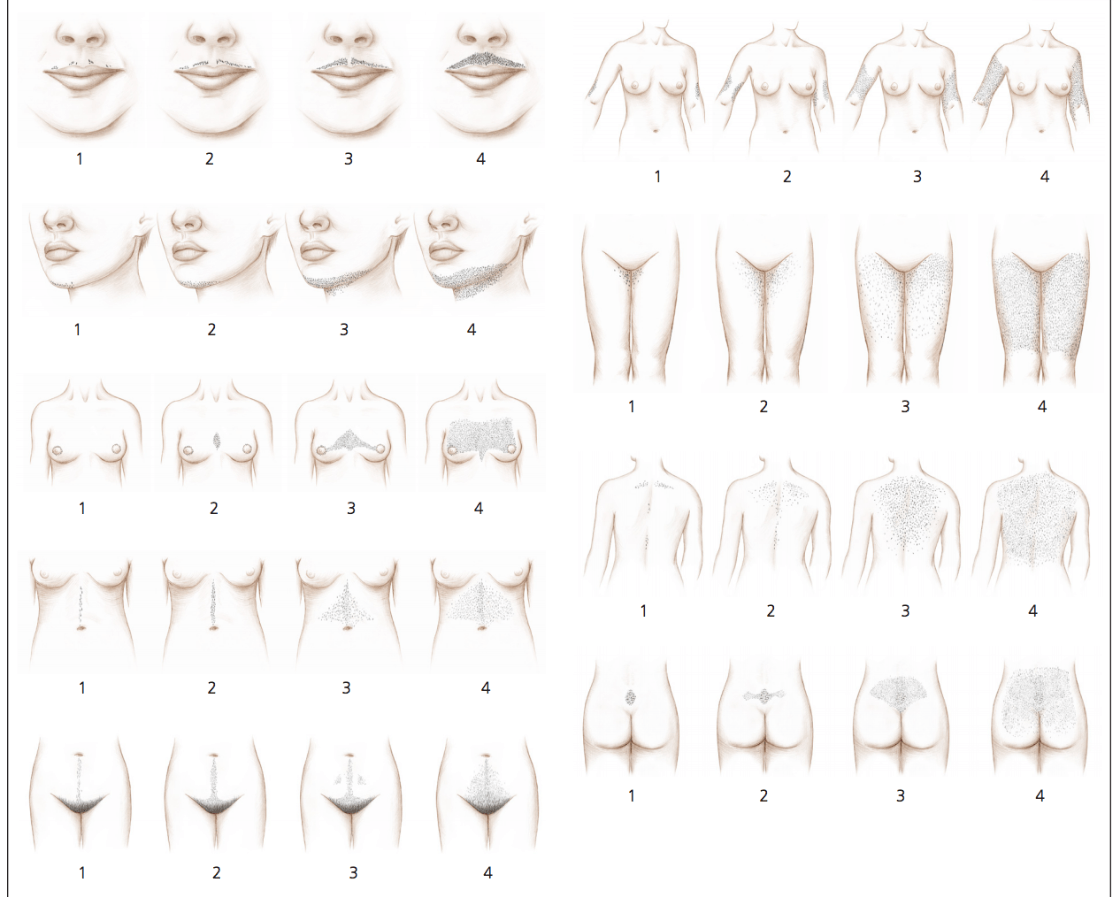
A score of 1 go 4 is given for 9 areas of the body.
The total score therefore can range from 0 to 36 with a score of ≥ 8 is considered hirsutism in CAUCASIAN women (<8 = normal)
Score of 8-15: mild hirsutism
Score of >15: moderate or severe hirsuitism
Score of 0: absence of terminal hair
Infants with this subtype of a neurologic condition presents at <6 months are often noted to be in frog-leg position on examination, with tongue fasciculations, a weak cry, and generalized hypotonia + muscle weakness
What is Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) Type 1 (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease)
- SMA results from atrophy of the anterior horn cells in the spinal cord
- 4 types: 1 - 4, with 1 being the most severe
- Type 1 has onset <6 months, Type 2: 7-18 months, etc...
- Mental function is typically preserved (appear very bright)
This complication of treatment is more commonly seen following intervention for polydactyly with a bony articulation compared to polydactyly with a soft tissue stalk
What is an AMPUTATION NEUROMA?
- The most important factor dictating intervention for supernumerary digits is the presence of a bony articulation of the digit with the remaining hand structure
- Postaxial polydactyly type A (additional digit at the MCP joint or CMC joint) may require orthopedic referral becuase of the increased risk of painful neuromas when using suture ligation. Thus sharp excision for postaxial polydactyly is now used: after identifying the accessory digital nerve, it is transected as far proximally as is safe to decrease the risk of neuroma, and then the divided nerve is covered with soft tissue
A 2-month-old female is started on this medication after she is noted to have several episodes of rhythmic flexor-extensor episodes of her neck, trunk, and arms lasting 2-3 seconds, in association with a progressive increase in difficulty with head control and developmental regression over the past few weeks
What is ACTH (aka Corticotropin)?
- This patient has clinical signs/symptoms of infantile spasms, which is often associated with developmental regression
- Other 1st line treatments include Vigabatrin, but ACTH has been shown more efficacy
A 4-year-old boy with sickle cell disease presents to the ED for his 3rd seizure in 4 months. He is initially post ictal and his neuro exam is concerning for a lack of withdrawal of the left upper extremity upon painful stimulation. After 24 hours, he is back to baseline, except that he is still unable to move his left upper extremity. A CT shows hypodensity in the right cerebral hemisphere. What vascular disease process is most likely responsible for his symptoms?
What is MOYA MOYA DISEASE
- Moya Moya is a chronic, progressive cerebrovascular disorder that is characterized by a network of abnormally dilated collateral vessels, formed in response to progressive stenosis in the terminal portions of the internal carotid arteries and their main branches
- Can present with stroke, TIA, a history of chronic headaches, or with new onset of seizures
- Trisomy 21, Tuberous sclerosis, sickle cell disease, collagen vascular disorders, and NF type 1 are all associated with this disorder
- Treatment is aimed at improving cerebral blood flow through neurosurgical revascularization
This aneuploidy syndrome characterized by an extra chromosome is associated with Cutis Aplasia Congenita
What is PATAU SYNDROME (TRISOMY 13)
- Cutis aplasia is a congenital focal absence of the skin in the scalp; usually involves both epidermis and dermis, and results from failure of ectodermal fusion. Often covered by a tense membrane that mimics a fluid-filled bulla. Lesions usually re-epithelialize over several months and form a hypertrophic or atrophic scar
- Usually isolated, but sometimes can be associated with T13
- Patau Syndrome is less common and more often associated with severe structural malformations than T21 or T18
- >75% of affected fetuses die in utero and <20% of newborns survive past a month of age
This nutrient deficiency is well known to be associated with neonatal seizures that are particularly resistant to treatment with conventional anticonvulsant therapy
What is VITAMIN B6 (Pyridoxine)
- Seizures in neonates who do not respond to conventional anticonvulsant therapy may be due to pyridoxine deficiency
- Infantile spasms may also occur
- Pyridoxine is required for the synthesis of GABA
- Can be given IV
This classic EEG pattern is seen with this form of epilepsy that often presents with brief episodes of seizures at night, characterized by twitching, numbness, or tingling of the face or tongue, speech difficulty, and sometimes also evolving into a generalized seizure
What is Centrotemporal sharp waves
- Benign Rolanding Epilepsy (BRE) typically starts in children between the ages of 6 and 8 y.o
- The majority of pts with BRE will outgrow the seizures by puberty
- Many physicians don't treat BRE with AEDs if the episodes are infrequent and occur only at night