What are two medical diagnoses/patient histories that might put the patient at high risk for violence?
History of violence
Drug/alcohol misuse
Psychiatric illnesses: schizophrenia, personality disorders, mania, depression with psychosis
Dementia/Cognitive Impairment
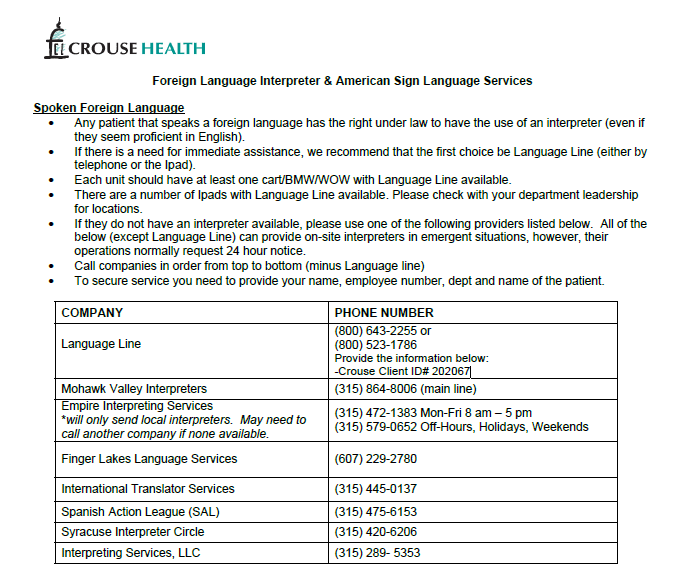
You are taking care of a patient who speaks Spanish and needs a translator. What do you do?
Sensory Diminished/Loss & Limited English Proficient Persons Services(P0226)
Language Line via iPad or Phone-call nursing supervisor to obtain. Document interpreter ID # in assessment.
A patient is starting to raise his voice and swearing at you. You try to leave the room, but he corners you while yelling about wanting his pain meds. What do you do?
Abusive Patients and/or Visitors - Patient and Visitor Conduct Contract (P1294)
•Scope of Workplace Violence in Healthcare setting: Use of force, behavior that diminishes dignity of others, threats from staff, patients, visitors
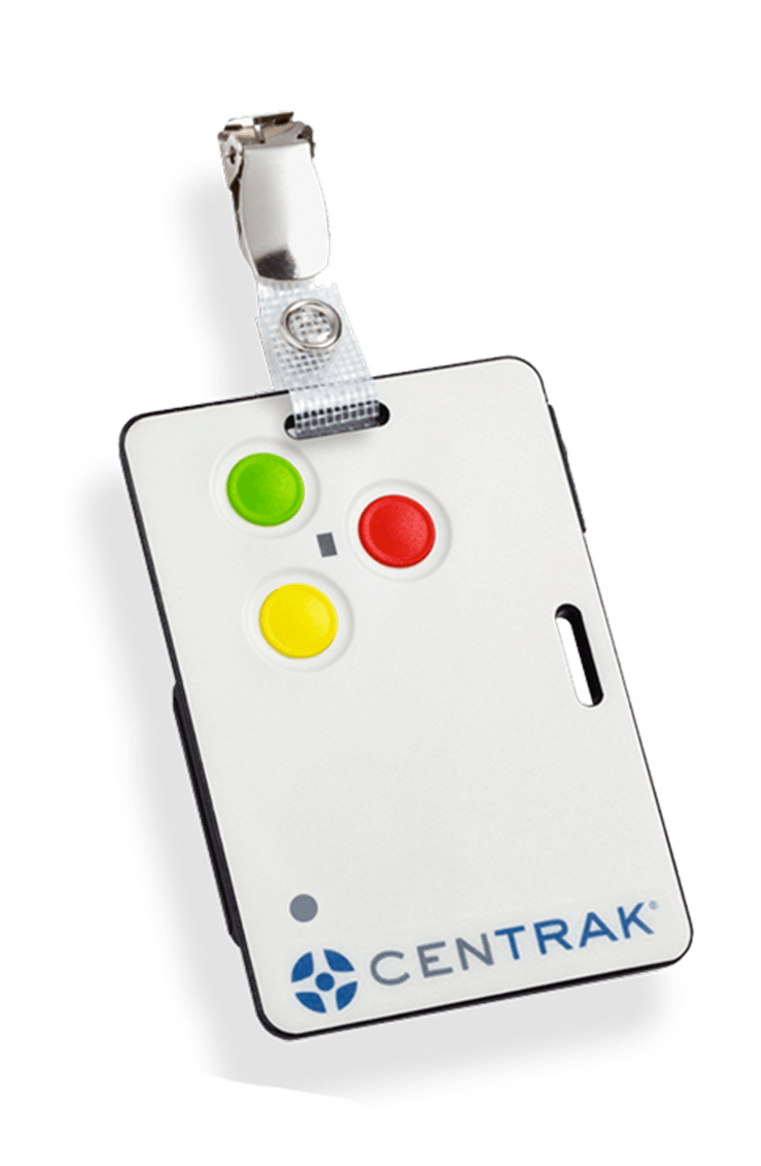
• Call for help and utilize duress badge
•Complete an occurrence report on the incident as well as employee injury if injury has occurred.
•Monday-Friday during the day: contact immediate supervisor
•Off-shifts, weekends, holidays: immediate supervisor or Administrative Nursing Supervisor

Change in Patient Condition?
Who to notify?
Condition Change: Report to Attending Physician or Designee (P1094)
•Rapid response team (RRT) or notifying provider
•Ext. 7555
•Updated set of vitals
•Reminder as a bedside nurse to stay with patient (patient history)
Patient is Suicidal
Safety Watch, Security Watch and Suicide Watch (Also Includes Violence, Homicidal and Detoxification Concerns) (P0696)
Notify charge, nursing supervisor, and provider
Place patient on 1:1
Psych evaluation to be determined by provider
Documentation: 1:1 Safety Watch Observation Chapter and Safe Environment Risk Assessment
Assigned 1:1 will stay arm’s length away from the patient at all times including toileting and bathing
Ensure breaks for the 1:1 coverage as needed
Give two reasons why a patient may need continuous oximetry monitoring?
Patients who a Registered Nurse or Respiratory Therapist assess as being in need of monitoring for ventilation or respiratory status
Patients with a provider order for continuous oximetry
Post-operative patients who received general anesthesia or sedation for the first 24 hours or for outpatients until discharge criteria is met
Patients who are using PCA or receiving continuous narcotic infusion via PCA for duration of treatment and for 4 hours after the PCA or infusion has been discontinued
Patients receiving supplemental oxygen > 5 liters or > 50% FiO2
Patients with a tracheostomy
Patients with suspected sleep apnea
Patients with diagnosed sleep apnea with or without sleep disordered therapy devices
Masimo Patient SafetyNet Monitoring System for Pulse Oximetry (P1301)
Patient Falls: Provide three nursing interventions/things you could do?
Fall Protocol (P0602)
Call for Help! Send someone to notify the Charge Nurse* who in turn will place a call to the physician/designee who needs to come assess patient.
Do not move the patient. Make a mental note of how you found the patient (position, direction and the immediate environment) for your charting.
Assess the patient’s orientation and pain
Note any apparent abnormal physical findings (such as bleeding, reddened areas, obvious deformities or swelling).
Patients who cannot independently move from floor to bed should be placed on hover jack to be assisted back to bed.
RN/Provider completes spine assessment algorithm (neck/cervical pain)
If spinal immobilization is indicated in the med/surg areas contact ED/SWAT to assist with application and backboard if necessary.
Once immobilization is applied patient must be cleared of injury by MD prior to removal.
Family notification
Documentation:
An objective description of the entire incident (witnessed or not).
Include the time and position of the patient on the floor with a description of the immediate environment.
Occurrence report

Patient complains of chest pain and 24 hour order for telemetry is expiring. What do we need to do?
•Assess the pain, vital signs, reproducibility
•Notify charge nurse, and provider. Rapid response if necessary. Obtain EKG.
•Potential interventions provider will recommend:
-Nitroglycerin, Pain medications, Oxygen if needed
•Potential further testing: stress tests, echocardiogram, CTAs
•Could be non- cardiac anxiety related, GERD, stress
Telemetry Monitoring (P0264)
-Telemetry will need to be renewed by hospitalist
-24-hour telemetry orders will be discontinued by the nurse after 24 hours unless there are no new arrhythmias or worsening patient condition. (RN to call CCT prior to removal)
-48-hour telemetry orders will be discontinued or reordered after 48 hours by cardiology or primary team. Decisions are not made by off shift coverage. If expiring hour falls on night shift, it is to be addressed prior to day shift ending if possible or ASAP the morning after.
-Once patient has written discharge order telemetry can be removed.
Your patient wants to leave AMA. What do you do?
•AMA: Refusal of Service (P0848)
•Attempt to encourage the patient to stay and receive treatment/service
•Contact attending provider ASAP
•If refusing to wait for discharge plan/instructions, accept copy or sign paperwork, note on the form
•Discusses the risks of leaving the hospital and declining care
•Refusal of Services Form
•Signed by patient, two hospital personnel and placed in chart
•Legally, we cannot keep patients in the hospital against their will

Concerns for Safety: Danger to self/others (suicidal, homicidal, under the influence, altered mental status, etc)
•Psychiatric consult
•Leaving the unit: Security, Nursing Supervisor contacted along with Syracuse Police Department
•Legally, we cannot keep patients in the hospital against their will but do need to contact appropriate personnel.
Your patient has a PICC and a CBC and BMP is ordered for your patient. You go to draw the labs from the PICC and cannot get blood return. What do you do?
tPA: Tissue Plasminogen Activator (Alteplase) - Obstructed Catheters & Ports (P0511)
NEVER USE FORCE TO INSTILL FLUID
Declotting a CVAD/Midline Using One Syringe:
- Clamp CVAD and attach the syringe containing tPA – 1mg/ 1ml to the catheter hub.
- Hold tPA filled syringe vertically with the plunger end up.
- Unclamp catheter. Gently pull back on the plunger reaches the 8-9 ml mark and hold it to create negative pressure in the catheter. This will allow the evacuation of any substance in the catheter between the hub and the thrombus formation and will provide a clear pathway for the tPA to be instilled into the catheter.
- Slowly release the plunger and the negative pressure on the syringe; this will allow the tPA to be drawn into the catheter.
- Label catheter/port “TPA in lumen- DO NOT USE”, time and employee # using a red medication additive sticker to alert and allow tPA to remain in the catheter for 30 minutes.
- After the allotted time, attach empty, sterile 10 ml syringe and gently attempt to aspirate blood from lumen
- If no blood returns, allow the tPA to remain in catheter an additional 90 minutes (for a total of 120 minutes or 2 hours).
- If blood returns with aspiration into the empty 10 ml syringe: clamp catheter, discard syringe of blood and catheter contents, flush with 20mls of saline using pulse technique
- If catheter function is not restored after two doses, contact provider.
You go to assess your patient and give 1000 meds and the patient is nowhere to be found. What do you do?
Code Gray - Elopements (Missing Patients) (P0939)
Immediately notify the charge nurse who will contact the Administrative Supervisor and Security with a brief description of the patient (gender, age, general appearance, clothing, etc.). A unit search will be initiated and if the patient is not immediately located, the charge nurse will call 17555-Code Gray. The Administrative Supervisor/Nurse Manager will then decide if law enforcement agencies are to be involved.
If the patient is located and will not be returning to the Hospital, the patient is to be discharged from the unit.
If the patient is gone from the facility for more than one hour and returns back to the Hospital the patient must be brought to the emergency department for evaluation.
Complete an Occurrence Report.
Your patient has a chest tube connected to suction and has to go down for a CT scan. What do you do?
If patient has to be transported, do not clamp chest tube. If on wall suction disconnect the suction tubing from wall suction and leave to water seal. (Make sure have an order to travel off of suction)
Chest Tube Care (P0842)
Patient needs med surg restraints for device protection
-Who to call?
-What to do?
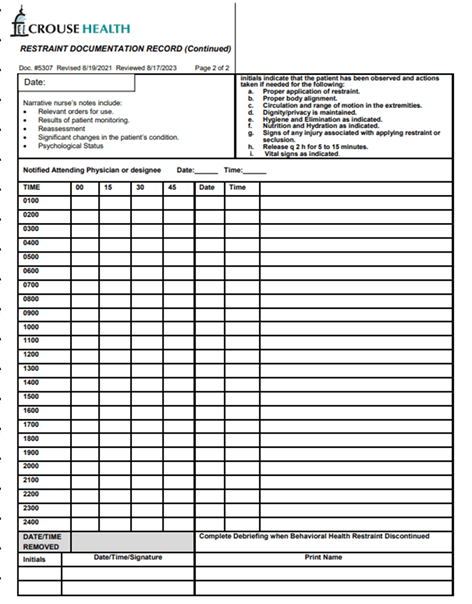
Restraints: Medical/Surgical or Behavioral Health Restraints and/or Seclusion (P0010)
Notify Security (x7826), Attending Provider, CNS, SWAT, Nursing Supervisor, Nurse Manager
Restraints can be used when it is necessary to ensure the immediate physical safety of the patient, staff or others
Need order from Licensed Provider prior to implementation except emergent situations, Medical/Surgical Restraint Order Form in chart.
Need an assessment/evaluation within 1 hour of application of emergency restraints
Order is time limited up to 1 calendar day
Assessment/Monitoring by staff every two hours or more frequent if needed
Narrative Note
Your patient has a neph tube.
-How often does it need to be flushed and explain the steps of flushing the tube
-How often does the Stayfix dressing need to be changed?
Catheter, Drainage (Biliary, Nephrostomy, Pigtail), Care, Dressing Changes and Flushing (P1235)
-StayFix® dressing placed over the skin insertion is changed every 7 days or as needed, whenever it is wet, loose, or soiled.
Flushing neph tube:
-Scrub port with alcohol prep.
-Insert 10 ml syringe into the portal of the 3-way stopcock.
-Turn the “OFF” arm (lever) of the stopcock off to the drainage system.
- Gently flush the drainage catheter with 10 ml of flushing solution or with amount ordered by physician.
IF RESISTANCE IS MET, DO NOT CONTINUE FLUSHING. NOTIFY PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. AMOUNT SHOULD NOT BE GREATER THAN 10 ML. ALLOW SOLUTION. TO DRAIN OUT BY GRAVITY. DO NOT ASPIRATE.
-Turn the “OFF” arm lever of the stopcock off to the syringe.
- Remove syringe from the portal and place new red cap on the stopcock port.
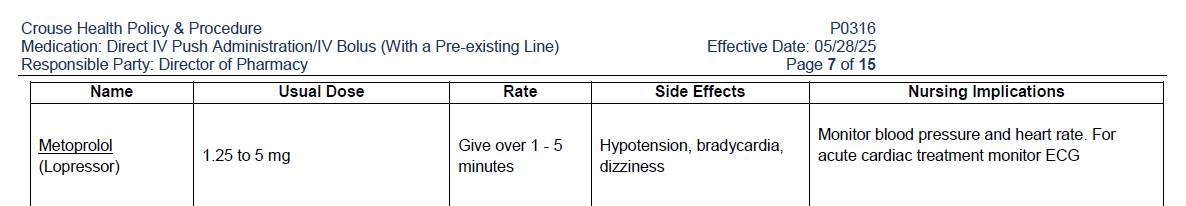
Provider orders 5mg Metoprolol IVP for your patient's uncontrolled A. Fib. Where would you go to find the rate of administration?
Medication: Direct IV Push Administration/IV Bolus (With a Pre-existing Line) (P0316)
Micromedex
Your patient is starting to complain of SOB and you take the patient's vitals. BP 100/50, HR 110, RR 24, O2: 84% on 2L NC. What are your next steps?
•Sit the patient up, boost at 45-90 degrees
•Respiratory assessment and calling respiratory therapy
•Notify charge nurse, and provider of deterioration
•Call Rapid Response if not able to manage with application of oxygen.
•Potential interventions provider will recommend:
•Chest X-Ray, Oxygen, ABG
•Potential further testing: stress tests, echocardiogram, CTAs
•Nasal cannula
-Low flow: 1-6 L/minute
-Salter: 6-15 L/minute
-AIRVO-high flow: 15 L+/min
-Humidify the air above 4 L/minute
•Simple Face Masks: Venturi Masks: 6-10 L/minute
•Partial Rebreather mask: 10-12 L/minute
•Non-Rebreather mask: 10-15 L/minute
Where do we document restraint use? How often for med surg restraints?
You come into your shift and look at the morning labs and find that the patient's potassium is 3.2 and Mg 1.3. What do you do?
Routine Electrolyte Replacement (P1487)

Provider Asks to Put in a Verbal Order
•Verbal orders “should be used only to meet the care needs of the patient when it is impossible or impractical for the ordering practitioner to write the order or enter it into an electronic prescribing system without delaying treatment. Verbal orders are not to be used for the convenience of the ordering practitioner" (CMS)
•Exceptions:
-A phone order is acceptable if the provider is off the unit and unable to get to a computer
-Emergency situation
-Order source: Verbal order-Read back or phone order read back
Orders: Transcribing Electronic Provider’s Orders (P0036)
Your patient complains of left sided weakness, and you notice slurred speech. What are two next interventions?
•Notify charge and call RRT
•Assess the patient and find out these questions:

•Code B (Stroke Code)
-Called by SWAT, 6N Charge RN, CNS, Educator, Provider

Codes (P0006)