Greek who first hypothesized about the atom and defined the word atom.
Who is Democritus?
What is the quantum energy level number of oxygen
Oxygen's valence electrons are in the 2nd energy level.
What is the first level orbital that is occupied by electrons?
s
What is the Aufbua Principle
Electrons occupy the lowest energy level state first, which explains why 4s comes before 3d.
(Aufbau in German means "to build.")
H - electron confiuration
1s1
How do you create an ion?
Add or subtract an electron?
Atomic model of Hydrogen that says electrons must orbit the nucleus in discrete energy levels. His model was a modification of Rutherford's nuclear model which worked perfectly, but only for hydrogen.
Neils Bohr Atom
Double: Name often given to his model of the atom?
What is the total number of electrons in the 1st energy level?
2
How many total electrons can occupy a single sublevel orbital like s or p?
2
How can two electrons occupy the same orbital when they each have negative repelling charges.
Hund's Rule, the electrons rotate or spin in opposite directions creating magnetic fields that attract each other.
Li
1s2 2S1
What is an ion?
An ion is an atom with a net charge?
Heisenberg is famous for this. (Are you certain your know the answer?)
The Heisenberg uncertainty principle?
+ 100: Can you explain it?
What is the total number of electrons in the 2nd and 3rd energy levels?
2nd: 8 and 3rd: 18
2(22) = 8 and 2(32) = 18
What equation tells us the number of total sublevel orbitals in any level.
n2
What is meant by the ground energy level in an atom.
The lowest energy level occupied by electrons, that are not excited.
S
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
What group typically forms a 2- ion and why
Group 6A (oxygen family) since it needs two electrons to fill it outer shell.
+ 100: What group typically forms a 1+ ion and why do they rarely exist as an element in nature?
What does the Heisenberg Uncertaintly Principle state about the electron in an atom?
We can never know both the position and the energy of an electron with certainty at the same time.
How can we calculate the total number of electrons in any energy level?
2n2
What are the first four orbitals in order of energy in an energy level.
s, p, d, f
Why do salts and metals tend to give off colors when they are burned?
The heat excites their electrons, causing them to jump to higher energy levels. When these excited electrons return to their original energy levels, they release energy in the form of light, and the specific color corresponds to the energy difference between the levels.
C abbreviated electron configuration
[He] 2s2 2p2
Which element has the highest electronegativity and what is the number?
Fluorine. 4
+ 100: Give two reasons why.
Explain Schrodenger's cat below
The cat is BOTh alive and dead at the same time... until looked at - which causes it to be in one state.
Simarly, in quantum mechanics an electron can be considered to be in more than one state at a time until it is looked at.
How can we calculate the number of sublevels in any energy level?
n2
2List the first four sublevels and state how many different orbitals are in each.
Also, what is the equation we would use to determine hoe many electrons in an energy level?
s = 1 p = 3 d = 5 f = 7
2n2 So energy level 3 has (2)(32) = 18 e-
What color is copper in the salt flame test?
Blue
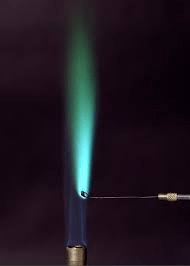
Copper (Cu) abbreviated electron configuration (z = 29)
[Ar] 3d9 4s2
+ 100: Ar] 4s1 3d10
Explain how atomic radii change in the periodic table AND how atomic radii affects electronegativity.
Atomic increases down the periods and right to left.
The smaller the radii the stronger the electronegativity since the nucleus is closer to those outer shell electrons (valence electrons) and hence they spend more time with such atoms in covalent bonds.