Your DKA patient in the ICU has been improving with the fluids and insulin gtt that you have ordered for him. On his last ABG, his pH is 7.36 and his last renal shows an AG of 22, bicarb of 18 and glucose of 180. You correctly decide to do this for his insulin gtt (turn off or keep on) and add this additional gtt.
This condition commonly presents as poorly localized, progressive pain described as a deep aching with an insidious onset. Pain is also frequently worse at night and in cold weather. In addition to pain, patients with this condition frequently have decreased shoulder mobility as the disease progresses.
Adhesive capsulitis
Conditions that can lead to this include diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, previous surgery or trauma, prolonged immobilization, autoimmune disorders, and stroke.
Name this condition.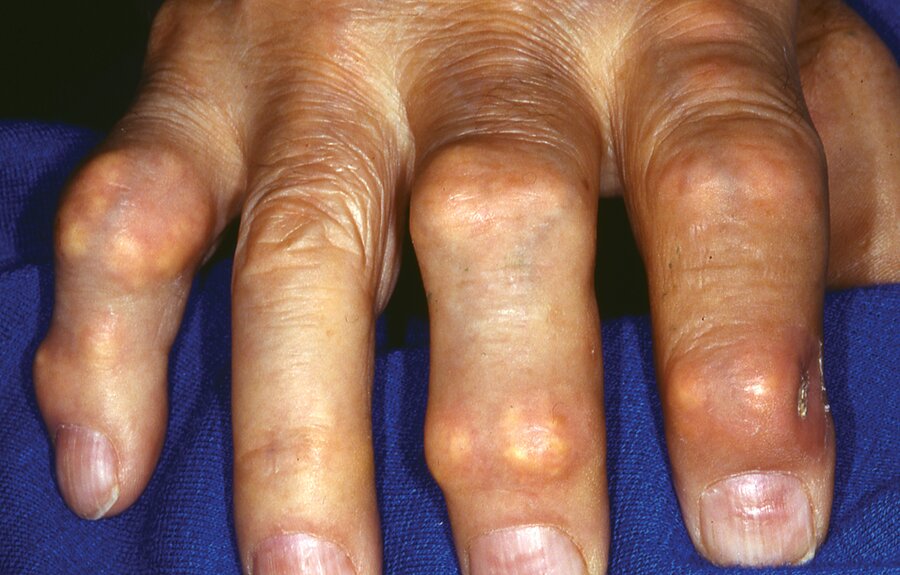
Tophaceous gout (will accept tophi or gout)
Medication given prior to endoscopy to improve gastric visualization of an upper GI bleed and decreases the need for repeat endoscopy
IV erythromycin
Most common virus in viral meningitis
Enterovirus
At what size do you consider surgical repair of an ascending aortic aneurysm
5.5 cm or larger (or rapid growth: > 0.5 cm/year, or > 0.3 cm/year over 2 years)
In patients with sarcoidosis, PTH will be this (high/low/normal) and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D will be this (high/low).
Low and low
Granulomatous diseases, such as sarcoidosis, cause hypercalcemia through increased 1-α-hydroxylation activity that increases 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels and calcium reabsorption.
This medication, should be used alone or in combination with nicotine replacement therapy for patients with nicotine dependence after a recent cardiac event.
Varenicline is the most effective monotherapy for smoking cessation and should be considered in smokers with a recent cardiac event.
Name an anti-hypertensive medication that has a uricosuric effect
Losartan or dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker
CT finding of the pancreas in autoimmune pancreatitis
“Sausage-shaped” pancreas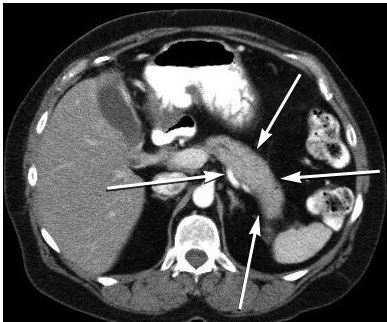
Indications for treatment of asymptomatic bacteruria
Pregnant patients
Patients scheduled to undergo an invasive procedure involving the urinary tract
Name 3 antihypertensives that can be safely administered during pregnancy
Labetalol, nifedipine, methyldopa, hydralazine
These 2 medications are used to treat patients with suspected myxedema coma (give both medication names and in the correct order).
Intravenous hydrocortisone THEN thyroid hormones
This is first line therapy for patients with insomnia
Cognitive behavioral therapy
CBT which combines components of sleep hygiene with cognitive therapy and behavioral interventions, is first-line therapy for insomnia.
The combination of these two antibodies has the greatest specificity for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor
Treatment for post-Lyme disease syndrome (characterized by persistent fatigue, arthralgia, myalgia, and impairment of memory or cognition)
Reassurance
Name 3 first line therapy medications for stable angina
Aspirin, statin, beta blocker
Patients with primary adrenal failure require treatment with these two drug classes.
Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid replacement therapy.
An example of appropriate regimen is hydrocortisone twice daily and fludrocortisone once daily
A 65-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-month history of an ulcer on the left lower leg that will not heal. This is the diagnosis and treatment for the below image:
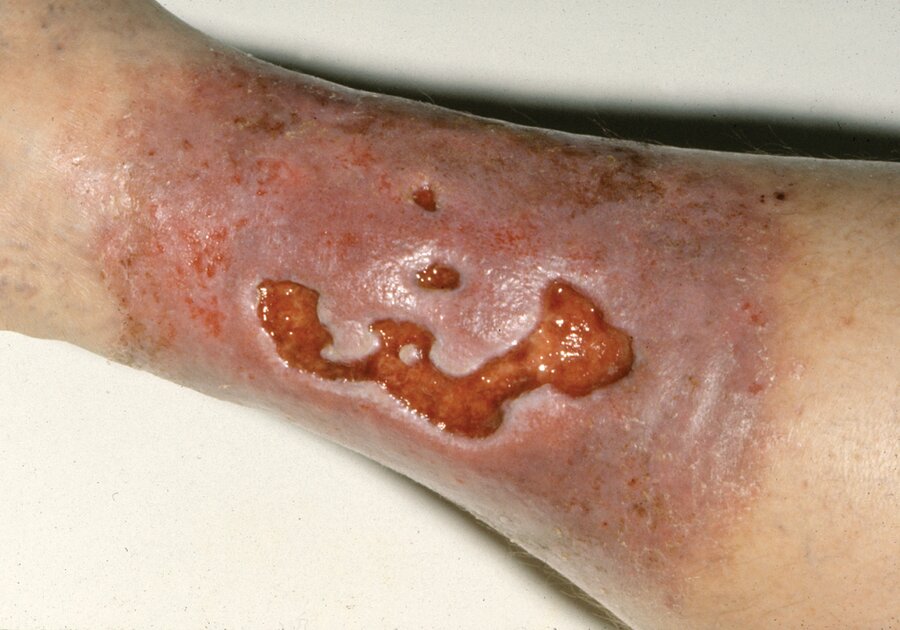
Venous stasis ulcer, compression therapy (will accept leg elevation)
Name one of the 1st line treatments for achalasia (be specific)
Pneumatic balloon dilation
POEM
Surgical myotomy
Botulinum toxin (more frequent relapses than the other 3 – for poor surgical candidates)
Antifungal agent of choice for patients with histoplasmosis WITHOUT severe lung disease/disseminated infection
Itraconazole
Acute pericarditis is diagnosed by 2 of 4 criteria. Name 2 of the criteria
Typical chest pain
Pericardial friction rub
New EKG changes
New pericardial effusion
To screen for Cushing syndrome, biochemical evidence of hypercortisolism must by one of these 3 tests (name all 3).
1-mg dexamethasone suppression test, 24-hour urine free cortisol testing, and/or measurement of evening salivary cortisol levels.
This is the diagnosis for a 46-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-month history of right anterior knee swelling. The swelling began insidiously and has gradually worsened. It is now the size of a golf ball and interferes with his ability to kneel, which is vital to his job as a carpet layer.
Both acute and chronic prepatellar bursitis can be caused by repetitive trauma, infection, or gout; fluid aspiration and subsequent analysis should be performed in all patients.
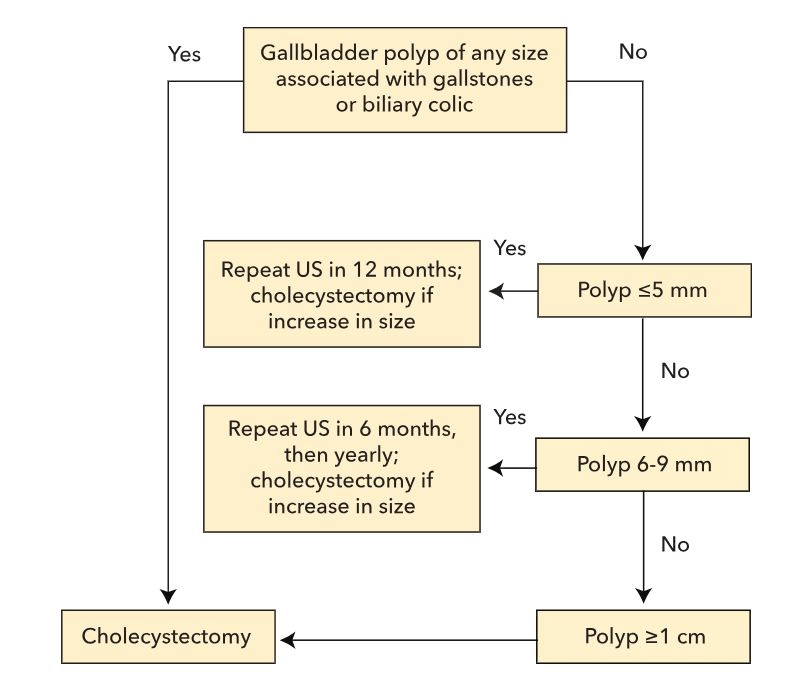
Treatment/surveillance for asymptomatic gallbladder polyp >1cm
Cholecystectomy
First line treatment for latent TB
Rifapentine + Isoniazid for 3 months
Rifampin + Isoniazid for 3 months
Rifampin daily for 4 months
Frequency of PVCs, even if asymptomatic, that require treatment
>10% of all beats or 10,000 PVCs per day