What is a free margin? Name some examples
Bonus: why do most of these areas require Mohs or more advanced techniques?
Anatomic structures that are in some way discontinuous with adjacent skin
Ex. lips, helices, eyelids, nostrils
Mohs gets paid the big bucks because tension vectors are unevenly distributed in these areas which can lead to functional + cosmetic disasters! It takes careful consideration of vector orientation and anatomical preservation
You are seeing a 6 week old baby in clinic. Parents say these red bumps came on abruptly 2 weeks prior and are growing. What is the next step in management?
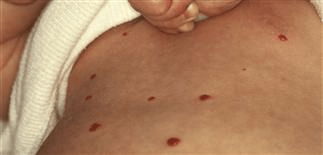
This baby has > 5 infantile hemangiomas consistent with hemangiomatosis. We do not know if they are only limited to the skin, so a liver U/S +/- TSH* should be ordered. Additional concerns include intestines, brain, eyes, spleen, kidneys, and lungs.
If there is internal organ involvement, we are concerned about liver failure and/or high-output cardiac failure. Oral propranolol should be started!
*TSH is checked because IHHs produce excess type 3 iodothyronine deiodinase leading to consumptive hypothyroidism.
Undermining plane of the SCALP
Sub-galeal
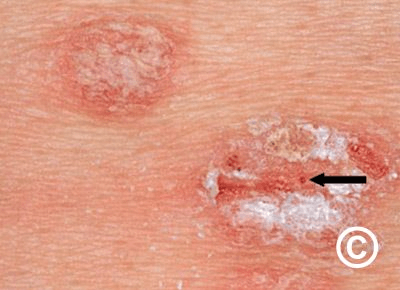 1) What is this condition and 2) what is this sign?
1) What is this condition and 2) what is this sign?
Auspitz sign - pinpoint bleeding when a psoriatic plaque is scratched
Patients experience full vasoconstriction with epinephrine in how much time?
7-15 minutes. That that ish sit on the scalp!!!
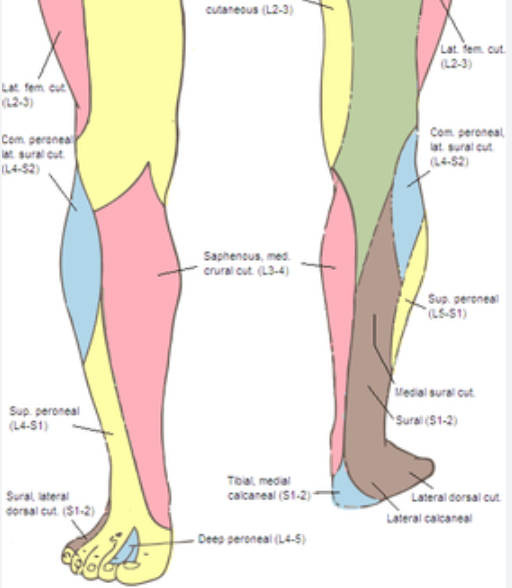
You plan to excise a large SCC on the lateral foot. Which nerve should be blocked?
Sural n.
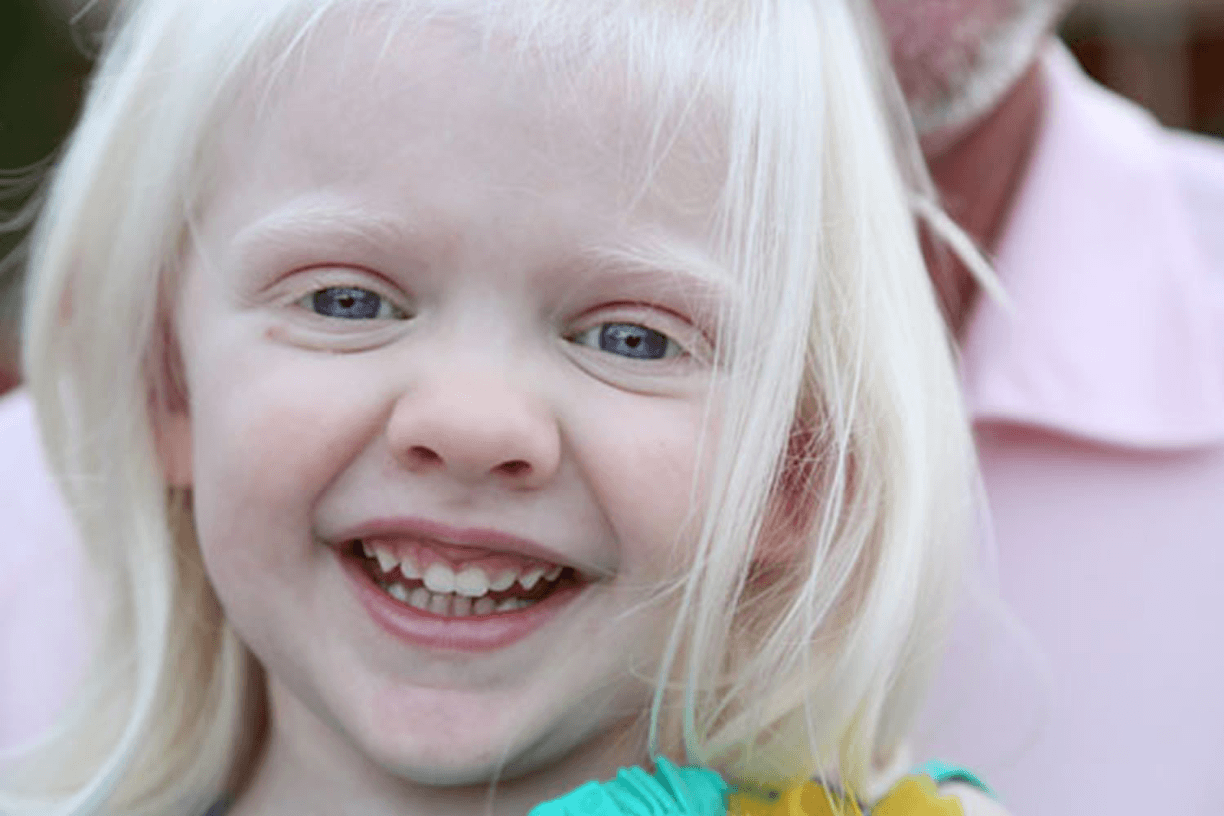
Differential after seeing this girl?

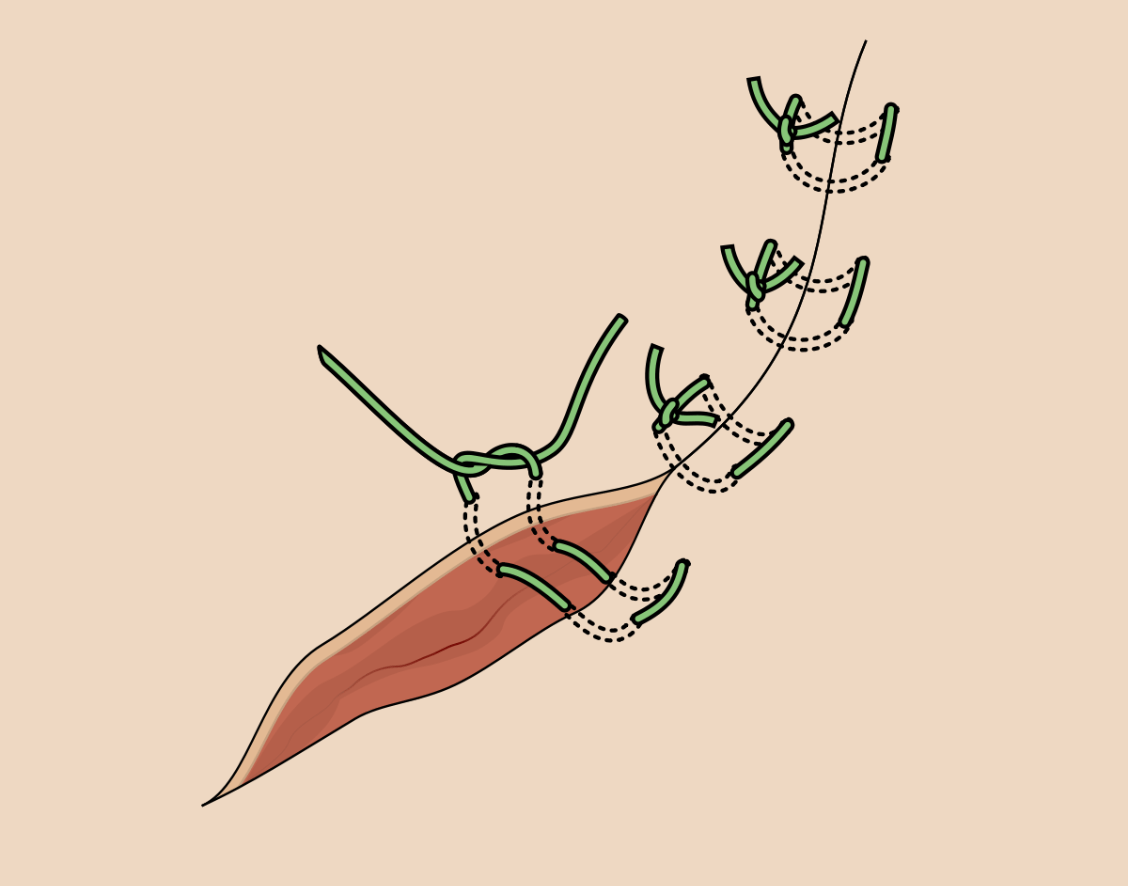
Benefits of using horizontal mattress
- Hemostasis
- Tension distribution, removes off edges of wound
- Cosmesis
Patient comes in with small bumps in a line that won't go away. Not painful or itchy, have been there for several weeks.
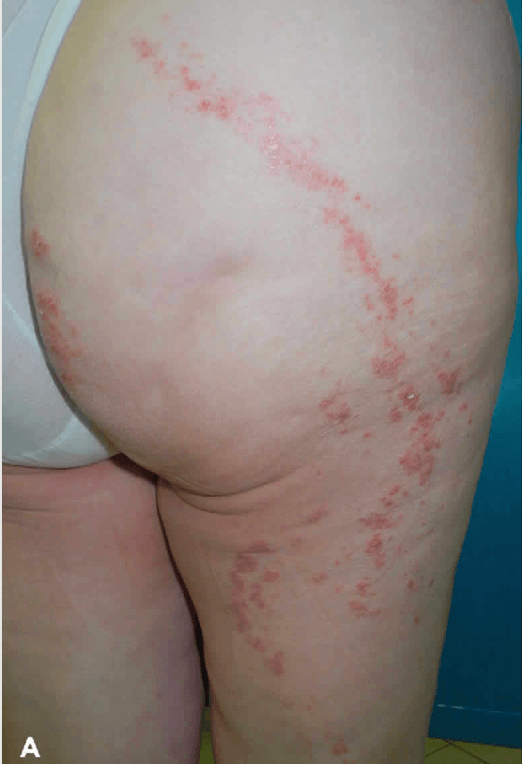
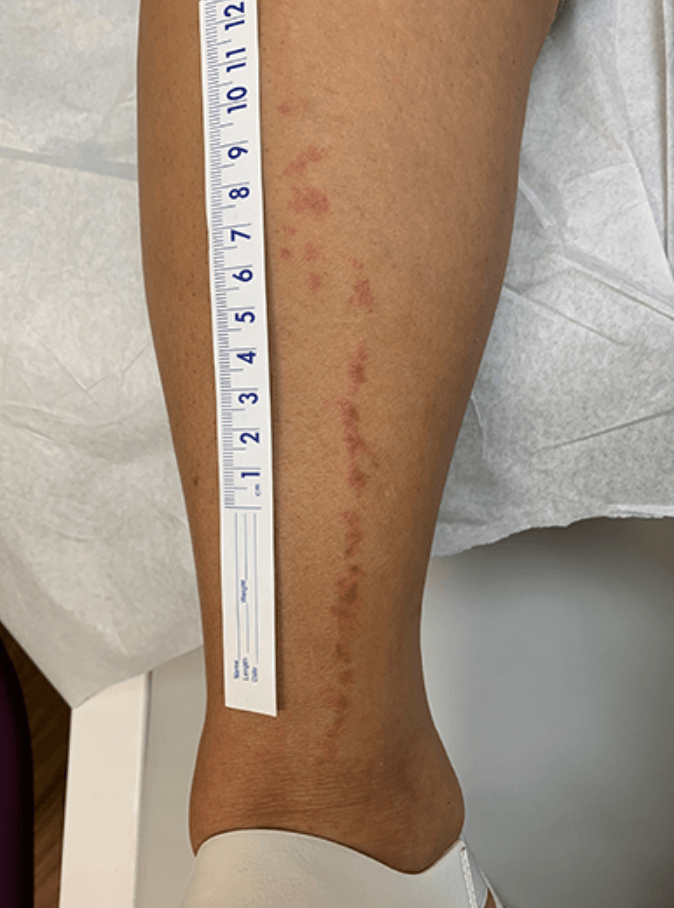
Lichen striatus - pink or hypopigmented scaly papules in linear arrangement on extremities > face/trunk
Common in spring/summer, may last for 3-24 months then spontaneously resolve. Nail dystrophy possible if involving fingers.
Can treat with TCIs + steroids
Anesthetic most associated with cardiac toxicity
Bupivicaine - NOT responsive to ACLS :(
You see a patient for follow-up after they had an extensive skin cancer removal on their left cheek. You notice a pronounced facial droop, with the left side of their mouth depressed both at rest and while talking. They are drooling a bit and cannot seal their lips. Which nerve was compromised?
Buccal nerve (motor); branch of CN VII
Innervates buccinator, depressor septi nasii, nasalis, orbicularis oris, LLS, LAO, zygomaticus, and risorius
Leads to accumulation of food, uneven smile at REST + MOTION, decreased lip seal, drooling, muffled speech, inability to wrinkle nose
"With BUCC, you're F*CKED!"
What is this finding called and which syndrome are we concerned for?

Dystopia canthorum: increased distance between medial canthi while pupillary distance remains normal.
Seen in Waardenburg syndrome - AD, PAX3/MITF/SOX10. White forelock, deafness (MITF), heterochromia irides, synophrys, broad nasal root, dystopia canthorum, UE abonormalities (PAX3), Hirschprung's (SOX10)
Absorbable sutures in order of REACTIVITY (most to least)
Gut > polyglycolic acid = polyglactin 910 (Vicryl) > polydioxanone (PDS) > poiglecaprone 25 (Monocyrl)
You get a consult from the hospitalist that says "vasculitis, needs biopsy". What do you think?
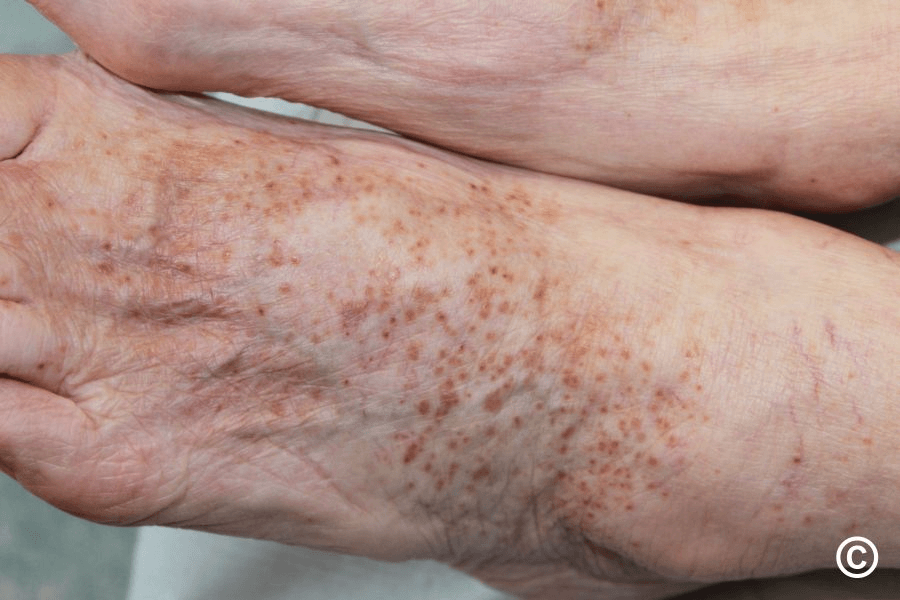
Capillaritis (pigmneted purpuric dermatosis), Schamburg type. This does NOT need biopsied and can be managed with lifestyle factors and topicals.
PPDs: Schamberg's purpura, Majocchi purpura, lichen aureus, Gougerot-Blum purpura and, eczematoid-like purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis.
Cross-reactivity with ester anesthetics
"PPPESTAA" = PPD, PABA, Paraaminosalycylic acid, Ethylenediamine, Sulfonamides, Thiazides, Anesthetics (esters), Azo dyes
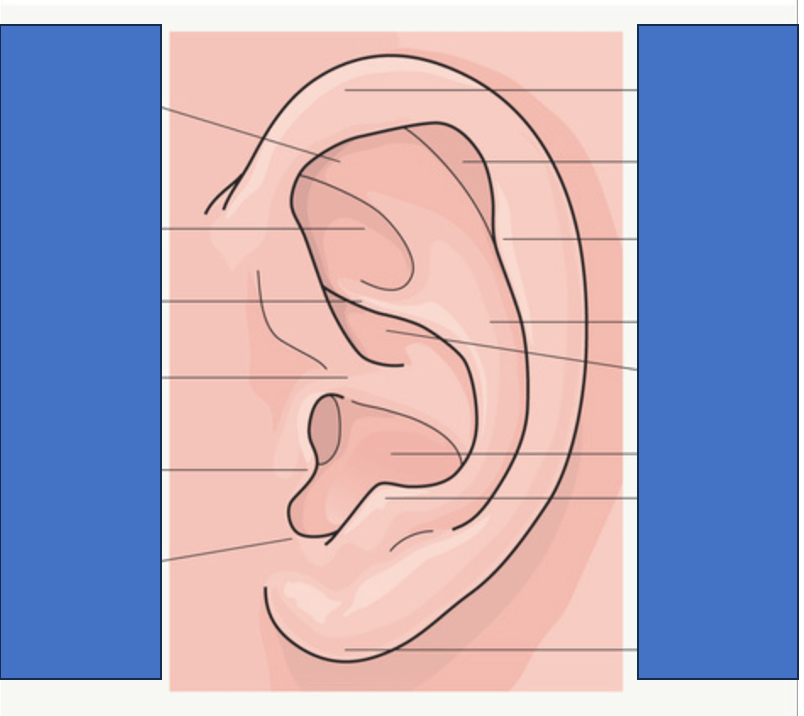
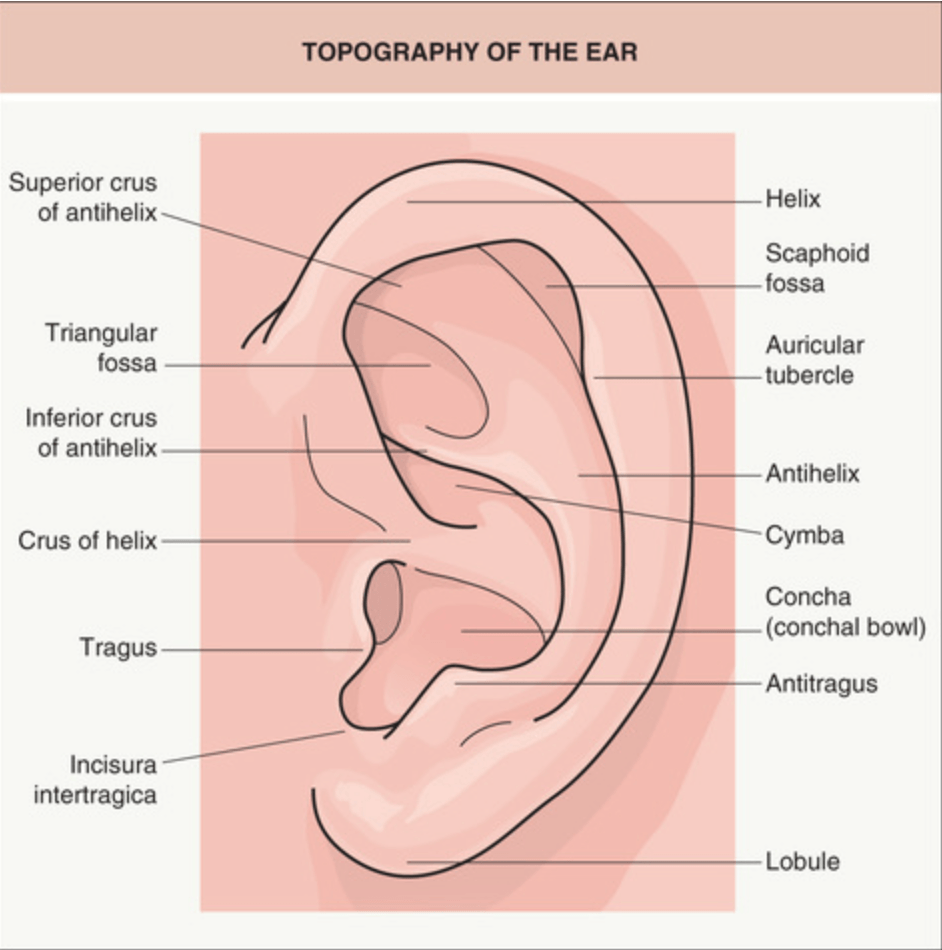
Correctly identify each anatomical landmark of the ear
Which referrals does this patient need?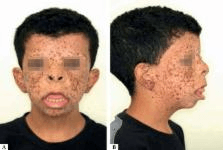
LEOPARD syndrome (AD, PTPN11)
Cardiology - conduction defects, pulmonic stenosis, aortic stenosis
Audiology - deafness
Urology - abnormal genitalia, cryptorchidism
Name these scalpels
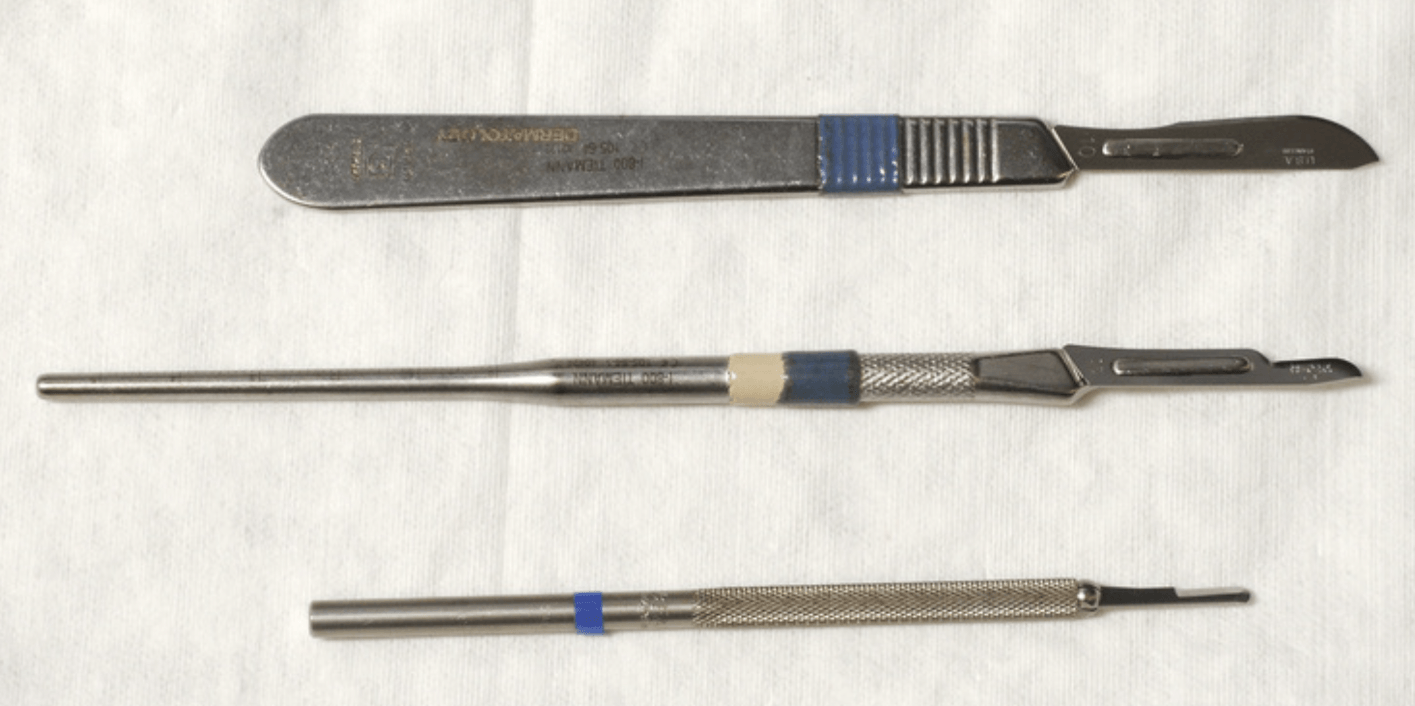
Top = Bard Parker
Middle = Siegel
Bottom = Beaver
Differential?
This is bullous pemphigoid. You will not always see tense bullae in photos (or in real life!).
Ddx: BP, EBA, bullous lupus, linear IgA, PF, IgA pemphigus, PV
Max dose of lido with epi in an adult?
Max dose of lido with epi in a child?
Max dose of tumescent?
Adult = 7 mg/kg
Child = 3-4.5 mg/kg
Tumescent = 55 mg/kg
Morgan wants her masseters injected again. You mark out your 3 sites after palpating during maximal contraction. What depth should neurotoxin injection occur at each site and why (hint: anatomy matters!)
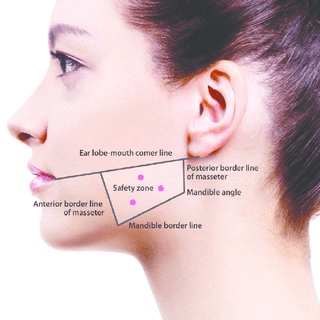
*Bonus: what could happen if you are too superficial throughout?
Masseter anatomy
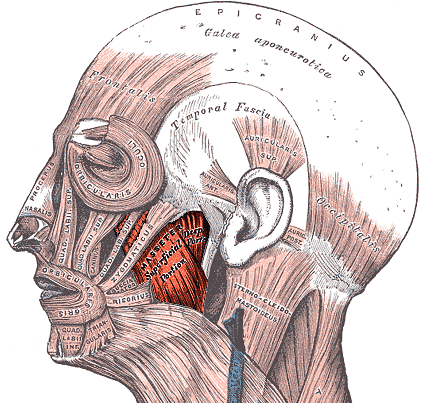
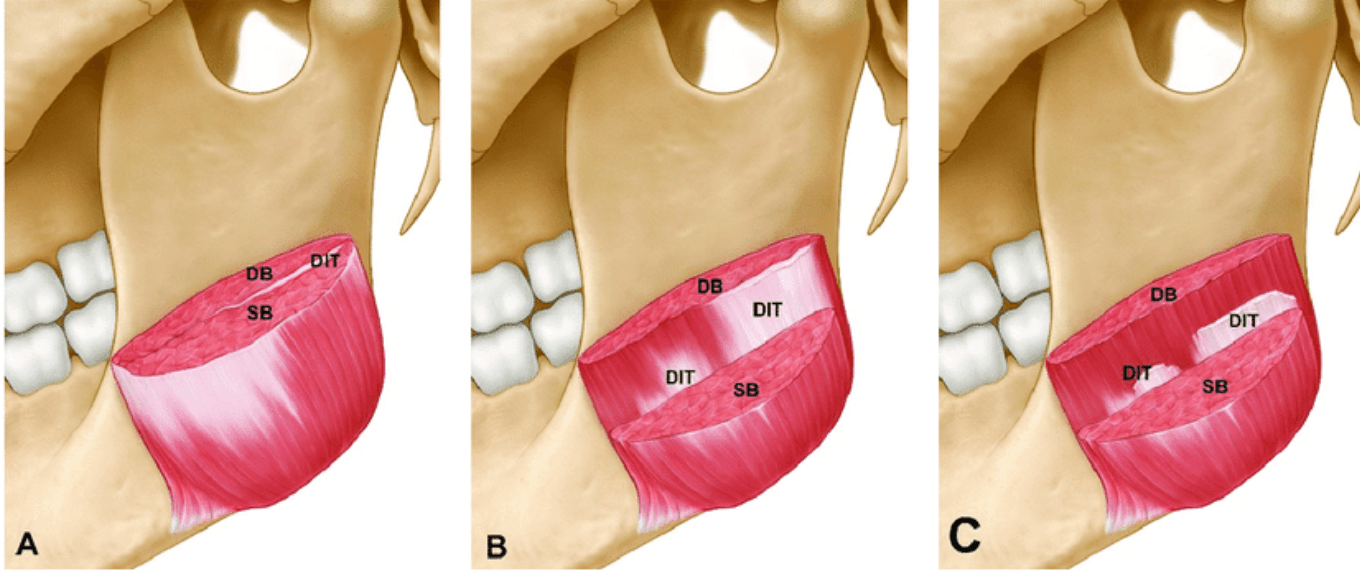
The masseter is made of of 2 muscle bellies (bilaminate), superficial and deep. The superficial component is more oblique while the deep courses vertically.
According to Dr. Rohrich, the posterior injection needs to hit the deep head which means you will almost hub your needle (w/ BD insulin syringe). The superior and anterior injection points can be more superficial. Classic masseter tox is 25u every 4-6 months. Majority should be placed deep into posterior site (~10-15u).
Bonus: without adequate depth to hit the deep belly, you risk a walnut effect
Extra bonus: over time, you will get compensatory strengthening of the temporalis which may or may not be flattering depending on the patient
This child is seen in clinic for a large "birthmark". On further questioning, parents mention recurrent fractures, hyperthyroidism, and changing shape of the right shoulder/arm. What are you concerned for?
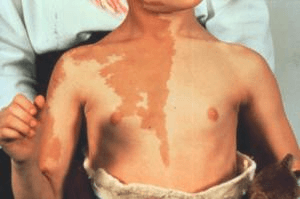
McCune-Albright syndrome - sporadic, GNAS1
Large segmental "coast of Maine" CALM, polyostotic fibrous dysplasia underlying, fractures, bowing of limbs, length discrepancy, precocious puberty, hyperthryoidism
Refer to Ortho + Endo
Biopsy comes back as a superficial spreading melanoma with Breslow depth = 1.1 mm. What are your surgical margins?
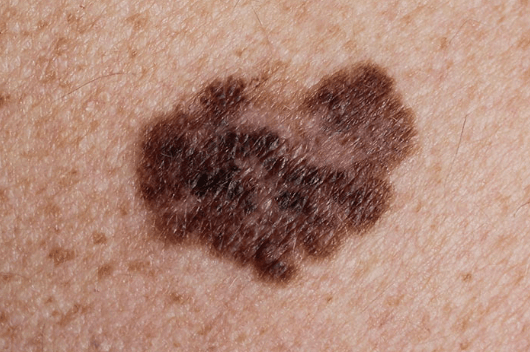
2 cm surgical margin +/- SLNB depending which criteria you follow
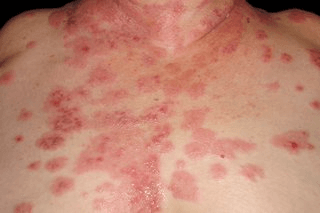
Potential causes of this full body rash?
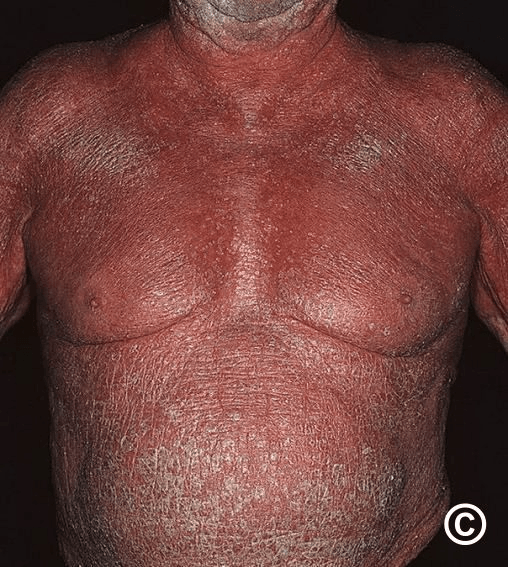
Erythroderma: erythema + scale >90% BSA
"SCALP'D" = seb derm, contact/CTCL, atopic derm, lymphoma, PRP/psoriasis, drugs
#1 most common = psoriasis
What are the components of EMLA and why do most institutions no longer use it?
2.5 mg/ml lidocaine + 2.5 mg/ml prilocaine in oil-in-water emulsion
Risk of MetHb with prilocaine in infants!
Corneal injury!
Requires 60 min exposure under occlusion