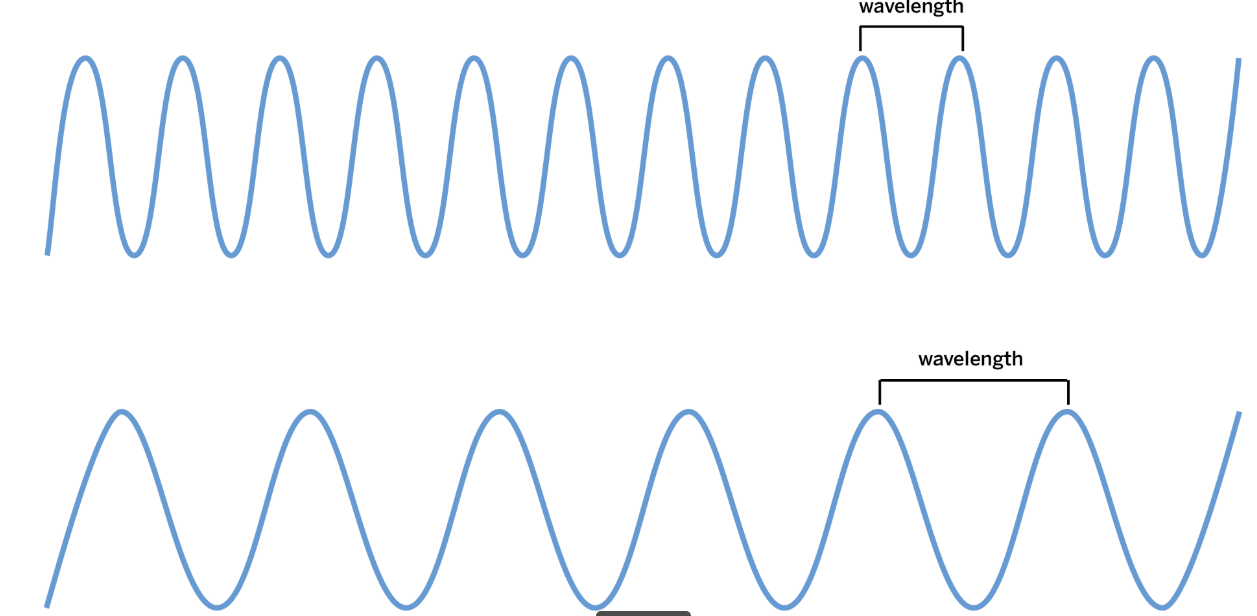
What is the distance between one crest and the next crest called?
Wavelength
What do we call light bouncing off a mirror?
Reflection
Which type of light has the shortest wavelength: UV, visible, or infrared?
Ultraviolet (UV)
What happens to wave energy when amplitude increases?
Energy increases
Can sound travel through space?
No, sound needs matter to travel.
Which wave property determines how much energy a wave carries?
Amplitude
Why does a straw look bent when placed in a glass of water?
Light is refracted as it moves between air and water.
Which colors of visible light are most important for photosynthesis?
Red and blue light
Why does sound get quieter as you move farther from the source?
The amplitude of the sound wave decreases over distance.
Can light travel through space?
Yes, light does not require a medium.
If a wave’s amplitude increases, what happens to the energy it carries?
Energy increases
Why does black paper heat up more than white paper in sunlight?
Black absorbs more light energy.
Which type of light from the sun is most likely to cause skin damage?
Ultraviolet (UV)
Why is a book dropped from a higher height louder than a book dropped from a lower height?
It has more potential energy, which becomes more sound energy.
Why must astronauts use radios to talk to each other in space?
Sound cannot travel in a vacuum.
Wave A has a shorter wavelength than Wave B. Which wave carries more energy?
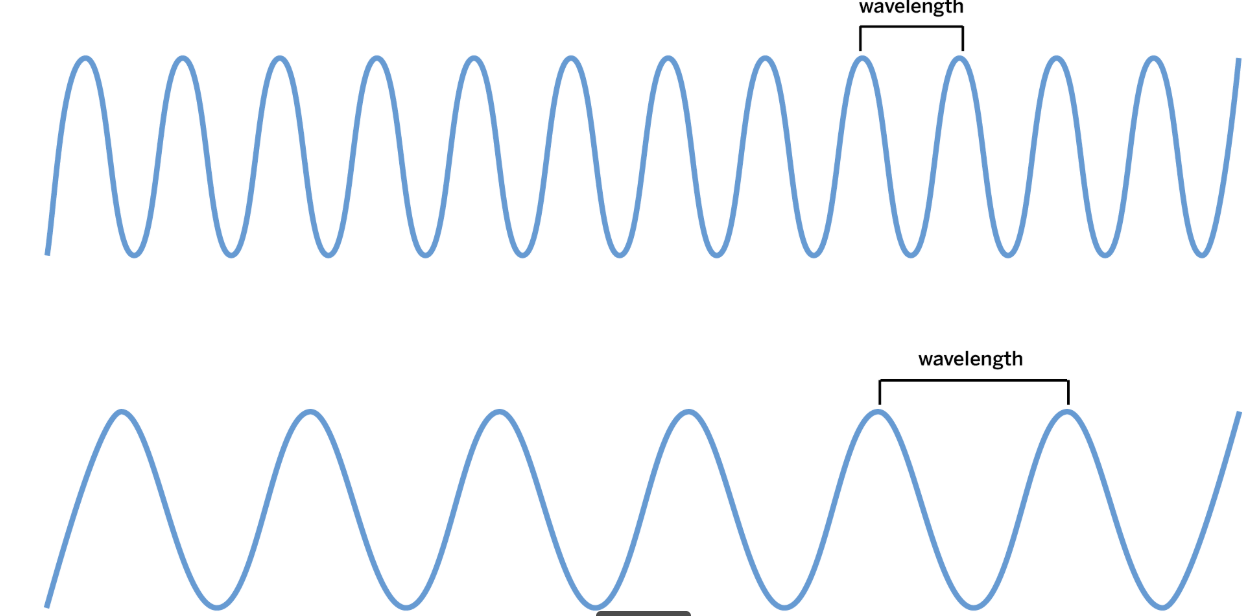
Wave A (the top one)
What happens to light energy when a material absorbs it?
The material gains energy (often as warmth or change).
Why can we see visible light but not infrared or radio waves?
Human eyes detect only visible wavelengths.
Which wave property determines pitch(high sound) in sound?
frequency (dog whistle example)
Why can we see an explosion in space but not hear it?
Light travels through space, but sound does not.
Why does changing wavelength in the Light Wave Simulation change the type of light produced?
Different wavelengths correspond to different types of light, and shorter wavelengths have more energy.
Why can ultraviolet light damage genetic material while infrared light cannot?
Ultraviolet light has shorter wavelength and higher energy, which can break down molecules.
Why can’t a household light bulb cause skin cancer?
It emits visible and infrared light only, not ultraviolet light.
Why does amplitude decrease with distance while wavelength stays the same?
Energy spreads out over distance, but wavelength is a fixed property of the wave.
Why can’t compression waves form in space?
There is no matter to compress and move.