Q: Yellow protein and lipid deposits in macular degeneration
Drusen
Only the muscarinic antagonist is FDA-approved for Asthma
A: Tiotropium bromide (accept tiotropium or Spiriva)
Q: Most common metal causing a type IV hypersensitivity reaction
Nikel
Q: Indication for shoulder imaging for rotator cuff injury
A: Suspected full-thickness rotator cuff tear (accept weakness)
Q: Resin found in poison ivy and mango peel that causes dermatitis
A: Urushiol
Q: Systemic disease most commonly associated with arteriovenous nicking

A: Hypertension (accept high blood pressure)
Q: Expected increase in the alveolar-arteriolar oxygen gradient for each decade of life
A: 1 mmHg
Q: Syndrome causing noninfectious fever and rash during the neutrophil recovery phase after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
A: Engraftement syndrome
Q: Immune-mediated condition associated with inflammation in cartilaginous structures
A: Relapsing polychondritis
Q: Initial medical therapy for patients with thrombocytosis-associated stroke
A: Aspirin and cytoreductive therapy (accept hydroxyurea, anagrelide, or pegylated interferon for cytoreductive therapy)
Q: Eye drop that causes blood vessel blanching in episcleritis used to differentiate it from scleritis
A: Phenylephrine (accept Neo-Synephrine)
Q: Imaging follow up for ≤ 5 mm solid pulmonary nodule in low risk patient
A: None
Q: Recommended treatment for nonallergic (vasomotor) rhinitis
A: Intranasal glucocorticoid or intranasal antihistamine spray (either; accept intranasal steroid or corticosteroid)
Q: Generic term describing disk space narrowing and arthritic changes of the facet joints
A: Spondylosis or spondyloarthritis
Q: Poisoning with this alcohol is associated with visual blurring, central scotomata, and blindness
A: Methanol
Q: Medical term for this finding
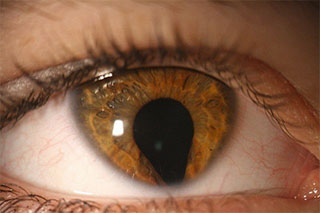
Iris coloboma (accept coloboma)
Q: Most common CT finding associated with pulmonary adenocarcinoma-in-situ
Ground-glass opacification (accept ground-glass nodule or subsolid nodule)
Q: Characteristic endoscopic appearance of eosinophilic esophagitis
A: Stacked circular rings (accept linear furrows or attenuation of normal vascular pattern)
Q: Deposition disease associated with familial Mediterranean fever
A: AA amyloidosis (accept amyloidosis)
Q: Antidote for methanol poisoning
A: Fomepizole (accept ethanol)
Q: Class of medication associated with floppy iris syndrome complicating cataract surgery
A: Alpha-1-antagonists
Q: Eponym for an area of increased lucency on x-ray suggestive of pulmonary embolism
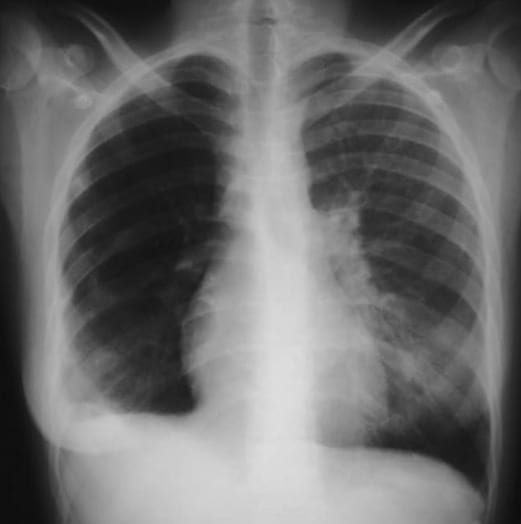
A: Westermark sign
Q: Most common gastrointestinal infection associated with IgA deficiency
Giardiasis
Q: The most common myositis-specific autoantibody directed against aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) synthetases
A: Anti-Jo-1 antibody
Q: Syndrome characterized by chronic collapse of the right middle lobe
A: Middle lobe syndrome (accept right middle lobe syndrome; Lady Windermere syndrome)