In the reaction: 2NO2 → 2NO + O2 at 3000 °C, the concentration of NO2 decreased from 0.0150 M to 0.0115 M in 100 s. What is the rate of disappearance of NO2 in M/s?
What is the rate of reaction?
rate = - (Delta [A] )/ (Delta t)
The rate constant for a reaction is 1.5 x 10-4 M-1s-1 at 100 oC, and 1.2 x 10-3 M-1s-1 at 150 oC. What is the energy of activation?
What is Arrhenius equation?
ln((k2)/(k1)) = -(Ea)/R (1/(T2)-1/(T1))
Calculate the rate at which N2O4 is formed in the following reaction at the moment in time when NO2 is being consumed at a rate of 0.0592 M/s. 2NO2(g) → N2O4(g)
What is the relative rate equation?
Rate of reaction= 1/(coeff) * Rate
"t" represents:
What is time.
"t1/2" represents:
What is half-life.
For the reaction 2A + B → C, what is the rate constant, k?
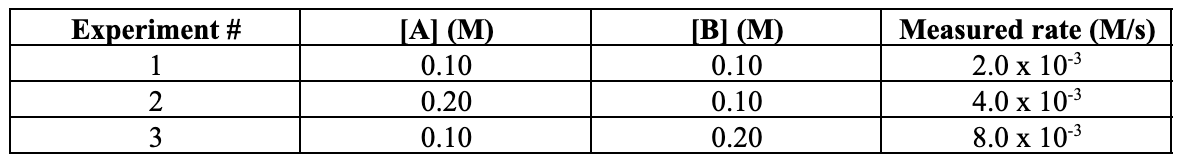
What is generic rate law?
(rate1)/(rate2)
The reaction A → B is third order with respect to A. What happens to the rate of reaction when the concentration of A is doubled?
What is rate law?
New Rate = x*Old Rate
A first-order reaction has a rate constant of 4.4x10-3 s-1 at 350 K and a rate constant of 9.8x10-2 s-1 at 580K. What is the activation energy?
What is Arrhenius equation?
ln((k2)/(k1)) = -(Ea)/R (1/(T2)-1/(T1))
The units for the gas constant, R.
J/(mol*k)
The units of the activation energy, Ea.
J/(mol)
Calculate the rate at which N2O4 is formed in the following reaction at the moment in time when NO2 is being consumed at a rate of 0.0592 M/s: 2NO2 (g) → N2O4 (g)
What is the relative rate equation AND rate of reaction?
Rate of reaction = 1/(coeff) * Rate
For the reaction 2A+3B → C + 2D, what is the order of reaction with respect to A?
What is generic rate law?
(rate1)/(rate2)
Consider the zero order reaction: 2NH3 (g) → N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
What is the rate constant if it takes 60 seconds for a 0.50 M NH3 to decompose to 0.25M?
What is integrated rate law? (Zeroth order)
[A]t = - kt + [A]0
t1/2 = "[A]o"/(2k)
The units for rate of a reaction (rate of appearance/disappearance).
M/s
The units for rate constant (zeroth order reaction).
M s-1
Consider the first order reaction:
Br2 → 2Br
How long does it take for 15% of the reactant to be consumed (initial [Br2] = 0.50 M)?
What is integrated rate law?
ln([A]t) = - kt + ln([A]0)
A reaction is in first order of the reactant A. A solution initially has 0.120 M of A is found to have 0.015 M after 54 min. What is the half-life?
What is integrated rate law AND half-life? (First order)
ln([A]t) = - kt + ln([A]0)
t1/2 = ln2/k
A → product is a first order reaction. If the initial sample contained 100. g, what is the amount of A left over after 6 half-lives?
What is half-life?
100. g * (½)6 = 1.56 g
(This is a conceptual question that confirms you know what the definition of half-life is. You don't need to use the first order half-life equation because this question isn't asking for the value of half-life (t1/2) or for the value of k.)
The units for rate constant (first order reaction).
s-1
The units for rate constant (second order reaction).
M-1s-1
A reaction with activation energy of 120 kJ/mol has a rate constant of 0.25 s-1 at 310 K. What will be the temperature for the rate constant to be doubled?
What is Arrhenius equation?
ln((k2)/(k1)) = -(Ea)/R (1/(T2)-1/(T1))
Consider the following reaction: 2NOBr (g) → 2NO (g) + Br (g)
The rate constant has the value 0.036 M-1s-1. How long does it take for the reactant to decompose to 25% (initial [NOBr] = 0.90 M)?
What is integrated rate law? (Second order)
1/([A]t) = kt + 1/([A]0)
A reaction is known to obey 2nd order kinetics, with k = 0.45 M-1s-1. Calculate the rate of this reaction if the concentration of starting material is 0.15 M.
What is rate law?
The units for rate constant (third order reaction).
M-2s-1
The units for rate constant (fourth order reaction).
M-3s-1