hot fluid or semifluid material below or within the earth's crust from which lava and other igneous rock is formed on cooling.
Magma
A _______ Scale measures the amount of energy released by an earthquake
Richter
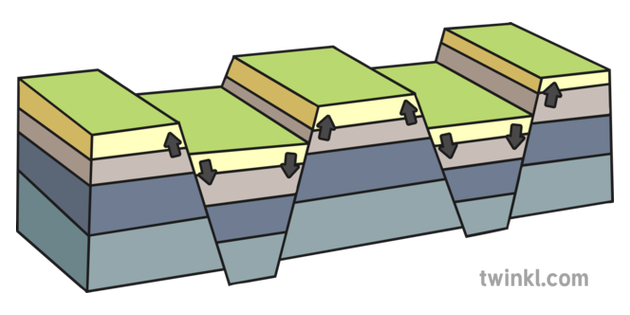
Fault block
Seismic Wave
an elastic wave in the earth produced by an earthquake or other means.
cracks in the earth's crust and lithosphere
faults
A _____ Scale measures the effects of the earthquake
Mercali Intensity

Folded Complex Mountain
Plate Tectonics
a theory explaining the structure of the earth's crust and many associated phenomena as resulting from the interaction of rigid lithospheric plates which move slowly over the underlying mantle
the point on the earth's surface vertically above the focus of an earthquake.
epic center
The _____contains over 1/2 of the world's volcanoes
Pacific Ring Of Fire

Upwarped mountains
Earthquake
a sudden and violent shaking of the ground, sometimes causing great destruction, as a result of movements within the earth's crust or volcanic action.
waves that travel fast , move through solid and liquid layers of earth, and pull and push rock creating a back and forth motion
____ are volcanoes that have very steep sides
Cindercone

Volcanic mountains
Lava
. hot molten or semifluid rock erupted from a volcano or fissure, or solid rock resulting from cooling of this:
waves that travel slower than p waves, only moves through solid rock, and moves at right angels to primary waves causing works to move up and down and side to side
Secondary waves
The volcano which has the most violent eruption type is _____
Composite Volcano

Composite Volcano
P wave
a longitudinal earthquake wave that travels through the interior of the earth and is usually the first conspicuous wave to be recorded by a seismograph.