the Vampire Slayer
The pH number representing absolute neutrality is __.
What is 7?
7 is absolute neutral on the pH scale.
 1. Name the three buffer systems in the body.
1. Name the three buffer systems in the body.
2. Of these, this one is the most powerful and also the slowest to react.
What are:
1. Blood buffers
2. Respiratory buffers
3. The kidneys
The kidneys are the most powerful and also the slowest to react.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 503
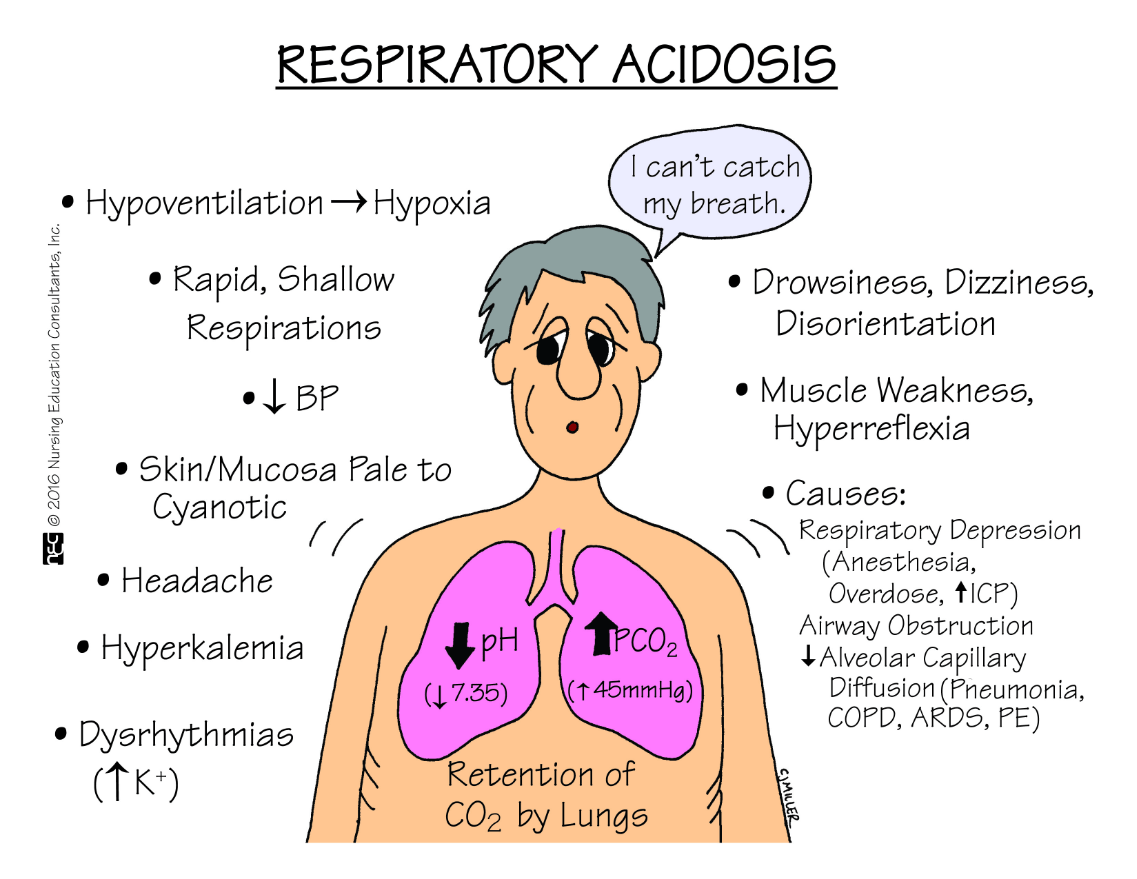
Name two conditions that can lead to respiratory acidosis.
Any condition which impairs normal ventilation and prevents the respiratory system from eliminating CO2.
See box 18.10 on p. 504
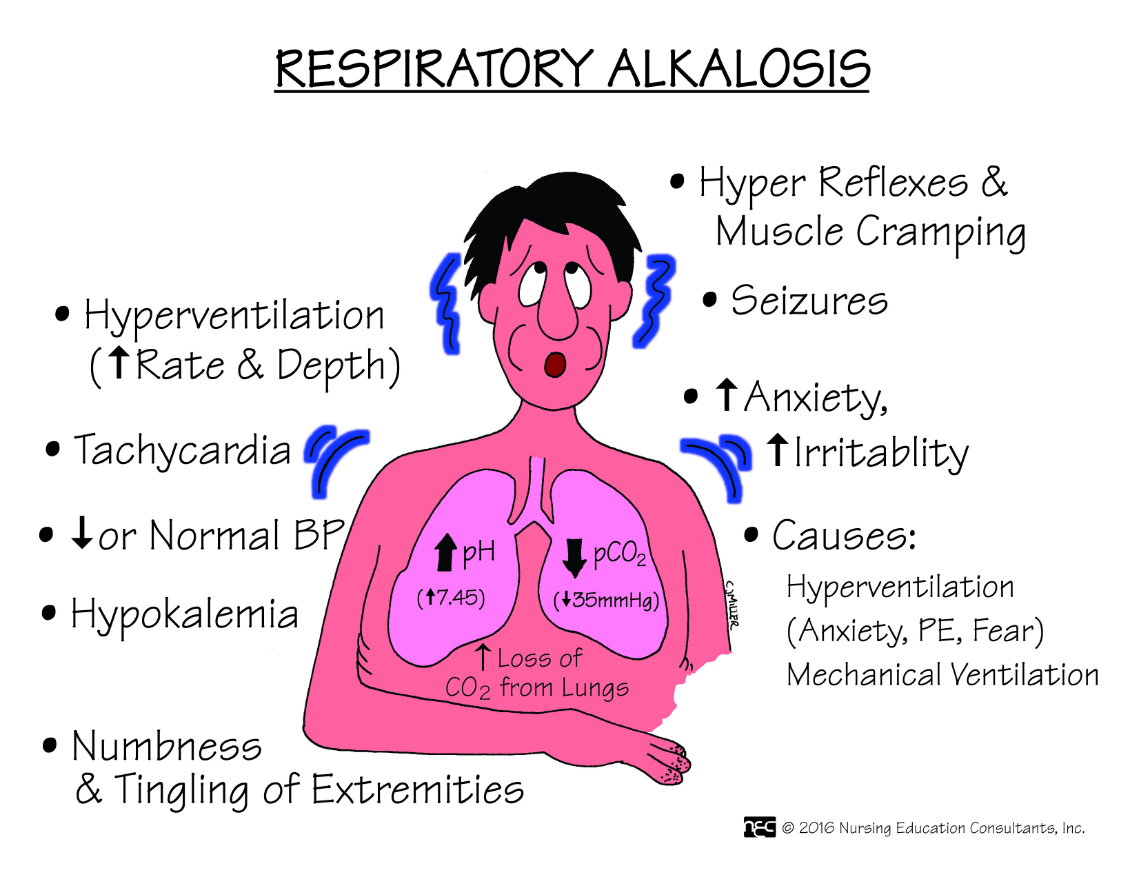
Name two conditions that cause respiratory alkalosis.
See Box 18.11 on p. 505
Anemia, *Asthma, Hyperventilation
Name three causes of metabolic acidosis.
What are: (any three)
1.Dehydration
2. Diabetic Ketoacidosis
3. Renal Failure
4. Severe diarrhea
5. Starvation
Name three causes of metabolic alkalosis.
What are: (any three)
1. Cushing's disease
2. Excessive vomiting
3. *Prolonged gastric suctioning
4. Overdose on antacids (Mylanta, Sodium Bicarbonate)
The normal range for Oxygen on an ABG is _________.
What is 80 - 100 mmHg?
When hydrogen ion concentration increases, the pH decreases, indicating an acidic environment. How do the lungs adjust to balance the hydrogen ion concentration?
The lungs speed up or slow down respirations. If the pH is low, the lungs will increase the respiratory rate. If the pH is high, the lungs will decrease the respiratory rate.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 503, The Respiratory System
When the CO2 rises, what happens to the pH?
It lowers, becoming more acidotic.
When the CO2 lowers, what happens to the pH?
The CO2 lowers, the pH rises, becoming more alkaline.
When the bicarbonate level falls, what happens to the pH?
When the bicarbonate level falls, the pH falls as the patient becomes more acidotic.
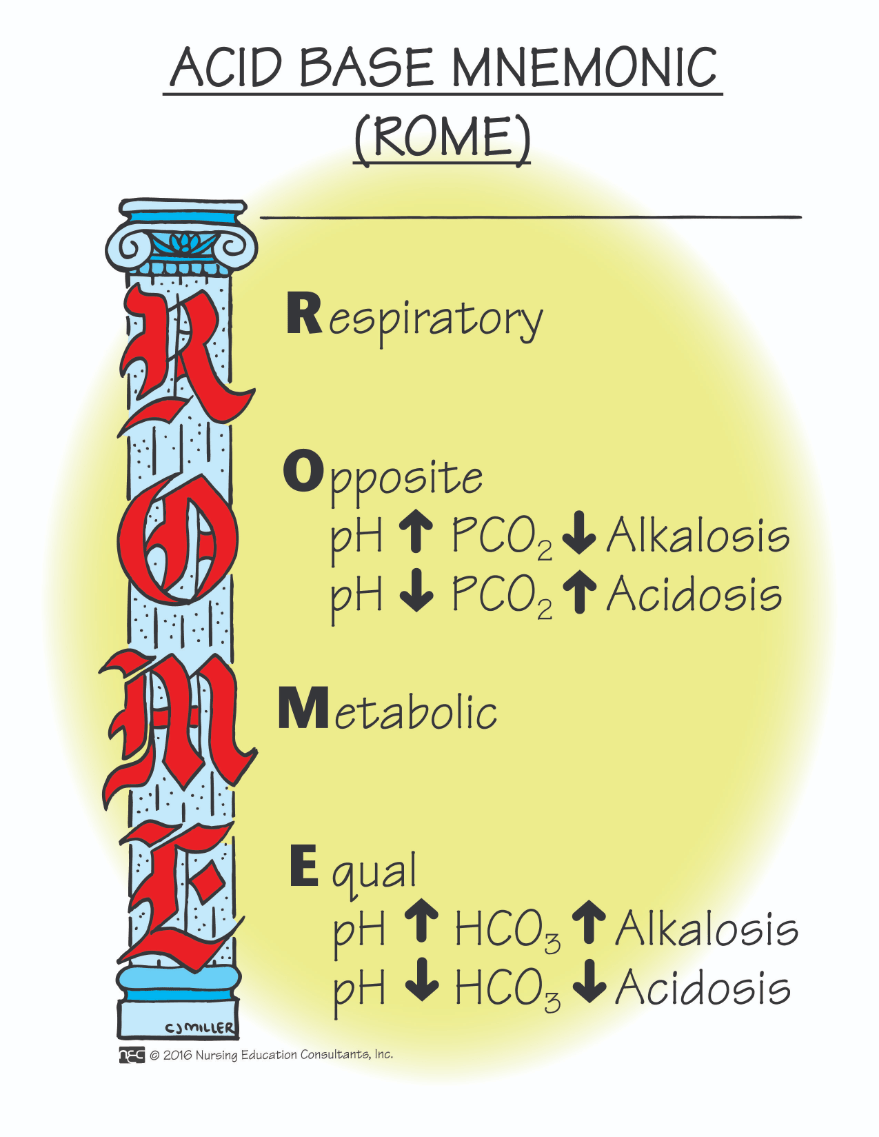
When the bicarbonate level rises, what happens to the pH?
When the bicarbonate level rises, the pH rises, as the patient becomes more alkaline. 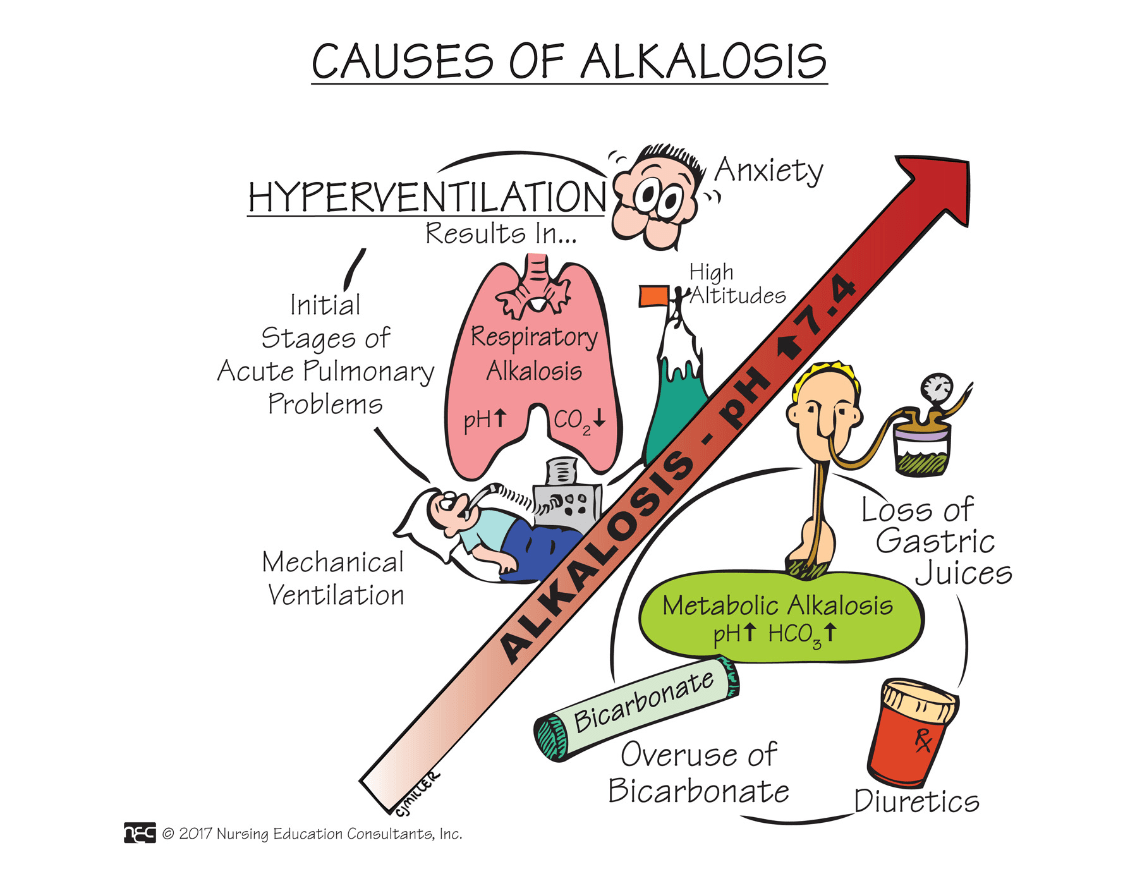
The normal range for Bicarbonate on an ABG is ____________.
What is 22-24 mEq/L?
We know the kidneys are the most powerful, but how do they regulate acid-base balance?
The kidneys excrete acids or alkalines as needed to adjust the pH level.
What is the normal pulse ox reading for a client?
The normal pulse ox reading is 95-100%
The normal O2 on an ABG is 80-100.
Name three symptoms a client may display with respiratory alkalosis from hyperventilation.
What are: (any 3 of the following)
1. lightheadedness
2. tingling hands, arms
3. blurred vision
4. increased HR
5. confusion
Name three signs and symptoms a client with metabolic acidosis may exhibit.
What are (any three):
1. Coma
2. Headache
3. N/V/D
4. Lethargy
5. Warm, flushed skin
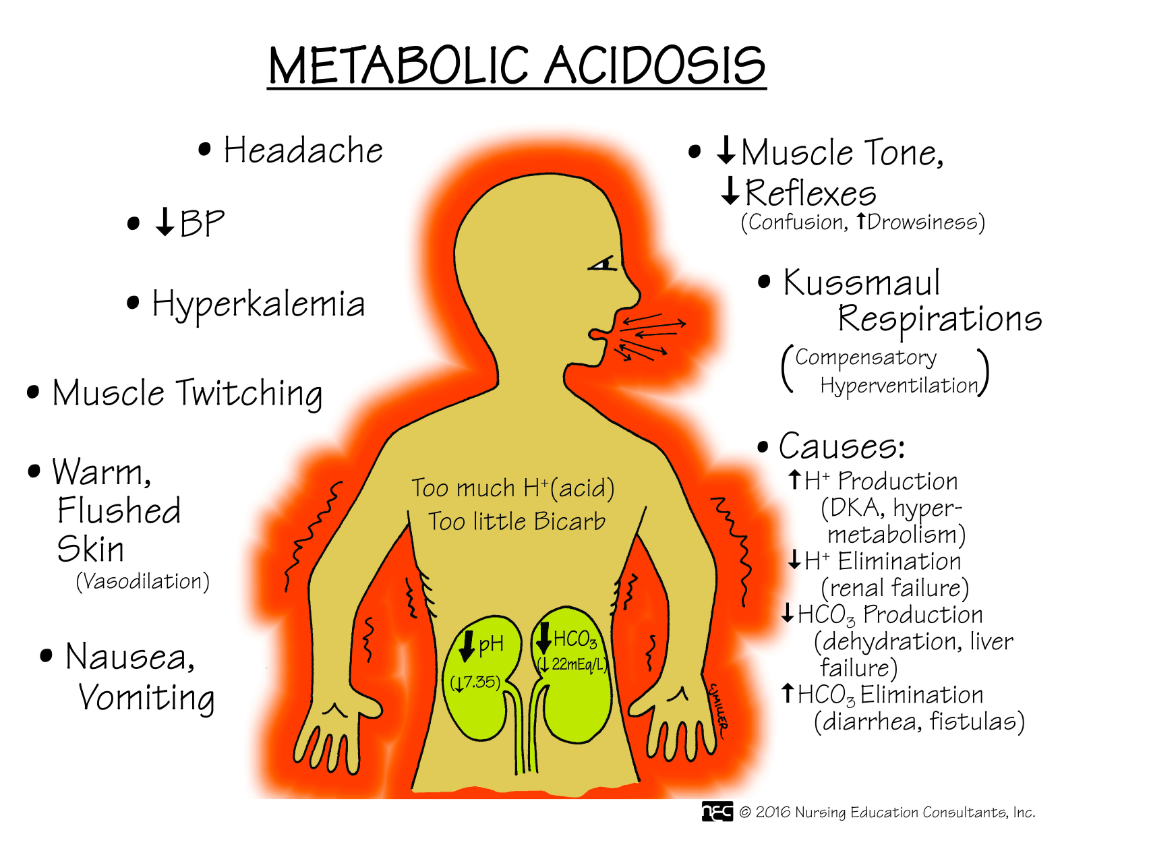
Name three signs and symptoms a client with metabolic alkalosis may exhibit.
What are (any 3):
1. Decreased LOC
2. Irritability
3. Slow, shallow respirations
4. Vomiting
5. HCO3- level on ABG greater than 26
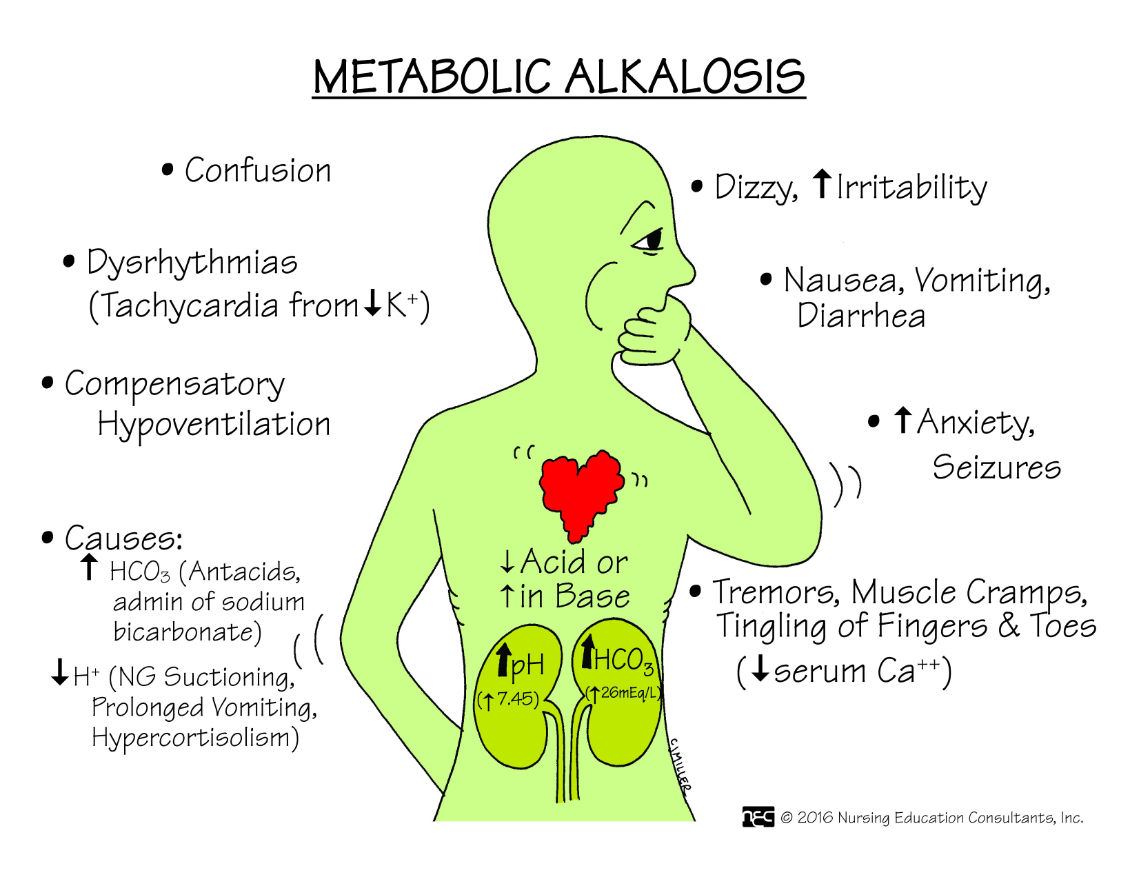
The normal range for Carbon Dioxide on an ABG is _________.
What is 35-45 mmHg?
What part of the brain controls respiratory effort?
The medulla oblongata
If the client increases their respiratory rate, what happens to the pH?
It rises, becoming more alkaline, because the client is breathing off the CO2.
If a client decreases their respiratory rate, what happens to their pH?
When CO2 increases, pH decreases, becoming more acidotic.
Complete the following statement:
Metabolic acidosis is the result of a ______ of hydrogen ions, or a _________ of bicarbonate.
What is a
gain of hydrogen ions
or a loss of bicarbonate?

When a client has a NG tube in place, and the nurse aspirates fluid to check the pH, should the nurse replace the fluid? Why or why not?
1. Yes, what is "yes"?
2. To offset the pH disturbance. Nurses need to be careful not to aspirate too much because it can alter the client's pH when they lose the H+ (hydrogen) ion from the stomach acid contents.
The pH range for an ABG.
If carbon dioxide acts as an acid, in the ABG, what acts as the alkaline component?
What is bicarbonate?
pH 7.26 O2 88 CO2 67 HCO3- 24
What acid/base imbalance does this ABG represent (and define your answer)?
Respiratory acidosis
Low pH High CO2

Why does breathing into a paper bag work for patients who are hyperventilating?
Because it forces them to rebreathe exhaled CO2, which increases their CO2 level bringing it back towards normal, and making their pH more acidotic.
Hyperventilation causes respiratory alkalosis, because the client hyperventilates all of the CO2 off.
pH 7.26 O2 92 CO2 45 HCO3- 18
What acid/base imbalance does this ABG represent (and define your answer)?
Metabolic acidosis
pH low bicarbonate low
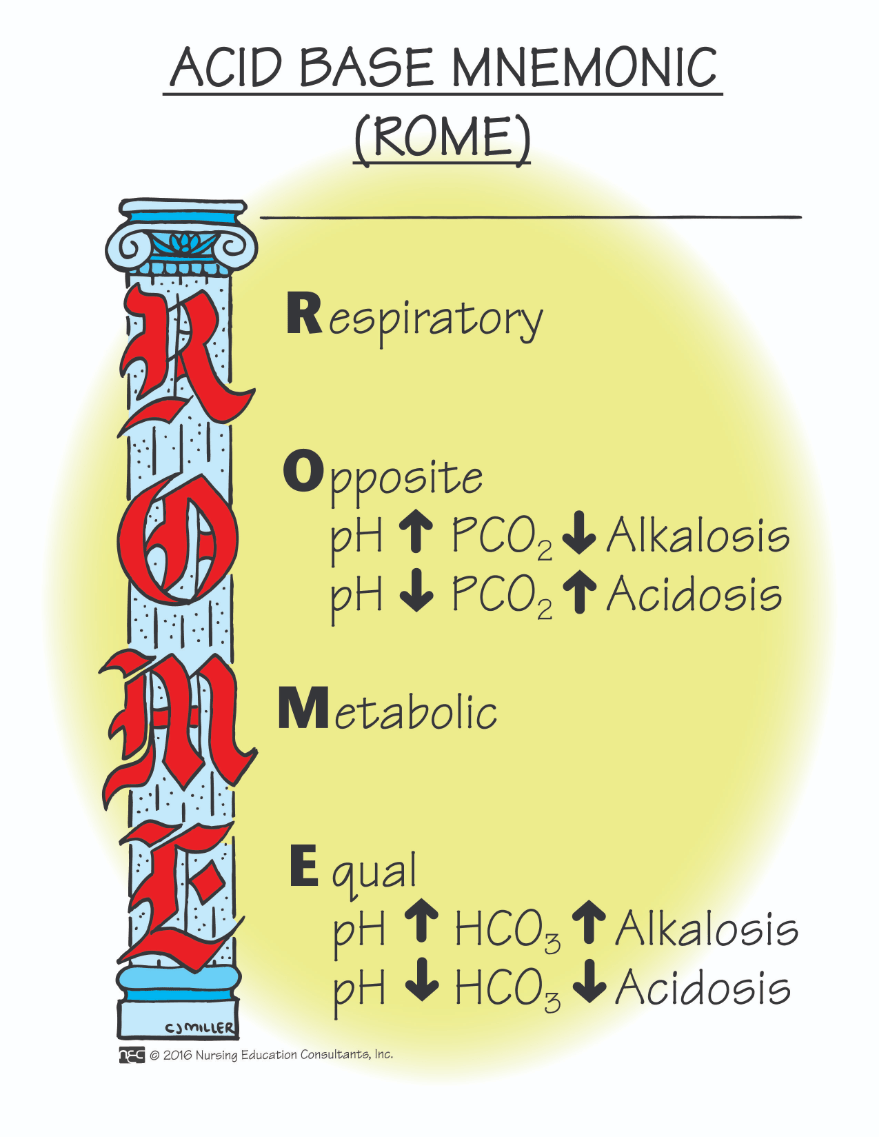
How is metabolic alkalosis treated?
The cause must be detected and treated, then the acid-base imbalance will correct.
