Definition of Inductive Reasoning
What is noticing patterns in data and making a conjecture (conclusion/idea)
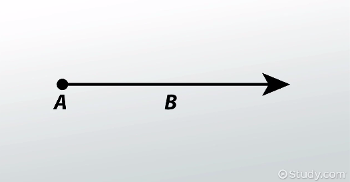
Definition of a line
What is a line is a straight path that goes on forever in both directions.
What is the definition of reflection
What is a type of geometrical transformation, where an object is flipped to create a mirror or congruent image.
What is the definition of Scalene Triangle

What is a triangle in which all three sides are in different lengths, and all three angles are of different measures.
What is the definition of an isosceles trapezoid?

What is a trapezoid where the two non-parallel sides are equal in length
What is the inverse of this statement If it rains, then they cancel school?
What is if it does not rain, then they do not cancel school.
How many endpoints are there on a Ray
what is one endpoint
What type of transformation is this? 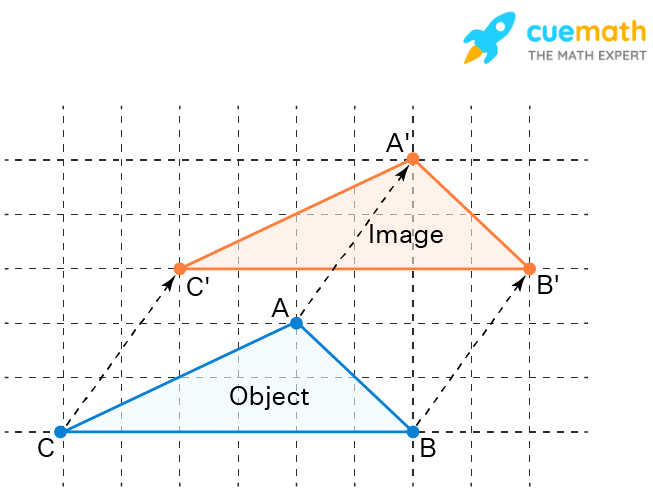
What is translation.
What are three classifications for triangles based on their sides?
What is equilateral (all sides equal), isosceles (two sides equal), and scalene (no sides equal)
Complete the Statement with sometimes, never, or always
A rectangle is _____ a square
What is Sometimes
What is the converse of this statement If it is raining, then the ground is wet?
What is If the ground is wet, then it is raining.
These are all lines: True or False

What is true
What are 4 main transformations in Geometry?
What is translation (sliding), rotation (turning), reflection (flipping), and dilation (enlarging or shrinking).
Which triangle congruence conjecture states that
if all three sides of one triangle are congruent to the corresponding three sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
What is SSS
In rectangle BEAR, diagonal BA is a line that bisects angel B and angle A. Line ER bisects angle E and angle R. Given this information, which of the following is the best classification of quadrilateral BEAR
A) Rectangle
B) Rhombus
C) Kite
D) Square
What is D) square
Indicate what type of statement this is after it is changed (inverse, converse, or contrapositive)
Original: If it is raining, then the grass is wet.
Changed: If the grass is not wet, then it is not raining
What is a contrapositive statement
What are 3 examples of parallel lines? Please draw a picture of each example of parallel lines.
What is corresponding, alternate, and co-interior

Describe the movement of a polygon that is transformed according to the rule (x,y) to (x+2,y-7)
What is right 2 down 7
Find the value of x.

What is 55 degrees
What are the characteristics of a rectangle?
Four right angles: Each corner of a rectangle is a right angle (90 degrees).
Parallel opposite sides: Opposite sides of a rectangle are parallel to each other.
Equal opposite sides: Opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
Diagonal properties: The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other and are equal in length.
What is the Inverse and Contrapositive of this statement?
If I get good grades, then Mrs. Lorentz will be happy.
What is
Inverse: If I do not get good grades, then Mrs. Lorentz will not be happy.
Contrapositive: If Mrs. Lorentz is not happy, then I did not get good grades.
Find the midpoint of the segment with these endpoints (use midpoint formula) (9,7) (1,1)
What is (5,4)
How can you determine if two shapes are congruent after a series of transformations?
What is if all corresponding sides and angles align perfectly after the transformations, then the shapes are congruent.


Please give a two-column proof. One column is statement and the other is reason. There are 4 proofs in total

What is this shape and what are the characteristics of it?

What is Rhombus
Characteristics:
- Equal sides: All four sides of a rhombus are the same length.
- Parallel opposite sides: Opposite sides are parallel to each other.
- Equal opposite angles: Opposite angles are equal in measure.
- Perpendicular diagonals: The diagonals of a rhombus intersect at a 90-degree angle.
- Diagonal angle bisectors: Each diagonal bisects the pair of opposite angles it crosses.