In the diagram what is the optimal temperature for the enzyme sucrase?
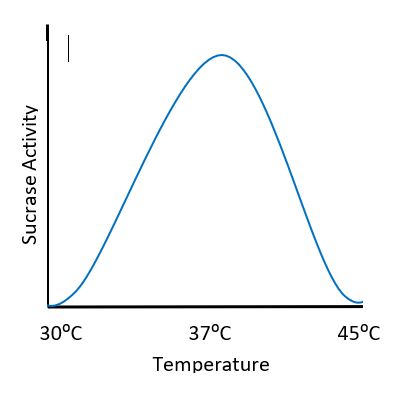
37 degrees C
In a hypotonic solution, this occurs to Animal cells.
Lysis (burst)
White Blood cells engulf bacteria through this process.
Phagocytosis (Endocytosis)
Define Homeostasis.
When the external environment changes, your internal environment remains relatively constant.
Which of the following is an example of negative feedback?
A. Flipping a switch turns on a light.
B. Turning on the lights increases the rate of plant growth.
C. Turning up a dial on the oven increases the temperature.
D. The thermostat shuts off the furnace as the room temperature reaches 20°C.
D. The thermostat shuts off the furnace as the room temperature reaches 20°C.
Every chemical reaction in your body requires an enzyme to lower this.
Energy of Activation
A cell would tend to gain water if it were moved from
A. an isotonic solution to a hypotonic solution.
B. an isotonic solution to a hypertonic solution.
C. a hypotonic solution to an isotonic solution.
D. a hypotonic solution to a hypertonic solution.
A. an Isotonic Solution to a hypotonic solution
This macromolecule acts as a carrier molecule for facilitated diffusion and catalyzes chemical reactions.
Protein
Blood vessels dilating, due to high body temperature is an example of
Negative Feedback
It is _____________ that holds the cell firm and provides the characteristic shape of plant structures such as leaves.
Turgor Pressure.
This type of Inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme so that the substrate can't bind.
Competitive Inhibitor
The cytoplasmic concentration of solute in a cell is 0.05%. This cell is placed in a solution that causes the cell to swell and burst. The solute concentration of this solution is
A.0.005% B.0.05% C.0.5% D.5.0%
A. 0.005%
Bulk Secretion of neurotransmitters out of the cell is an example of
Exocytosis
This is an example of a positive feedback mechanism in homeostasis?
milk production in the mammary glands
or
Contractions in child birth
Set of metabolic pathways that break larger molecules into smaller ones.
Catabolic pathways/reactions
When the product of a reaction binds to the active site of an enzyme as negative feedback this an example of...
Allosteric properties of an enzyme
This a factor that affects diffusion rate across a cell membrane
temperature, surface area, concentration gradient, charge of molecules, or size of molecules...etc.
This is the movement of material across the membrane against its concentration gradient. (low to high)
Active Transport
The Homeostatic control center in the brain that receives messages from sensors to initiate a nervous/hormone response.
Hypothalamus
Why would drugs like penicillin destroy bacteria but have no effect on human cells?
A. Human enzymes would be denatured by penicillin.
B. Bacterial cells would use penicillin as a coenzyme.
C. Penicillin would fit the active site of bacterial enzymes.
D. Enzymes in human cells would use penicillin to produce excess energy.
C. Penicillin would fit the active site of bacterial enzymes.
This graph shows a reaction for a specific enzyme. What has occurred between point B and C
Enzyme is Saturated
Describe the process of reverse osmosis.
Which of the following will be affected directly if the mitochondria in a cell are not functioning properly?
A. Absorption of alcohol by the cell.
B. The movement of water into and out of the cell.
C. The movement of oxygen across the cell membrane.
D. The movement of sugar from a low to a high concentration.
D. The movement of sugar from a low to a high concentration.
What happens when blood sugar levels become too high?
A. Insulin is secreted, causing the conversion of glucose to glycogen.
B. Glucagon is secreted, causing the conversion of glucose to glycogen
C. Insulin is secreted, causing the conversion of glycogen to glucose.
A. Insulin is secreted, causing the conversion of glucose to glycogen.
This is a portion of some enzymes that help activate the enzyme and are composed of metal ions(minerals like Zn, Fe, Ca)
Cofactors