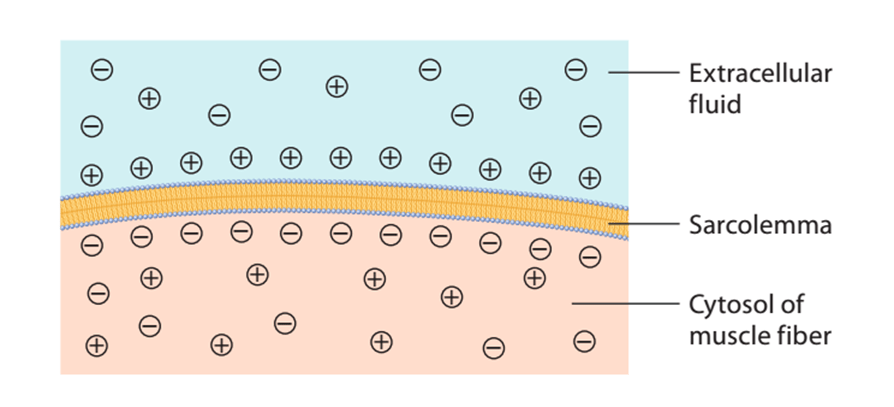
What creates the electrochemical gradient?
The seperation of charges across the plasma membrane
What are the words used to describe skeletal muscle tone that is abnoamally low or abnormally high?
Hypotonia - Abnormally low
Hypertonia - Abnormally high
BONUS: Which one is typically due to a nervous system disorder?
What are the clusters of neurons and the clusters of axons called in the CNS and PNS? (I am looking for
CNS neurons- Nuclei
PNS neurons- Ganglia
CNS axons - Tracts
PNS axons - Nerves
Does myelin increase or decrease the speed of an action potential?
Increase
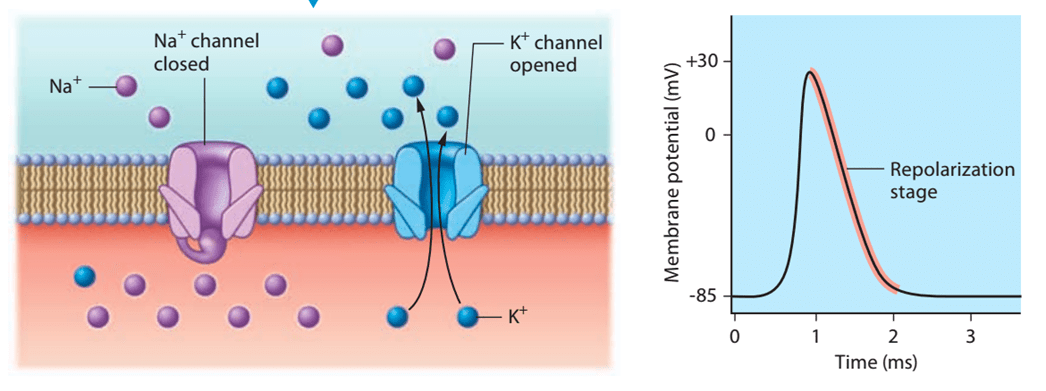
Explain everything you know about the repolarization stage of an action potential
• Na+ channels close
• Voltage-Gated K+ channels open and K+ leaves the cell
• The membrane potential is now more negative again
• This marks the end of the action potential
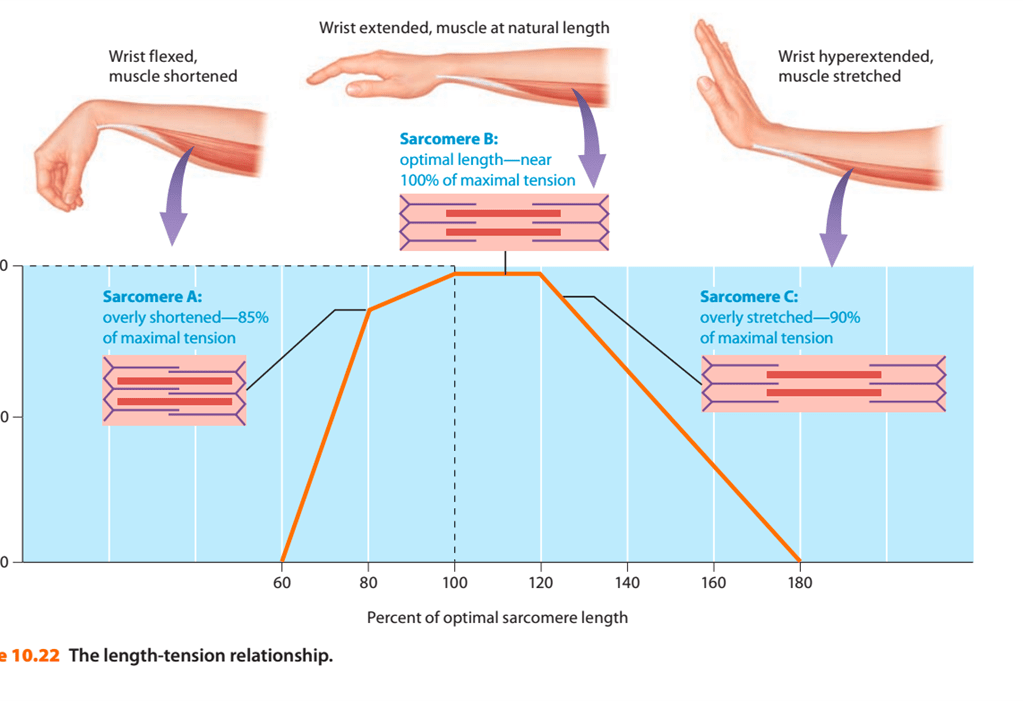
What is the length-tension relationship?
The number of crossbridges that can form within each sarcomere. The LTR is a factor that determines the amount of tension produced by a twitch contraction.
BONUS: What is a muscles optimal length?
Draw a neuron and label the dendrites, axon hillock, myelin sheath, Node of Ranvier, axon terminals, and axon collateral.
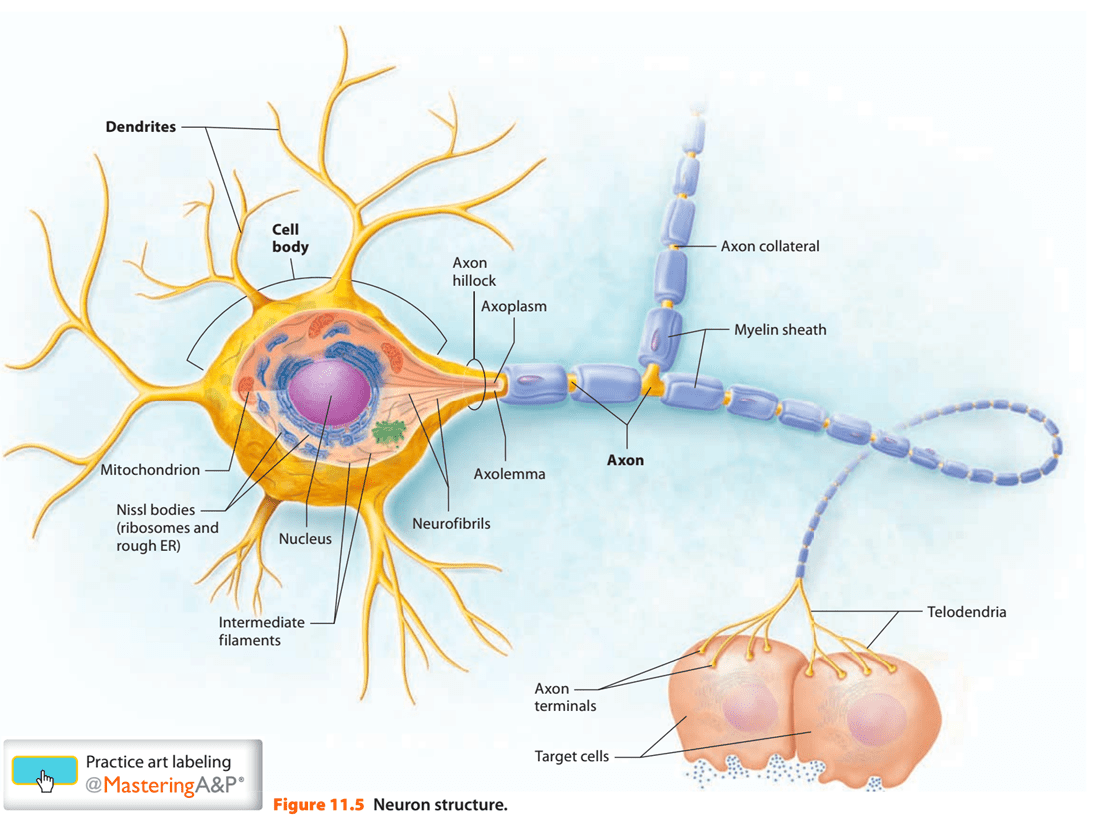
Which one of these structures gets pruned as they grow to accomodate for nervous system changes?
What are the four types of glial cells in the CNS?
1. Ependymal Cells
2. Astrocytes
3. Oligodendrocytes
4. Microglia
BONUS: Which type of glial cell is most abundant in the CNS?
Label two numbers of your choosing.

1. Epimysium
2. Fascicle
3. Perimysium
4. Endomysium
5. Myofibrils
BONUS: What is the structure between 4. and 5.?
Which type of tetanus is worse for the respiratory muscles and why?
Fused tetanus. In fused tetanus, the muscle contractions are continuous and do not allow for any relaxation. This can severely impair the ability of the respiratory muscles to function properly which can lead to significant breathing difficulties and even respiratory failure.
Damage to astrocytes has been seen in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. What specific symptoms might someone display if their astrocytes are damaged?
Blood vessels and neurons may become un-anchored which will disrupt the transport of nutrients and gases from blood vessels to neurons
There will be an excess buildup of extracellular K+ ions and neurotransmitters
The BBB will become more pourous due to dysregulation of tight junctions
Brain injury will not heal as rapidly, if at all
In which nervous system can nervous tissue regenerate?
The PNS
Draw out a motor end plate.
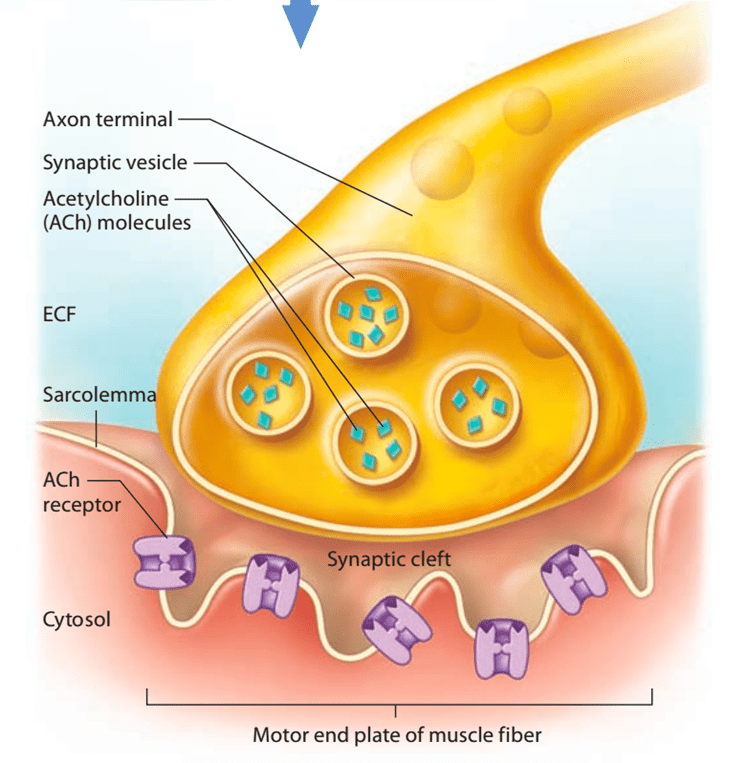
BONUS: What is the ligand in this picture?
Describe the zone of overlap when the wrist is hyperextended.
Long sarcomeres, very small zones of overlap
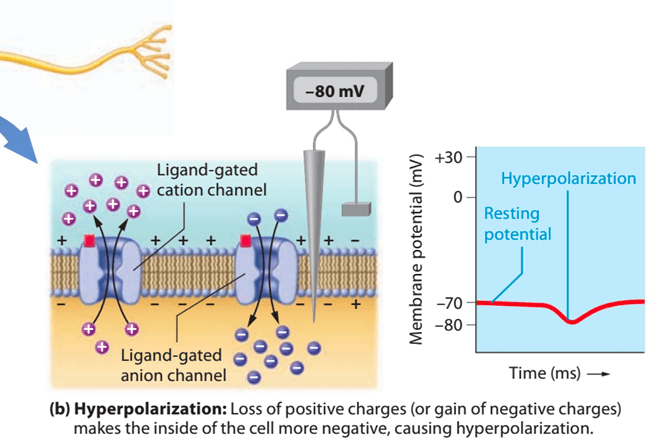
What is hyperpolarization and how does it relate to the action potential in a neuronal cell?
As the outflux of K+ ions continues after repolarization, it causes the membrane potential to become even more negative than the resting potential. It typically occurs because the K+ channels close slower than the Na+ channels
Draw out a sarcomere.
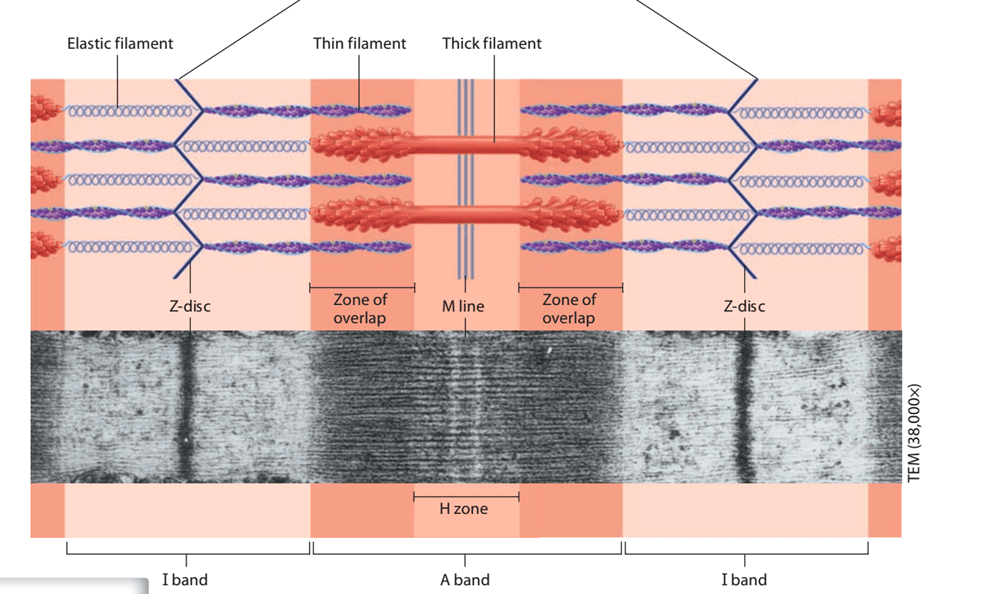
BONUS: How does the sarcomere change when muscle contraction occurs?
BONUSSS: In which part of the sarcomere are only thick filmants found?
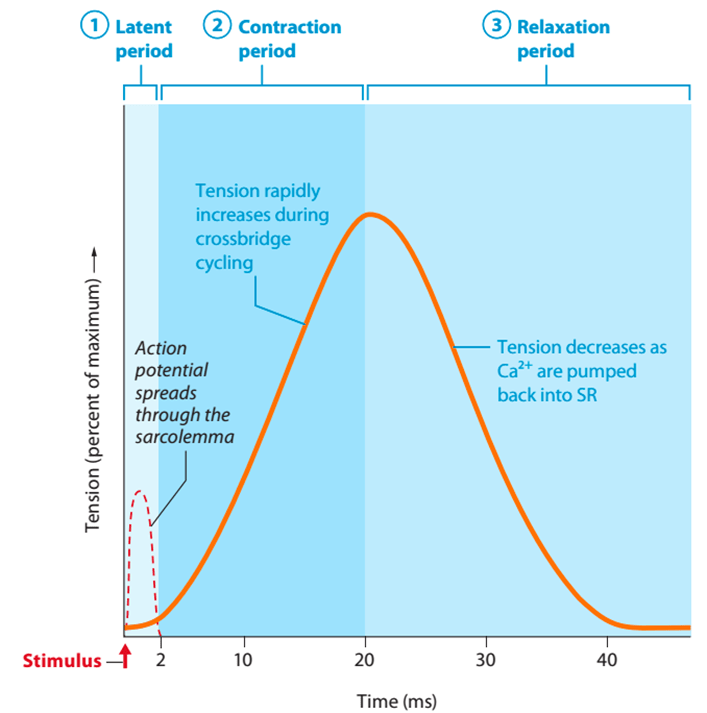
What are the three periods of twitch contraction and how long do they typically last?
Describe the three states of voltage-gated Na+ channels.
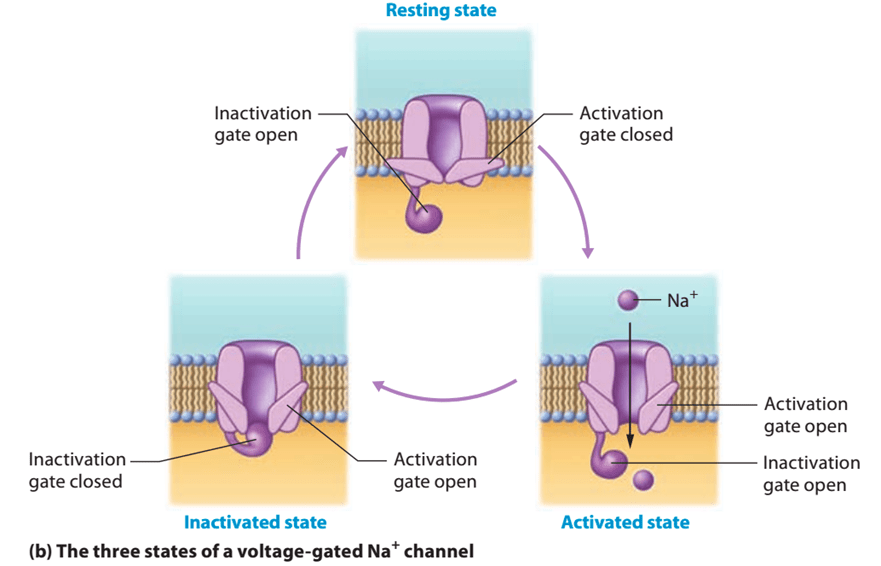
How are these states different from a voltage-gated K+ channel.