HR > 90; Temp > 100.9 F; RR > 20; suspected or confirmed infection
What is SIRS criteria?
Condition characterized by:
- Increased confusion and disorientation at night.
What is sundowner's syndrome?
Temporary delivery device for patient that is not oxygenating well and showing signs of respiratory distress.
What is a non-rebreather mask?
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) corrects what metabolic state.
What is acidosis?
When vital signs need to be obtained.
What is prior to unit pick up, at start, first 15 minutes, hourly and upon completion?
Use of external incontinence devices; no dependent loops; daily necessity review; q shift catheter care; securing catheter with Statlock
What is the CAUTI bundle?
Two assessments that must be completed when CT of the Head is ordered.
What is: NIHSS and Dysphagia screening?
Objective assessment findings:
Bronchial breath sounds in affected area. Dull sound to percussion.
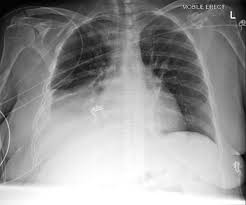
What is pneumonia?
What is potassium?
Patient has a known history of transfusion reaction. Name a drug you may anticipate administering prior?
What is: Benadryl, Tylenol, or Steroids?
History of diarrhea or abx usage. The stool must be collected within 3 days of admission. If positive, Transmission based contact enteric precautions. Requires terminal cleaning upon discharge. Hand washing with soap and water. Bleach wipes only.
What is the C. Diff Protocol?
Name this condition that may be normal:
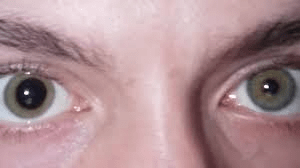
What is anisocoria?
Abnormal retention of air in the lung where it can’t be expelled completely. Can be seen in patients with hx of asthma or COPD.
What is air trapping?
What are you correcting:
a rapid infusion of intravenous fluids, typically crystalloids like normal saline; blood products may also be administered alongside other resuscitation measures
What is hypovolemia?
Condition caused when transfusing too rapidly.
What is TACO? (Transfusion Associated Circulatory Overload)
Oval shaped flat bodies with short broad heads. 6-10mm long, brown and wingless. Bite at night, usually on exposed areas. Requires contact isolation, thorough vacumming, disinfection of all surfaces, removal of all bed linens and patient clothing. Contact EVS.
What are bed bugs?
Which score evaluates eye opening, verbal response, and motor response.
What is the GCS (Glasgow Comma Scale)?
Objective assessment findings:
Absence of breath sounds on one side of chest; hypotension; heart sounds not in usual place for auscultation; tracheal deviation (late sign)
What is a tension pneumothorax?
High quality CPR and delivery of 100% oxygen corrects what.
What is hypoxemia?
Period of time to begin transfusion from pick up or to return to blood bank. (no cooler)
What is 30 minutes?
Fungal infection risk for patients that have been in a LTAC (within 90 days) or SNF (within 30 days).
What is Candida Auris?
The following modifiable factors could lead to which neurological condition:
Aspirin Use
Anticoagulant Use
Recent Falls
ETOH/Tobacco abuse
Uncontrolled HTN
What is an Intracranial Hemorrhage?
Intervention verification:
Deliver 5-6 breaths- looking for rise and fall of chest; color change of chemical capnography; no gurgling over epigastrium, imaging.
What is endotracheal tube placement?
What are you correcting with rapid core rewarming through methods like administering warmed intravenous fluids, using a warming blanket, and in severe cases, utilizing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) to provide circulatory support while rewarming the blood.
What is hypothermia?
Blood products would you anticipate administering when using a mass transfusion protocol.
What are FFP, PRBC, and PLT? (1:1:1)